Real-World Applications
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Intro to Real-World Applications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into the real-world applications of timers, GPIO, and 7-segment displays. What functions do you think each of them serves in a practical device?

I think timers are used for keeping track of time and events.

Exactly! Timers provide the precise time signals necessary for many applications. And how about GPIO? What role does it play?

GPIO is like the interface for the processor to control other devices, right?

Correct! GPIO pins can be configured as inputs and outputs to interact with external devices. Now, can anyone tell me how 7-segment displays are used in these examples?

They show information like numbers, like in a clock?

Yes, they visually represent data for users. So, we see a clear synergy here: Timers give a time reference, GPIO manages the input/output, and displays present the results.

In summary, the combination of these components powers many everyday applications like digital clocks.
Exploring Specific Applications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s explore specific applications in more detail. How does a digital clock function?

The timer creates clock ticks, which update the time displayed by the 7-segment display.

Exactly! The timer generates those ticks, and GPIO controls the display to show the correct time. What about event counting applications?

In event counting, GPIO reads input from buttons, and the timer probably helps keep track of intervals.

Great observation! The timer keeps track of how long the events have been counted, and the 7-segment display shows the total in a visual format. Can you think why this would be useful in a scoreboard?

So people can see who is winning by counting the points or events automatically!

That's right! The integration of these components enhances usability and efficiency in real-world applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The integration of timers, GPIO, and 7-segment displays is crucial in embedded system design. This section highlights real-world applications, such as digital clocks and event counting displays, emphasizing how these components interact to fulfill practical tasks.
Detailed
Real-World Applications
In embedded systems, the integration of timers, GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output), and 7-segment displays allows for the realization of various practical applications. This section elucidates how these components come together to serve users effectively.
Digital Clocks
One of the most prevalent applications is the digital clock where the timer generates precise clock pulses, while GPIO controls the display of the current time on the 7-segment displays. This synergetic operation allows for real-time representation of time.
Event Counting and Display
Timely data management is also important in applications such as event counting. Here, GPIO pins monitor external inputs, such as button presses or sensor events. The timer keeps track of elapsed time, and the 7-segment display shows numerical results, making this setup useful in various contexts, such as counters or scoring systems in competitions.
Ultimately, the effective integration of these components enhances functionality and user experience in embedded system applications.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Digital Clocks
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
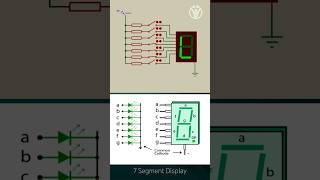
A timer generates clock pulses, and GPIO controls the 7-segment displays to show the current time.
Detailed Explanation
Digital clocks utilize timers to create regular pulses that represent the flow of time. The timer generates these clock pulses at a constant frequency. For instance, one pulse every second corresponds to one tick of real time. On the other hand, GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output) pins are used to drive the 7-segment displays, which visually show the current time. Each segment of a 7-segment display corresponds to a numeral. By activating the appropriate segments based on the time calculated by the timer, we can display hours and minutes to the user effectively.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a digital clock as a conductor leading an orchestra. The timer acts as the metronome, keeping the rhythm (timing) for the conductor to cue the musicians (the segments of the display). If the metronome ticks every second, the conductor can tell the musicians when to play the right notes at the right time, producing a synchronized performance that everyone can read as the time.
Event Counting and Display
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
GPIO pins are used to monitor external inputs (e.g., a button press or sensor event), and the timer keeps track of the time elapsed. The 7-segment display shows the result.
Detailed Explanation
In applications like electronic counters, GPIO pins are employed to detect events such as a button press or a signal from a sensor. Whenever an event is detected, the associated GPIO pin sends a signal, and this can be counted using a timer mechanic. The timer helps track how many events have occurred over time and can even keep a history of elapsed time since the last event. The cumulative count is displayed on a 7-segment display, allowing users to see how many events have happened or how long it has been since the last reset.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a clicker used to count how many people enter a store. Each time a customer walks in, a button is pressed (representing the GPIO event), and the clicker keeps a tally (the timer counts). Just like checking the register to see how many customers visited throughout the day, the 7-segment display shows the total count at all times, making it easy for the store owner to see how busy they are.
Key Concepts
-
Integration: The collaboration of timers, GPIO, and 7-segment displays enhances application functionality.
-
Digital Clocks: Utilize timers for accurate timekeeping and GPIO for display control.
-
Event Counting: Involves monitoring inputs and displaying results, demonstrating practical applications.
Examples & Applications
Example 1: A digital clock uses a timer to increment time and GPIO to control the display.
Example 2: An event counter uses GPIO to read button presses and a timer to track time intervals.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
A timer ticks, the GPIO links, 7-segment shows as time winks.
Stories
Imagine a clock that uses a timer to tick away the seconds. The GPIO dances, controlling the display segments to show the time as it moves, always accurate and bright.
Memory Tools
To remember key uses: T-G-7 (Timers give, GPIO governs, 7-segment shows).
Acronyms
DIG (Display, Input, Generate) helps to recall the roles.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Timer
A component that generates time-based signals for timing applications.
- GPIO
General Purpose Input/Output pins for interfacing with external devices.
- 7Segment Display
An electronic display used for showing numbers, consisting of seven segments.
- Digital Clock
A clock that displays time in a numerical format with the help of electronic components.
- Event Counting
The process of counting external events, typically using sensors or buttons.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
