Multiplexing
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Multiplexing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will be discussing multiplexing, particularly how it applies to controlling multiple 7-segment displays. Can anyone share what they think multiplexing means in this context?

I think it's about displaying numbers on more than one 7-segment display at the same time.

That's close! Multiplexing allows us to control multiple displays but actually illuminates one at a time, and by switching quickly, it appears all are lit simultaneously. Can anyone explain why this is beneficial?

It saves on using a lot of GPIO pins, right?

Exactly! By sharing pins among the displays, we optimize resources. Remember, we use the acronym 'MANY' to recall that multiplexing Allows_Numerous_7-segment_displays to share pins.
Mechanics of Multiplexing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's dive into how this switching is done—what do you think is key to making multiplexing effective?

Is it how fast you can switch between the displays?

Exactly! If we switch displays quickly enough, the human eye won’t notice the flickering. Who can tell me what timing control helps achieve this?

It helps in determining how long each display stays active!

That's right! If each display is on for just a fraction of a second, it gives the effect of all displays being on at once. This is the basis of multiplexing—efficiency in timing!
Applications of Multiplexing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's talk about where you might encounter multiplexing in real life. What are some uses of this technique?

I think it’s used in digital clocks and counters!

Yes! In digital clocks, multiple digits are displayed but the system needs to conserve space and energy. What other applications can you think of?

Maybe in devices like scoreboards?

Great example! Multiplexing is vital for any application where you need multiple outputs without taking up too many resources.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explores how multiplexing allows microcontrollers to manage multiple 7-segment displays effectively. The process illuminates one display at a time, yet quick switching enables a perception of simultaneous display of multiple numbers. It is crucial for efficiency in resource-limited embedded systems.
Detailed
Multiplexing in 7-Segment Displays
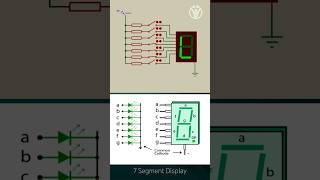
Multiplexing is an essential technique in embedded systems that enables a microcontroller to control multiple 7-segment displays. In a single microcontroller, resources such as GPIO pins can be limited, resulting in a need for efficient usage of these resources. Multiplexing achieves this by activating one display at a time while rapidly switching between displays to create the illusion that all are illuminated simultaneously. This technique ensures that each display receives its appropriate control signals using a shared set of pins.
Key Points:
- Definition of Multiplexing: A method that allows multiple 7-segment displays to be driven sequentially rather than all at once.
- Efficiency: Reduces the number of GPIO pins required when displaying numbers. Instead of using a dedicated pin for each segment of every display, multiplexing allows many displays to share pin resources.
- Timing Control: It relies on timing control, where a display stays active for a fraction of a second before switching to the next one. If done fast enough, the human eye perceives all displays as being simultaneously lit.
- Implementation: Typically involves a microcontroller outputting signals in a round-robin fashion—turning one display on, then off, and immediately switching to the next display.
- Applications: Commonly used in clocks and counters where multiple digits need to be displayed but space and power consumption are critical concerns.
Understanding multiplexing is key for engineers designing compact and efficient systems that require displaying numerical information.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Multiplexing in 7-Segment Displays
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In systems with multiple 7-segment displays, multiplexing is used to drive each display in turn. Only one display is illuminated at a time, but rapid switching between displays gives the illusion that all displays are showing numbers simultaneously.
Detailed Explanation
Multiplexing is a technique that allows multiple displays to share the same set of control signals by illuminating them one at a time very quickly. For instance, imagine you have three 7-segment displays showing the numbers 1, 2, and 3. Instead of trying to light up all three displays at once, the microcontroller lights up the first display for a brief moment, then switches to the second display, and then to the third. This switching happens so fast that to the human eye, it seems like all three displays are illuminated at the same time. This method reduces the number of pins needed from the microcontroller to the displays, as fewer connections are needed, while still being able to show multiple numbers.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a stage performance where there are multiple performers taking turns to shine under a spotlight. Only one performer is illuminated at a time, but the lighting is switched quickly between them. The audience perceives it as all performers being present under the spotlight, creating a dynamic and engaging experience without needing multiple spotlights.
Digital Encoding for Display Control
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
To drive a 7-segment display, a binary or BCD (binary-coded decimal) value is encoded into a 7-bit control signal that corresponds to the required segments. This encoding ensures the correct number or character is displayed.
Detailed Explanation
Driving a 7-segment display involves converting the desired number (like 0 to 9) into a format that the display can understand, called binary-coded decimal (BCD). For example, to display the number '2', the microcontroller sends a 7-bit signal where each bit corresponds to whether a specific segment should be turned on or off. There are 7 segments in total, and the bits in this signal will determine which segments light up to form the shape of the number '2'. If the segments are correctly illuminated, the display will show '2' clearly to the viewer.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are giving instructions for a new game to your friends. Instead of telling them everything at once, you provide concise instructions (like using a code) for each part of the game. Just like your friends will only follow the parts of the instructions relative to their roles, the display only lights up the segments necessary to form the specific number you want to show.
Key Concepts
-
Multiplexing: A technique to control multiple 7-segment displays using fewer GPIO pins by activating displays one at a time.
-
Timing Control: The key to making multiplexing effective, determining how quickly displays can be switched to create the illusion of simultaneous display.
Examples & Applications
In a digital clock, multiplexing allows the display of hours, minutes, and seconds using only a few pins to drive all the segments.
Scoreboards in sports often use multiplexing to display the current score, allowing quick updates while saving on pin usage.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a row the digits stand, One by one they show their hand. Bright and quick, not all at once, Multiplexing gives them just the right punch.
Stories
Imagine a busy restaurant where each waiter (the display) only comes to your table (the microcontroller) to take your order one at a time, but they move so fast that it feels like all are serving you at once.
Memory Tools
Remember 'MANY' for Multiplexing Allows_Numerous_7-segment_displays to share resources.
Acronyms
Use the acronym 'FAST' to remember
Fewer Active Segments Together represent 7-segment multiplexing.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Multiplexing
A technique that allows multiple displays to be controlled using fewer pins by activating displays sequentially.
- 7Segment Display
An electronic display device that uses seven individual segments to display numerical information.
- GPIO pins
General Purpose Input/Output pins, used for interfacing between the microcontroller and external devices.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
