Subgrade Compaction
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Importance of Subgrade Compaction
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are focusing on subgrade compaction, which serves as the foundation for the entire pavement structure. Can anyone tell me why this might be important?

I think it ensures the pavement doesn't settle too much over time.

Exactly! Proper compaction minimizes settlement and enhances load-bearing capacity. Remember, 'compact to last!' helps us recall the importance of this process.

What happens if it's not compacted properly?

Great question! It can lead to problems like cracking or even potholes. Would anyone like to guess the compaction level we aim for?

Isn't it 90-95% of the Maximum Dry Density?

That's correct! Excellent remembering. To summarize, effective subgrade compaction is crucial for long-term pavement durability.
Methods of Achieving Compaction
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's explore how we achieve that compaction. Can someone tell me about the methods we might use?

I know rollers are often used for compaction!

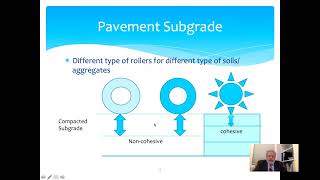
Correct! Various rollers, such as sheepsfoot and vibratory rollers, are effective depending on the soil type. Let's remember, 'sheepsfoot for clay, vibrate for sand!'

What about the moisture? Does it play a role?

Absolutely! The right moisture content is crucial for achieving optimal density. Too much or too little can hinder compaction.

Is there a specific target moisture content?

Yes, it usually aligns with the optimum moisture content derived from laboratory tests. In summary, using the right methods and moisture content ensures effective compaction.
Impact of Poor Compaction
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

What do you think the consequences are of inadequate subgrade compaction?

Maybe it would lead to more repairs?

That's right! It can cause increased maintenance and repair costs. Remember, long-term performance depends on this foundational work!

Could it also impact the surrounding environment?

Good thought! Poor compaction can lead to increased water infiltration, which might negatively influence nearby structures.

So, it's really a long-term investment to do it right the first time?

Exactly! In summary, investing in adequate subgrade compaction today helps prevent larger issues tomorrow.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section emphasizes the importance of subgrade compaction in highway and pavement construction as it acts as the foundational layer supporting the entire structure. Achieving a compaction level of 90-95% of the maximum dry density is crucial for ensuring durability and minimizing future problems.
Detailed
Subgrade Compaction
Subgrade compaction represents a critical process in highway and pavement construction, forming the foundational layer that supports the entire pavement structure. This section outlines the objectives of achieving proper subgrade compaction, which include enhancing the load-bearing capacity, reducing settlement, and ensuring overall long-term durability of the pavement.
The compaction level required for the subgrade should reach a minimum of 90-95% of the Maximum Dry Density (MDD) as determined by laboratory tests like the Modified Proctor Test. This level of compaction improves shear strength, decreases permeability, and mitigates potential problems such as frost heaving or soil expansion.
The significance of achieving the optimal compaction density cannot be overstated; inadequate compaction could lead to increased maintenance costs and structural failures in the future. Proper methods and techniques must be employed to ensure that the subgrade is uniformly compacted and capable of supporting the loads that will be placed upon it.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Importance of Subgrade Compaction
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Forms the foundation of the pavement.
Detailed Explanation
The subgrade is the bottom-most layer upon which the entire pavement structure is built. It is essential to ensure that this layer is properly compacted as it provides stability and support to the layers above it. If the subgrade isn't adequately compacted, it can lead to issues such as uneven surfaces, cracking, and sinking of the pavement over time.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the subgrade like the foundation of a house. If the foundation is weak or poorly constructed, the entire house may settle unevenly, leading to cracks in the walls and floors. Just as a strong foundation is crucial for a house, so is proper subgrade compaction for pavement.
Compaction Standards for Subgrade
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Compacted to minimum 90–95% of MDD.
Detailed Explanation
MDD stands for Maximum Dry Density, which is determined through laboratory tests. This percentage indicates how densely the soil should be compacted to ensure it can adequately support the weight of the pavement and its expected traffic loads. Achieving a compaction level of at least 90% to 95% of MDD means that the soil has been densified sufficiently to prevent excessive deformation under load.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine packing a suitcase for a trip. If you only fill the suitcase partially, it might get crumpled or lose shape when you add more weight. Packing it tightly ensures that it holds its shape and supports the items inside properly, similar to how proper subgrade compaction helps the pavement maintain its structure under traffic loads.
Key Concepts
-
Subgrade Compaction: Essential for foundation strength in pavement construction.
-
Maximum Dry Density (MDD): The targeted density for effective compaction.
-
Compaction Techniques: Different methods suited for various soil types.
Examples & Applications
A highway constructed with subgrade compacted to 92% MDD is less likely to settle than one at 85% MDD.
Using a sheepsfoot roller for clay soils ensures better density compared to a smooth wheel roller.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
If the ground feels loose and sway, it’s time to compress it right away!
Stories
Imagine building a tall castle on sand. If the sand isn’t packed firm, the castle will tumble. Just like a pavement!
Memory Tools
Remember the acronym C.L.A.P. - Compact, Level, Assess, Protect – to ensure proper subgrade compaction.
Acronyms
COMP
Compact Optimal Moisture Percentage for successful subgrade compaction.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Subgrade
The layer of soil prepared to support the pavement structure.
- Maximum Dry Density (MDD)
The highest density of a soil achieved during compaction under specific moisture conditions.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
