Importance of Ratio Analysis
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Decision-making Tool
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore how ratio analysis acts as a decision-making tool for management. It essentially transforms raw financial data into useful information for strategic planning.

Could you provide an example of how management might use ratios in their decisions?

Absolutely! For instance, if a company has a low current ratio, management may decide to increase short-term financing or restructure their inventory to maintain liquidity. This highlights the importance of monitoring financial ratios.

What are some common ratios that management focuses on for decision-making?

Some critical ones include the liquidity ratios like the current ratio, and profitability ratios like the net profit ratio. Remember the acronym ‘LPP’ for Liquidity, Profitability, and Performance!

How often should management review these ratios?

It varies by company, but typically, financial ratios should be reviewed quarterly to guide timely decisions. Let's summarize: Ratio analysis helps management strategize based on solid financial data.
Financial Health Assessment
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In this session, we shift focus to how investors and banks utilize ratio analysis to evaluate financial health.

What exactly do they look for when assessing financial risk?

They often check the solvency ratios, like the debt-to-equity ratio. A high ratio may signal greater financial risk, influencing lending decisions.

So, does that mean a company with a low debt-to-equity ratio is more favorable?

Correct! Lower leverage can imply lower risk. Remember the mnemonic ‘Less Debt, Less Stress’ to keep this in mind!

How about investors? What do they prioritize?

Investors often analyze return on equity. A high ROE indicates that the company is efficiently utilizing its equity. To summarize, financial ratios are crucial for evaluating the financial health and guiding investment decisions.
Comparative Analysis
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss the significance of comparative analysis through ratio analysis.

How do companies benchmark against their competitors using ratios?

Good question! Companies might compare profitability ratios like gross profit margins with those of their competitors to understand where they stand globally within the industry.

Are there specific ratios that also vary significantly across industries?

Absolutely! Different industries have distinct standards. For instance, a high asset turnover indicates efficiency in retail but could be alarming in manufacturing. Remember ‘Industry Standards Vary’ when thinking about ratio comparisons!

So if ratios differ widely, how do businesses strategize?

They typically analyze their ratios alongside industry averages to pinpoint strengths and weaknesses, making adjustments as needed. In summary, comparative analysis through ratios enables businesses to maintain a competitive edge.
Performance Evaluation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, we’ll delve into performance evaluation with ratios.

What role do ratios play in tracking performance?

Ratios provide measurable indicators for management to assess operational efficiency. For instance, a strong return on capital employed shows effective use of capital. Remember ‘Performance Metrics Matter’!

Do organizations set specific ratio targets?

Yes! Firms often set benchmark ratios based on industry standards or prior performance as goals. Such targets help motivate teams and improve strategy!

Can managers adjust these targets?

Certainly! Targets can be dynamic, depending on market conditions. To sum up, performance evaluation through ratio analysis is crucial for successful management and strategic adjustments.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section highlights the significance of ratio analysis as a decision-making tool for management, investors, and creditors. It focuses on assessing financial health, enabling comparative analysis, and evaluating performance, all of which are vital for strategic planning and investment decisions.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Importance of Ratio Analysis
Ratio analysis plays a pivotal role in financial statement analysis by providing insights into a company's financial health and performance. This section outlines the importance of ratio analysis through various perspectives:
- Decision-making Tool: Ratio analysis aids management in evaluating business strategies by providing quantifiable metrics that can guide decision-making processes.
- Financial Health Assessment: Investors and banks often rely on these ratios to assess risks associated with investments or lending. Understanding the ratios allows stakeholders to gauge a company’s ability to meet its financial obligations and profitability potential.
- Comparative Analysis: Ratio analysis enables businesses to benchmark their performance against competitors or industry standards. This comparative aspect can identify areas of strength or weakness in a firm’s financial position.
- Performance Evaluation: Managers utilize these ratios for goal setting and performance tracking. They can measure their progress against pre-established financial targets or industry norms.
Overall, ratio analysis is an indispensable tool in translating raw data from financial statements into actionable insights, making it essential for BTech CSE students aiming for careers in entrepreneurship or management.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Decision-Making Tool
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Decision-making tool: Helps management evaluate business strategies.
Detailed Explanation
Ratio analysis serves as a crucial decision-making tool. By analyzing various financial ratios, management can evaluate the effectiveness of different business strategies. This helps them to identify what is working well and what needs adjustment. For instance, if a company’s profitability ratios indicate a downward trend, management may need to rethink its pricing strategy or reduce costs.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a coach assessing a sports team’s performance through detailed statistics on wins, losses, and player performance. Similar to how a coach adjusts strategies based on player data, management uses ratio analysis to fine-tune business strategies based on financial performance trends.
Financial Health Assessment
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Financial health assessment: Investors and banks analyze risks before investing or lending.
Detailed Explanation
Financial ratios provide insights into a company's financial health, which is essential for investors and banks. Before they invest or lend money, they analyze ratios like solvency and liquidity to evaluate the risks involved. A company with strong liquidity ratios, for example, is more likely to meet its short-term obligations, making it a safer investment.
Examples & Analogies
Think of investors as doctors conducting a health check-up. Just as a doctor looks at various vital signs—like heart rate and blood pressure—to assess a patient's health, investors check financial ratios to gauge a company's financial stability before committing their resources.
Comparative Analysis
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Comparative analysis: Enables benchmarking against competitors or industry averages.
Detailed Explanation
Ratio analysis allows companies to benchmark their performance against competitors or industry standards. By comparing their ratios with those of similar firms, they identify areas of strength and weakness. This comparative perspective can uncover competitive advantages or highlight strategic areas for improvement.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a classroom where students are graded on their test scores. A student would naturally look at their score compared to the average score of the class to understand their standing. Likewise, businesses analyze their financial ratios against industry averages to determine how well they are performing compared to their peers.
Performance Evaluation
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Performance evaluation: Managers use it for goal setting and performance tracking.
Detailed Explanation
Managers utilize ratio analysis to evaluate departmental and overall company performance. By setting performance goals based on financial ratios, they can track progress over time, determine if targets are met, and make adjustments if necessary. This method promotes accountability and motivates teams to achieve financial objectives.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a fitness program where individuals track their weight loss or muscle gain through measurable goals. Similarly, managers set financial targets and use ratio analysis to monitor progress towards those goals, much like tracking health metrics to achieve a desired fitness outcome.
Key Concepts
-
Decision-making Tool: Ratio analysis aids in evaluating strategic business decisions.
-
Financial Health Assessment: Ratios help investors and banks assess financial risks.
-
Comparative Analysis: Enables benchmarking against competitors and industry standards.
-
Performance Evaluation: Managers use ratios for goal tracking and performance measurement.
Examples & Applications
A company with a low current ratio may seek additional short-term financing to improve liquidity.
Investors analyzing ROE to assess a company's efficiency in generating profit from shareholders' investments.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When numbers dance and ratios sing, decisions made are a smarter thing.
Stories
In a crowded market, a wise manager used ratios to navigate tough decisions, comparing her company against the industry giants and adjusting strategies accordingly.
Memory Tools
LPP stands for Liquidity, Profitability, Performance — remember these to identify key areas in ratio analysis.
Acronyms
CAP for Comparative Analysis Performance - think CAP when addressing competition and evaluation.
Flash Cards
Glossary
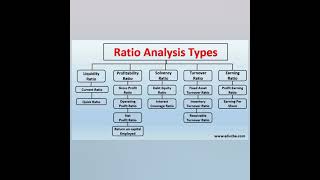
- Ratio Analysis
A quantitative tool used to extract insights from financial statements by establishing relationships between different figures.
- Liquidity Ratios
Ratios that measure a company's ability to meet short-term obligations.
- Solvency Ratios
Ratios that indicate a company's ability to meet long-term obligations.
- Profitability Ratios
Ratios that assess a company's ability to generate earnings relative to revenue, assets, or equity.
- Comparative Analysis
A method of comparing financial ratios against industry averages or competitors to assess relative performance.
- Performance Evaluation
The process of using financial ratios to assess operational efficiency and overall firm performance.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
