Vertical FETs (V-FETs)
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to V-FETs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to talk about Vertical FETs, or V-FETs. Can anyone tell me why vertical structures might be advantageous in semiconductor design?

I think vertical structures can save space, which is important as we make circuits smaller.

Exactly! V-FETs allow us to stack components, enhancing integration. This is particularly useful as we move towards 3D IC designs.

What about performance? Do V-FETs offer improvements there too?

Great question! V-FETs can provide stronger current drive and ease the challenges of managing power consumption, particularly as we scale down.

So they're better for reducing electrostatic effects as well?

Yes, V-FETs can handle electrostatic challenges more effectively than traditional layouts. Let’s summarize: V-FETs enable 3D integration, enhance current performance, and reduce electrostatic issues.
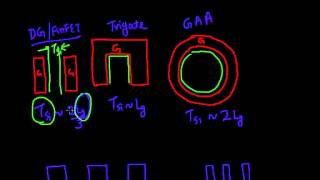
Comparison with FinFETs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, how do V-FETs relate to FinFETs? Why are we considering them as a next step?

FinFETs are great, but they have scaling limits, right?

Exactly! FinFETs have certain electrostatic limits that become problematic as we scale. V-FETs address these limits by changing the current flow direction.

Are there any downsides to using V-FETs yet?

Like any new technology, there are challenges to overcome in design and fabrication. However, the potential benefits make them a promising option for future developments.

So, in summary, V-FETs enhance performance and help with scaling issues faced by FinFETs.

Correct! They are a key part of our future in semiconductor technology.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explores Vertical FETs (V-FETs), focusing on their unique architecture where current flows vertically, which enhances 3D integration capabilities. The section also considers their potential benefits in overcoming some limitations faced by FinFET technology in future semiconductor designs.
Detailed
Vertical FETs (V-FETs)
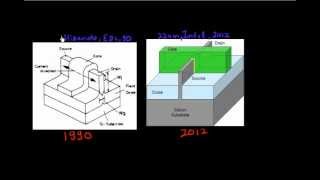
Vertical FETs (V-FETs) represent an innovative evolution in semiconductor technology. Unlike traditional planar and FinFET designs, V-FETs direct current flow vertically from source to drain, utilizing multiple layers of materials in a compact 3D structure. This architecture is particularly promising for future semiconductor designs, especially in the context of 3D integration where space constraints are critical.
Key Advantages of V-FETs:
- 3D Integration: V-FETs facilitate stacking of devices, enabling denser circuit layouts and integrated systems, which is crucial as technology trends move towards increased efficiency and miniaturization.
- Enhanced Performance: As device dimensions shrink, the ability to maintain performance is paramount. V-FETs are designed to deliver strong current drive capabilities while managing power consumption effectively.
- Reduced Electrostatic Effects: The vertical configuration may mitigate some electrostatic challenges associated with scaling in planar devices and FinFETs, potentially improving overall device reliability and yield.
V-FETs exemplify a critical step in the semiconductor industry's shift to address the limitations of existing technologies, driving forward the capabilities of integrated circuits and ensuring alignment with the ongoing demands for better performance in computing devices.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Vertical FETs
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Current flows vertically from source to drain.
● Promising for 3D IC integration.
Detailed Explanation
Vertical FETs (V-FETs) are a type of transistor where the electrical current moves from the source to the drain in a vertical direction, rather than the traditional horizontal flow seen in most other transistors. This design allows for a more compact structure, which can help optimize space in integrated circuits, especially for 3D configurations. This vertical orientation is particularly advantageous when integrating multiple layers of circuitry, as it enhances the density and performance of the circuit.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a multi-story building where different functions occur on different floors. Instead of spreading out wide like a single-story building (where horizontal transistors would imply lower integration density), a tall building (like V-FETs) allows for more functionalities in a smaller footprint, utilizing vertical space efficiently for residential or office purposes.
Benefits of Vertical FETs for 3D IC Integration
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Promising for 3D IC integration.
Detailed Explanation
3D IC integration refers to the stacking of multiple integrated circuits to create a single, compact device that can perform multiple functions without requiring additional horizontal space. V-FETs contribute to this technology by allowing vertical connections that save space and reduce the distance electrical signals must travel. This leads to improved performance, lower power consumption, and higher data transfer rates, making devices faster and more efficient.
Examples & Analogies
Think of 3D IC integration as a layered cake. Each layer represents a different function, and instead of spreading the cake out wide, you stack the layers on top of each other. Just as a stacked cake is easier to handle and contains more flavors in a smaller space, V-FETs make it possible to include more complex functions in a compact design of electronic chips.
Key Concepts
-
Vertical Current Flow: V-FETs utilize a vertical current flow architecture rather than horizontal, enhancing space efficiency.
-
Enhanced 3D Integration: V-FETs are ideal for 3D IC integration, allowing for multiple layers of devices.
-
Improved Performance: V-FETs can provide stronger current drive and better power management compared to traditional devices.
Examples & Applications
In a smartphone, V-FETs could enable more compact and power-efficient designs compared to traditional FETs.
V-FETs in high-performance computing devices may greatly enhance processing abilities while minimizing power consumption.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For V-FETs that stack and play, vertical currents lead the way!
Stories
Imagine a city where buildings are stacked vertically; this is how V-FETs utilize space to improve circuitry!
Memory Tools
Remember: V-FET = Vertical flow + Future integration.
Acronyms
V-FET
'Vertical Field-effect for Enhanced Technology.'
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Vertical FETs (VFETs)
A type of field-effect transistor that allows current to flow vertically from source to drain, facilitating higher levels of integration and performance.
- 3D IC Integration
The process of stacking integrated circuits in multiple layers to enhance performance and reduce footprint.
- Current Drive
The ability of a transistor to supply or control the flow of electric current.
- Electrostatic Effects
The physical phenomena caused by electric charges in semiconductor devices that can lead to performance degradation.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
