JVM Options
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Heap Size Options
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, let's discuss how the JVM heap size options like -Xmx and -Xms can impact our application performance. Who can tell me what these flags do?

I believe -Xmx sets the maximum heap size and -Xms sets the initial heap size.

Exactly! So, why is it important to configure these values correctly?

If we set them too low, we could run into memory issues, and if they are too high, it could lead to inefficient memory usage.

But how do we determine the right values to use?

Great question! It often depends on the application's requirements, including its memory footprint and performance metrics. Monitoring tools can help you get a clear picture. A good starting point is to set -Xms and -Xmx to the same value to prevent the JVM from resizing the heap during runtime.

So, remember the acronym 'SHR' for 'Set Heap Resolutely' when managing these options successfully.

To summarize, -Xmx sets the max heap, -Xms sets the initial heap, and it's crucial to set these values based on your application's needs.
Garbage Collection Options
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's explore garbage collection options. Who can explain what -XX:+UseG1GC does?

It enables the Garbage-First garbage collector, right? It focuses on optimizing for large heaps.

Exactly! G1 is configured for applications requiring a balance between throughput and pause times. How does this compare to other collectors?

I think traditional collectors like CMS work differently by trying to minimize pause times but can lead to fragmentation.

Correct! G1 and the newer collectors like ZGC are more modern approaches designed for better flexibility and efficiency. Remember, 'Garbage is G1's Gold' as an easy phrase to remember when choosing a collector.

In summary, selecting the right garbage collector like G1GC can significantly impact performance, especially for applications with large memory requirements.
The Impact of Logging Options
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s talk about logging with -Xlog:gc*. Why might we want to use this option?

To monitor garbage collection activities, right? It helps identify performance bottlenecks.

Absolutely! By observing GC logs, you can tune your settings further. What sort of information does it provide?

It usually includes details like the duration of GC events and memory freed during the process.

Exactly, and this data can guide you in making informed decisions about memory management. So, how can we remember this?

Maybe something like 'Logs Lead to Learning'?

That's a great mnemonic! To recap, using -Xlog:gc* lets you capture and analyze GC behavior, which is essential for tuning performance. Regular log analysis reveals patterns that may not be apparent otherwise.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section covers common JVM options that can be used to optimize the performance of Java applications. It highlights key flags for heap size, garbage collection, and logging, providing developers with tools to fine-tune their JVM settings according to their application's needs.
Detailed
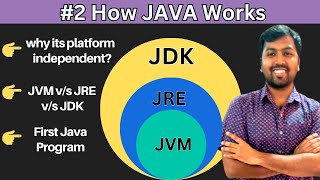
JVM Options
The JVM options allow developers to customize the behavior of the Java Virtual Machine for various applications. Understanding these options is crucial as they can significantly affect the performance and efficiency of Java applications. Common flags include:
-Xmxand-Xms: These options set the maximum and initial heap size, directly influencing how much memory the JVM can allocate for storing objects.-XX:+UseG1GC: This flag enables the Garbage-First (G1) garbage collector, designed for applications with large heaps and low-latency requirements.-Xlog:gc*: This logging option allows developers to track garbage collection events and performance, helping to identify potential issues and areas for optimization.
Each of these settings can be critical in managing resource usage in applications, especially in environments where memory management and performance are paramount.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Common JVM Flags
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- -Xmx, -Xms: Heap size
- -XX:+UseG1GC: Use G1 GC
- -Xlog:gc*: GC logging
Detailed Explanation
This chunk introduces common options that can be used when starting the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). The -Xmx and -Xms flags are used to set the maximum and initial heap sizes, respectively, which control how much memory the JVM allocates for its operations. -XX:+UseG1GC specifies that the JVM should use the G1 Garbage Collector, a specific algorithm designed to improve memory management. The -Xlog:gc* option enables garbage collection logging, helping developers monitor and tune memory usage.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the JVM as a restaurant. The -Xmx and -Xms options set the size of the kitchen: -Xms is the amount of space available at the start, while -Xmx is the maximum space the kitchen can expand to during busy hours. Choosing -XX:+UseG1GC is like picking a special cooking method that aims to efficiently manage the ingredients (memory) in the kitchen, while -Xlog:gc* is akin to keeping a diary of each meal prepared, allowing the chef to review when things ran out or took too long to cook.
Key Concepts
-
-Xmx: Maximum heap size setting for the JVM.
-
-Xms: Initial heap size when launching the JVM.
-
-XX:+UseG1GC: Flag to enable G1 garbage collector.
-
-Xlog:gc*: Command to enable GC logging.
Examples & Applications
Setting -Xmx2048m and -Xms1024m allows the JVM to allocate 2GB as the maximum heap size, starting with a minimum of 1GB.
Using -XX:+UseG1GC optimizes garbage collection on applications with large amounts of memory, providing a balance between pause times and throughput.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For heaps large or small, use -Xmx, keep your app on the wall.
Stories
Imagine a gardener who can only harvest as much as allowed by their storage box. If they fill it too quickly with -Xms, they'll run out of space. If they set -Xmx just right, they harvest efficiently.
Memory Tools
Remember the phrase 'Max out heaps' to recall that -Xmx deals with maximizing memory limits.
Acronyms
Use 'HGL' for Heap Growth Limits to remember -Xmx and -Xms.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Xmx
Defines the maximum heap size the JVM can allocate for the application.
- Xms
Defines the initial heap size available to the JVM.
- XX:+UseG1GC
Enables the Garbage-First garbage collector for optimized performance with large heaps.
- Xlog:gc*
Enables logging of garbage collection events for performance monitoring.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
