Heap Tuning
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Heap Tuning
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome class! Today we’re diving into Heap Tuning. Can anyone tell me why tuning the heap is important for JVM performance?

It helps in managing memory allocation, right?

Exactly! When we tune the heap, we optimize how memory is allocated for objects in our application. This can help prevent performance issues.

What parameters can we set for heap tuning?

Great question! We commonly use `-Xms` to set the initial heap size and `-Xmx` for the maximum heap size. Remember this: Initial size is the 'starting point' - think of it as your house foundation!

What happens if we set these values too low?

If we set them too low, our application might run out of memory, leading to `OutOfMemoryError`. So, we need to find the right balance.

What about the Eden and Survivor spaces? How do those come into play?

Good point! The heap is divided into different generations: Young Generation, which includes Eden and Survivor spaces, and Old Generation. Adjusting the Eden/Survivor ratio can enhance garbage collection efficiency.

Let’s recap: Heap tuning is about managing how our application uses memory to ensure it runs smoothly and efficiently. Always monitor your application performance after making adjustments.
Understanding Heap Size Parameters
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s discuss how to set the heap sizes. Who remembers what `-Xms` does?

It sets the initial heap size!

Correct! And `-Xmx`?

That’s the maximum heap size.

Right! Setting these values appropriately helps avoid memory shortages. What can happen if the maximum size is exceeded?

The application may crash with `OutOfMemoryError`.

Exactly! To avoid this, you must monitor your application and adjust these settings based on the workloads. Can you think of an application that might need a larger heap?

Perhaps a game or a large-scale enterprise application?

Absolutely! Larger applications require a well-thought-out memory strategy for optimal operation. Keep practicing with these concepts to master JVM tuning.
Adjusting Eden and Survivor Spaces
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's discuss how we can optimize the Eden and Survivor spaces using the `-XX:SurvivorRatio`. Who can explain what this does?

It adjusts the ratio of the Eden area compared to the Survivor spaces?

Exactly! This ratio determines how much memory is allocated to the new object allocation. A higher Eden space can improve allocation rates but also lead to longer garbage collection times.

So, how do we find the right balance?

You can monitor garbage collection logs to see how often collections happen and learn from that data. Always test different configurations.

What if I set the ratio too high?

Then you may face longer pauses during garbage collection. It’s a balancing act! Remember, adjust iteratively and monitor performance.

Can this be done dynamically?

Heap adjustments typically require a restart of the JVM. So plan your changes carefully!

To summarize, heap tuning includes setting the heap sizes and adjusting the Eden/Survivor ratio to optimize memory allocation and garbage collection.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Heap tuning is a critical step in JVM performance optimization. It encompasses setting the initial and maximum heap sizes using the -Xms and -Xmx flags, and adjusting the Eden/Survivor ratio to ensure efficient memory management, which can significantly impact application performance.
Detailed
Heap Tuning
Heap tuning refers to the adjustments made to the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) heap environment to improve application performance and memory utilization. The heap is where all Java objects and class instances reside, and its management can directly influence the behavior of garbage collection and application throughput.
Key Techniques for Heap Tuning
-
Setting Heap Size: Using the flags
-Xms(initial heap size) and-Xmx(maximum heap size), developers can control the amount of memory allocated to the heap. This is vital for preventingOutOfMemoryErrorand ensuring that applications have enough memory to perform optimally. -
Tuning Eden and Survivor Spaces: The heap memory is subdivided into the Young Generation (which includes the Eden space and two Survivor spaces) and the Old Generation. By adjusting the
-XX:SurvivorRatio, developers can tune the ratio of memory allocated to these spaces. A well-balanced configuration allows for better garbage collection performance, leading to fewer pauses and smoother application runtime.
These tuning parameters must be considered in conjunction with the application's needs, typical workloads, and the specific garbage collection strategy employed. Effective heap tuning can lead to significant enhancements in performance and responsiveness, especially for large-scale applications.
Youtube Videos



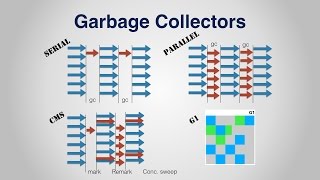




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Setting Heap Size
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Use -Xms and -Xmx to set initial and max heap.
Detailed Explanation
In Java, the memory allocated to the application is managed through a pool known as the heap. The -Xms parameter allows you to set the initial heap size when the JVM starts, while -Xmx determines the maximum size the heap can grow to during execution. This tuning helps ensure that your Java application has enough memory allocated for optimal performance without consuming excessive resources.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine filling a balloon. If you start with a small balloon (small initial heap size) and then inflate it to a larger size (maximum heap size), you might run out of air (memory) if you try to over-inflate. By setting a balanced initial size and maximum size for the heap, you can better manage how much balloon space you need for a successful result.
Tuning Eden and Survivor Spaces
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Tune Eden/Survivor ratio with -XX:SurvivorRatio.
Detailed Explanation
The heap in a Java application is divided into several parts for efficient memory management. The Young Generation consists of the Eden space and Survivor spaces. The Eden space is where new objects are created, and the Survivor spaces hold objects that have survived garbage collection. The -XX:SurvivorRatio parameter allows developers to adjust the ratio between the Eden space and the Survivor spaces. A well-tuned ratio can improve memory allocation and garbage collection efficiency.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the Eden space as a new classroom where students (objects) are initially placed. As students graduate (survive garbage collection), they move to a smaller holding area (Survivor space) before they are placed in a permanent classroom (Old Generation). By adjusting the size of the new classroom compared to the holding area, teachers (developers) can optimize the learning experience (memory efficiency) in the school (the JVM).
Key Concepts
-
-Xms: Sets the initial heap size for the JVM.
-
-Xmx: Defines the maximum heap size limit for the JVM.
-
-XX:SurvivorRatio: Configures the ratio for the Young Generation’s Eden space versus the Survivor spaces.
Examples & Applications
Example 1: Setting -Xms to 512m and -Xmx to 2048m, which sets the initial heap size to 512MB and allows it to grow up to 2GB.
Example 2: Using -XX:SurvivorRatio=8, allocating 8 parts to the Eden space and 1 part to each Survivor space.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For heap tuning to be right, set -Xms to start the flight, -Xmx gives room for the height!
Stories
Imagine building a tower. The base is strong with -Xms, but to reach the sky, -Xmx ensures there's enough space to grow further!
Memory Tools
REMEMBER: REScue Efficient Memory by Adjusting Ratios - for tuning heap spaces!
Acronyms
HEAP = Heap Efficiency Adjusted Performance - emphasizing the significance of tuning.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Xms
JVM command-line option to set the initial heap size.
- Xmx
JVM command-line option to set the maximum heap size.
- XX:SurvivorRatio
JVM parameter that configures the ratio between the Eden space and the Survivor spaces.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
