Native Method Stack
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Native Method Stack
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into the Native Method Stack. Can anyone tell me what they think this stack does?

Is it related to native methods being called in Java programs?

Exactly! The Native Method Stack is responsible for keeping track of information related to native methods, which are functions written in other languages like C or C++. These methods can interact with Java, allowing for additional functionality.

So, how does that help us as developers?

Great question! By understanding how the Native Method Stack works, we can better optimize our Java applications and debug issues when interacting with native libraries.

Do all threads have their own Native Method Stack?

Yes! Each thread in the JVM has its own Native Method Stack, allowing multiple native calls to be executed independently. This ensures thread safety when invoking native methods.

What happens if there’s an error in the native method execution?

If a native method fails, it can affect the Java application as a whole. This is why proper debugging and error handling for native methods is essential.

To recap, the Native Method Stack holds information relevant to native method invocations, helping us optimize performance and troubleshoot effectively. Any questions before we move on?
Threads and Native Method Stack
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's discuss how the Native Method Stack relates to threads. Why do you think having a separate stack for each thread is important?

I guess it prevents one thread from messing up another's method calls?

Exactly! Each thread maintains its own Native Method Stack, which helps keep method execution isolated. This increases safety and performance when multiple threads interact with native code.

Can that lead to increased memory usage, though?

Yes, it can. Each Native Method Stack consumes memory, and if there are many threads, the cumulative memory usage can grow. This is something we need to manage carefully.

How do you monitor that memory usage?

Tools like VisualVM can help you monitor memory usage patterns and track down performance bottlenecks in both Java and native code.

In summary, each thread has its own Native Method Stack, which promotes isolation and safety, albeit at a cost of potential higher memory usage. Let's keep these points in mind as we continue studying JVM internals.
Practical Implications of Native Methods
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Moving on, let's look at what it means to use native methods within Java applications. Why might a developer choose to use them?

To access system-level or performance-critical functions?

That's correct! Developers often use native methods to leverage existing libraries or achieve performance improvements for resource-intensive operations.

Are there downsides to using them?

Yes, using native methods can introduce complexity, such as dealing with memory management directly and potential platform dependencies.

How do we ensure safety while using native methods?

Always ensure proper exception handling and resource cleanup. Using Java’s built-in tools for memory management can help mitigate some risks, but caution is advised.

To conclude, while native methods can provide performance boosts, they bring added complexity and risks, requiring careful management. Do you have any final thoughts?
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
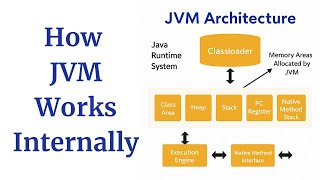
The Native Method Stack is a crucial component of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), storing necessary details for executing native methods that are not defined in Java but in other languages like C or C++. Understanding its role enhances JVM performance optimization and debugging efforts.
Detailed
Native Method Stack
The Native Method Stack is an integral part of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) that stores information needed for the execution of native methods. Native methods are those written in languages like C or C++ that can be called directly from Java code. This stack is separate from the Java stack and plays a vital role in bridging the gap between Java and non-Java code.
In JVM implementations such as Oracle's HotSpot, the Native Method Stack helps manage memory for native functions, maintaining a clear distinction between Java bytecode execution and lower-level native code. Each thread in the JVM has its own Native Method Stack, allowing multiple native calls to occur simultaneously without interference. Understanding the workings of the Native Method Stack is essential for developers looking to optimize performance and troubleshoot issues that may arise when interfacing Java with native code.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Native Method Stack
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Stores information for native (non-Java) methods.
Detailed Explanation
The Native Method Stack is a special area of memory that is used to store information required to execute methods written in languages other than Java, such as C or C++. These languages are referred to as 'native' languages. The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) supports these native methods so that developers can leverage system-level features or perform certain operations that Java itself does not directly support.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the Native Method Stack like a toolbox that a construction worker keeps with them. While most of their tasks can be done using standard tools, sometimes they need specialized equipment that is not part of their regular toolbox. Similarly, Java developers may use native methods for operations like hardware access or performance optimizations, which require specialized capabilities beyond what the Java environment provides.
Purpose of Native Method Stack
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• It enables Java applications to interact with the system and libraries written in other languages, offering flexibility and performance for specific tasks.
Detailed Explanation
Native methods can call functions and libraries written in other programming languages, which allows Java applications to perform a range of tasks that may be more efficient or straightforward in those languages. This is particularly useful for resource-intensive operations like graphics rendering or accessing operating system resources. The Native Method Stack is therefore essential for achieving performance enhancements and interoperability in Java applications.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a chef working in a restaurant that only serves Italian food but occasionally needs to prepare a dish from a completely different cuisine, say sushi. To do this, the chef relies on specialized knives and utensils not found in their usual kitchen tools. In this analogy, the native method stack is similar to those special utensils that help the chef create a unique dish, thus enhancing the restaurant's menu.
Key Concepts
-
Native Method: A method designed in non-Java languages that can be executed from Java applications.
-
Native Method Stack: The stack memory dedicated to native method calls and management in the JVM.
-
Thread Isolation: Each thread maintains its own stack for safe execution without interference.
Examples & Applications
Using JNI to call a C function from Java for performance-sensitive computations.
Implementing a native method in a Java application to access platform-specific features.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When Native Methods call, stacks for threads stand tall!
Stories
Imagine a kitchen where each chef (thread) has their own set of utensils (Native Method Stack) to prepare unique dishes (native methods) without mixing them up.
Memory Tools
KNIGHT: K = Keep track of Native methods; N = Native Method Stack; I = Isolated per thread; G = Gaining performance; H = Handle with care; T = Thread safety!
Acronyms
NMS - Native Method Stack
for Native
for Method
for Stack.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Native Method
A method defined in a programming language other than Java (for example, C or C++) that can be invoked from Java code.
- Native Method Stack
A stack memory area within the JVM responsible for storing information about native method invocations.
- Thread
A single sequence of execution within a program, where each thread has its own environment and can execute code independently.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
