Case Study 2: ASIC Design for Mobile Devices
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to ASIC Design Challenges
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are diving into ASIC design for mobile devices, focusing especially on the power management aspect. Can anyone tell me what challenges you might expect in such a design?

I think optimizing power efficiency is a big challenge since mobile devices rely on battery life.

Absolutely right! Power efficiency is crucial. We also need to consider minimizing the chip area. Why do you think that’s important, Student_2?

Well, mobile devices are getting smaller, so the components need to fit in tight spaces.

Exactly! Now, what about performance? What do we need to ensure here?

It has to run fast enough to handle power management tasks effectively, right?

Correct again! Along with performance, we also need to consider thermal constraints since efficient heat management is critical to device reliability. Great discussion!
Design Solutions in ASICs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we've discussed the challenges, let’s talk about solutions. How do you think Verilog plays a role in ASIC design for power management?

I think Verilog makes it easier to model and simulate different power management circuits.

Exactly! With Verilog's capabilities, designers can efficiently integrate circuits while ensuring they meet design specifications. How might thermal concerns influence your design decisions?

We’d probably need to include circuits that help dissipate heat or use materials that can withstand higher temperatures.

Good point! Implementing proper cooling techniques or designing the circuits to manage heat generation is essential. Can anyone recall a specific power management circuit we might integrate?

Maybe a voltage regulator or something to manage battery levels?

Absolutely! Integrating circuits like Voltage Regulators is vital for balancing performance and power consumption. Excellent input from everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this case study, we explore the use of VHDL or Verilog in designing an ASIC for a mobile device's power management system. The design involves challenges such as power efficiency, minimal chip area, high-speed performance, and thermal constraints, with a corresponding design solution to integrate these requirements.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
This section presents a detailed case study on ASIC design specifically tailored for mobile devices, emphasizing the critical role of power management systems.
Key Focus Areas:
- Power Efficiency: The design aims to optimize power consumption, essential for extending battery life in mobile devices.
- Chip Area Minimization: To ensure that the ASIC can fit into the compact form factors of modern mobile devices, minimizing the chip area is a crucial aspect of the design process.
- Performance Requirements: The ASIC must deliver high-speed operation, essential for efficient power management in active mobile usage scenarios.
- Thermal Constraints: Managing heat generation is vital to avoid overheating, which is a common issue in compact electronic devices.
Design Solution:
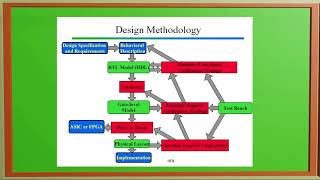
The proposed design utilizes Verilog to integrate various power management circuits into a single ASIC. This integration is focused on maintaining both efficiency in operation and adherence to the thermal and spatial constraints typical in mobile device applications. By employing structured design methodologies and best practices, the ASIC design addresses both performance and practicality in real-world applications.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of the Case Study
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In this case study, VHDL or Verilog is used to design an ASIC for a mobile device's power management system.
Detailed Explanation
This section introduces a case study that focuses on the design of an ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) specifically tailored for power management in mobile devices. ASICs are crucial for enhancing device performance and efficiency since they are customized for specific applications rather than general use. By utilizing VHDL or Verilog, engineers can create a detailed description and simulation of the hardware functionality before actual production.
Examples & Analogies
Think of ASICs like custom-made shoes. Just as some people may need shoes specifically designed for running while others need shoes for casual wear, ASICs are designed for particular tasks, like managing power in a mobile device, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
Design Challenges
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Design Challenges:
○ Optimizing for power efficiency and minimal chip area.
○ Ensuring high-speed performance while meeting thermal constraints.
Detailed Explanation
The design of the ASIC involves several challenges. Firstly, optimizing power efficiency means that the circuit should use as little energy as possible to prolong the battery life of the mobile device. Secondly, minimizing the chip area is crucial because a smaller chip can be cost-effective and can fit into more compact devices. Additionally, achieving high-speed performance is necessary; hence, the chip must operate quickly without overheating, which requires careful thermal management.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine making a sandwich for a picnic. You want to make it as small as possible (minimizing chip area) while still packing enough flavor (high-speed performance) and not letting it get soggy in the heat (thermal constraints). Each element must be balanced to create the perfect picnic sandwich, just like how designers must balance these challenges in ASIC development.
Design Solution
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Design Solution:
Using Verilog, design an ASIC that integrates multiple power management circuits into a small form factor, ensuring efficient operation in a mobile device.
Detailed Explanation
The design solution involves using Verilog, a hardware description language, to create an ASIC that consolidates numerous power management circuits. This integration is key to keeping the physical size of the ASIC small while ensuring that it operates efficiently within the constraints of a mobile device. By carefully designing the circuit structure and behavior using Verilog, engineers can simulate and verify that the ASIC meets both performance and power efficiency requirements before fabrication starts.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like organizing a toolbox. If you can fit multiple tools into a compact toolbox without sacrificing access or usability, that’s efficient design. Similarly, in this ASIC design, multiple circuits need to fit into one small chip without losing their effectiveness. Good organization ensures everything works seamlessly, just as a well-designed ASIC does.
Key Concepts
-
Power Efficiency: Ensuring that power consumption is minimized to extend battery life.
-
Chip Area Minimization: Designing compact circuits that fit within the limited space in mobile devices.
-
High-speed Performance: The need for real-time processing of power management tasks.
-
Thermal Constraints: Managing heat generation to prevent overheating and ensure device reliability.
Examples & Applications
A mobile device ASIC integrating power management circuits such as voltage regulators and battery control ICs.
Using Verilog to model different configurations of power management circuits to optimize power-to-performance ratios.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the compact world of chips, power we seek, / A management plan that’s not weak.
Stories
Imagine a small mobile device, trying to keep its cool while managing power. It learns to balance efficiency and performance, fitting perfectly in a tiny frame.
Memory Tools
Remember the acronym PEP-CT (Power Efficiency, Chip area, Performance, Thermal constraints) to focus on ASIC design aspects.
Acronyms
PEP-CT
Power Efficiency
Chip area
Performance
Thermal constraints.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- ASIC
Application-Specific Integrated Circuit; a type of integrated circuit customized for a specific use.
- Power Management System
A system that regulates power consumption in electronic devices to optimize battery life and efficiency.
- Verilog
A hardware description language used to model electronic systems.
- Thermal Constraints
Limitations regarding heat generation and dissipation that electronics must operate under to avoid damage.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
