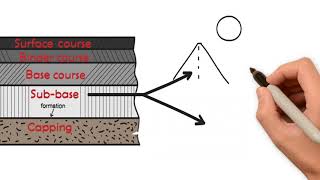
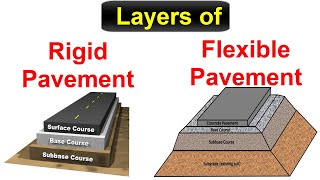
Subbase and Base Course
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Importance of Compaction in Subbase and Base Course
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're focusing on the subbase and base course layers in pavement systems. Can anyone tell me why compaction is important for these layers?

I think it’s to support the weight of vehicles?

Exactly! Proper compaction helps distribute loads effectively. The subbase and base must be compacted to withstand traffic loads without deforming.

Does that mean they get more compactive effort compared to other layers?

Yes, good observation! These layers receive higher compactive efforts to ensure their load distribution capability.

So, if they aren’t compacted properly, what could happen?

Improperly compacted layers can lead to issues like cracking or uneven surfaces in the pavements. Let’s remember the acronym 'LOAD'—Load distribution, Overall support, Adequate compaction, Durability. This can help us recall key points regarding the function of these layers.
Effects of Subbase and Base Compaction
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

How does proper compaction result in longer-lasting pavements?

Maybe because it minimizes how much the pavement can sink or settle?

Right! Compacted subbase and base layers minimize settlement, which is vital for maintaining pavement shape over time.

And it avoids water infiltration too, right?

Correct! Reduced permeability means less water can seep into layers, preventing potential weakening of the structure. 'SAVE' is a good mnemonic here—Settlement avoidance, Strength maintenance, and Water infiltration resistance.

Does proper compaction also impact costs?

Definitely! Properly compacted layers reduce future repair costs due to fewer structural issues. Maintaining the integrity of the pavement leads to long-term savings.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Subbases and base courses are critical components of pavement systems that require substantial compactive efforts. This section emphasizes the importance of proper compaction to ensure effective load distribution and enhance the overall structural support of pavements.
Detailed
Subbase and Base Course
In the context of highway and pavement construction, subbases and base courses are essential layers that contribute to the structural integrity and performance of the pavement system. The compaction of these layers is paramount as it ensures effective load distribution across the entire pavement structure, enhancing its durability and serviceability.
Key Points:
- Higher Compactive Efforts: Both the subbase and base course must undergo significant compaction efforts compared to other layers, primarily to ensure they can adequately distribute loads from traffic above.
- Load Distribution: These layers play a crucial role in distributing loads over a wider area, which minimizes the risk of excessive stress on underlying soils and helps in maintaining the shape and integrity of the roadway.
- Surface Support: An adequately compacted subbase and base course provide the necessary support for contiguous pavement layers, ensuring a stable and durable surface. This is critical in preventing future pavement failures such as cracking or deformation.
Overall, proper understanding and implementation of compaction techniques are vital to achieving long-lasting roadways that can handle the expected traffic loads and environmental conditions.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Importance of Compaction in Subbase and Base Course
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Subbase and Base Course
- Receive higher compactive efforts.
- Ensures load distribution and surface support.
Detailed Explanation
The subbase and base course layers in pavement systems are crucial for providing adequate support to the pavement structure. These layers are subjected to higher levels of compaction to ensure that they can effectively distribute loads from traffic across a wider area. Proper compaction in these layers helps maintain the integrity of the pavement over time, preventing issues such as cracking or uneven settling.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the subbase and base course like the foundation of a house. Just as a strong foundation distributes the weight of the house and prevents it from shifting or cracking, a well-compacted subbase and base course distribute the weight of vehicles on a road, ensuring a smooth and safe driving surface.
Compaction Techniques Used
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Receive higher compactive efforts.
Detailed Explanation
Compaction techniques for the subbase and base course often involve heavy machinery and advanced methods to apply substantial pressure and ensure that the materials are densified effectively. This might include the use of vibratory rollers, pneumatic rollers, or heavy static rollers. The goal is to reach a density level that optimally supports the pavement above while minimizing the potential for future settlement.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to pack a suitcase. If you just throw your clothes in, the suitcase won't close properly, and your items may shift around during travel. However, if you compact your clothes tightly and evenly, the suitcase remains firm and secure. In a similar way, effective compaction ensures that the subbase and base course of pavement stays solid and stable, avoiding future problems.
Key Concepts
-
Subbase: The foundational layer beneath the base course, crucial for load support.
-
Base Course: The layer providing structural integrity for the pavement surface.
-
Compaction: Essential process for densifying layers to improve load-bearing capacity.
-
Load Distribution: Important for maintaining structural integrity and preventing pavement failures.
Examples & Applications
In a highway construction project, the subbase is typically composed of granular materials such as crushed stone, providing good drainage and load distribution.
When constructing a parking lot, proper compaction of the base course ensures the stability of the surface, preventing the development of ruts and cracks.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When layers are compacted tight, pavements last just right!
Stories
Imagine a road where vehicles are heavy, but a compact base supports them steadily, keeping the path smooth and steady for all travelers.
Memory Tools
Remember 'LADS': Load distribution, Adequate compaction, Durability, Stability.
Acronyms
Use the acronym 'BASE' to remember
for Base
for Adequate compaction
for Support
for Even distribution.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Subbase
The layer of material beneath the base course that supports the pavement structure.
- Base Course
The layer immediately beneath the pavement surface that provides structural support and load distribution.
- Compaction
The process of applying mechanical energy to soil to increase its density by reducing air voids.
- Load Distribution
The process of spreading the weight of the pavement and traffic over a wider area to prevent excessive stress.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
