Method Area (MetaSpace in HotSpot)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to MetaSpace
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll discuss the Method Area of the JVM, which is known as MetaSpace in the HotSpot implementation. Who can tell me what general information is stored in the Method Area?

Is it where all the classes and methods metadata are stored?

Exactly! The Method Area stores class structures, method definitions, and constant values. It's crucial for the JVM to load and execute classes efficiently. To remember this, you can think of it as a library catalog—everything is organized for quick access!

What happens if a class is not used anymore? Does it stay there forever?

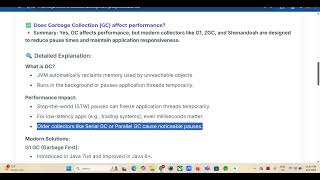
Good question! In HotSpot, the memory for classes can dynamically expand and contract, thus avoiding memory leaks and optimizing usage. This is done through garbage collection, which can reclaim the memory from classes that are no longer in use.

Can you explain more about how this garbage collection works?

Certainly! When a class is unloaded or no longer needed, its corresponding metadata in the Method Area can be marked for deletion during garbage collection cycles, freeing up that memory for new classes. Remember, efficient memory management is key for performance!

To summarize, the Method Area (MetaSpace) holds critical information that allows the JVM to execute Java applications efficiently and it can adapt dynamically to the needs of the application. Any questions before we move on?
Comparison with Previous Versions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's dive into some historical context. Before MetaSpace, the JVM used 'Permanent Generation' for class metadata. How does anyone think MetaSpace improves on this?

Isn't Permanent Generation limited in size? So maybe MetaSpace allows for more flexibility?

Correct! Permanent Generation had a fixed size limit which could lead to `OutOfMemoryError`. MetaSpace, on the other hand, uses native memory, allowing for better scalability as classes can be loaded and unloaded as needed without hitting strict memory limits.

Does this mean more classes can be loaded into memory at once?

Exactly! With MetaSpace, the JVM can handle more classes concurrently, which can lead to improved application performance and responsiveness. Plus, it tunes itself according to system resources, which is a big win.

So, is this all automatic, or do we have to configure anything?

While the JVM manages MetaSpace dynamically, you can set parameters like `-XX:MaxMetaspaceSize` to control how much native memory can be used if you have application-specific constraints. Always important to monitor your application!

In summary, MetaSpace enhances memory management for class metadata over the previous Permanent Generation approach, allowing dynamic allocation and improving overall application performance. Any further questions?
Significance for Performance Tuning
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's connect everything to performance tuning. Why should understanding the Method Area or MetaSpace be on every Java developer's radar for tuning?

I believe it affects how quickly classes can be loaded, impacting application speed?

Exactly! Loading times can affect startup performance. If you've optimized your classes but they don't load fast enough, you won't see the benefits. Monitoring the Method Area gives insights into how classes are being managed.

So if there are memory issues related to class loading, that's something we should check, right?

Yes! Mismanagement here could mean wasted resources and lag in performance. Regularly checking MetaSpace utilization will help avoid unnecessary overhead and ensure efficient memory use.

What tools can we use to monitor this part of the JVM?

Great question! Tools like JConsole or VisualVM can provide visual insight into MetaSpace utilization and help proactively manage Java application performance. Monitoring is key!

Summarizing our session today: understanding MetaSpace is crucial for efficient JVM performance. It's a dynamic area that impacts class management and overall application efficiency. We must stay vigilant on its utilization. Any final questions?
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The Method Area (or MetaSpace in HotSpot) is a crucial component of the JVM that stores metadata about classes, method data, and constants. This section explains its function and significance within the broader JVM architecture.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
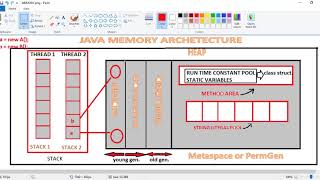
The Method Area, referred to as MetaSpace in the HotSpot implementation of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), plays a vital role in storing essential information for class execution. Unlike traditional heap memory, where objects and instances are stored, the Method Area maintains metadata about Java classes, including their definitions, method data, and constant pool information.
- Purpose: The Method Area keeps a structured representation of the class data, enabling the JVM to quickly reference and execute methods at runtime.
- Dynamic Nature: Unlike the Permanent Generation, which had limits on memory allocated for class structures, MetaSpace dynamically adjusts its size based on the demands of the application, leveraging native memory, thus improving performance.
- Garbage Collection: Important for optimizing memory usage, the Method Area can be cleaned up to prevent memory leaks caused by lingering metadata references from classes that are no longer in use.
Understanding the Map of the Method Area is critical for Java developers as it directly influences application performance, scalability, and memory management.
Youtube Videos



![🔥 How JVM Internally Works | JVM Architecture in detail | Learn About JVM [Hindi]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/48bHZPzCpGg/mqdefault.jpg)


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Purpose of the Method Area
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Stores class structure like metadata, method data, and constants.
Detailed Explanation
The Method Area is a crucial part of JVM's runtime memory. Its primary role is to store various pieces of information about classes that the JVM loads. When a Java application runs, classes are loaded into memory, and the Method Area saves their structure. This includes metadata (data about the class itself), method data (information about methods like their signature), and constants used in the program. Understanding this area helps developers optimize memory usage and speed up class loading.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a library where each book (class) is cataloged. The library system (Method Area) holds not just the books but also information about each book—its title, author, and genre (metadata), as well as its contents and key themes (method data). Having this catalog allows the library to find and access the books quickly.
MetaSpace vs. Permanent Generation
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
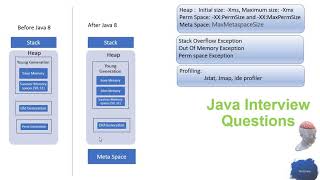
The Method Area in HotSpot has evolved from the Permanent Generation to MetaSpace in Java 8 and beyond.
Detailed Explanation
Before Java 8, the Method Area was referred to as the Permanent Generation. With Java 8, this part of memory was restructured into what is known as MetaSpace. Unlike the Permanent Generation, where memory was allocated from a fixed size within the heap, MetaSpace dynamically uses native memory (from the OS) for storing class metadata and other information. This change allows for better scalability and reduces out-of-memory errors related to class loading, as the limitation of fixed-size memory is removed.
Examples & Analogies
Think of Permanent Generation as a small storage room in a house. Once it's full, you have no space for new items (classes). In contrast, MetaSpace is like an infinite warehouse—you can store as many items as you need. If you need more room, just rent a bigger space. This flexibility makes managing the class definitions much easier and efficient.
Implications for Performance
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The shift to MetaSpace can improve performance and efficiency in handling class loading and unloading.
Detailed Explanation
With MetaSpace, developers see improvements in performance because the JVM can manage memory for class metadata more effectively. Since it uses native memory, it does not suffer from the fixed limitations of the heap size fixed for the Permanent Generation. This impacts class loading times positively, especially for large applications with many classes. Additionally, the garbage collector can more efficiently clean up unused metadata, leading to overall better memory utilization.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine running a factory with a fixed number of assembly lines (Permanent Generation) versus a factory where you can add or remove assembly lines as needed (MetaSpace). The second factory can handle varying production volumes better, quickly adjusting to demand spikes. Similarly, the JVM can adapt to the number of classes being used, leading to smoother performance.
Key Concepts
-
Method Area: Stores class structures and metadata for JVM operations.
-
MetaSpace: A dynamic implementation of the Method Area in the HotSpot JVM.
-
Garbage Collection: Enables automatic memory management by reclaiming unused memory.
-
OutOfMemoryError: Indicates insufficient memory for class loading or allocation.
Examples & Applications
In a large-scale application where many classes are dynamically loaded and unloaded, MetaSpace can adjust to use only the memory necessary, unlike the fixed size of Permanent Generation.
When tuning a Java application, monitoring MetaSpace utilization helps in identifying if class loading delays are affecting performance, enabling timely adjustments.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
MetaSpace, a memory place, for class data in its rightful space!
Stories
Imagine a library where books can appear and disappear, representing classes in MetaSpace that manage themselves according to need.
Memory Tools
M.E.M.O.R.Y: MetaSpace Enables Memory Optimization for Releasing yield!
Acronyms
M.A.P.
Method Area for Performance!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Method Area
Part of the JVM that stores class-related metadata, method data, and constants.
- MetaSpace
The implementation of the Method Area in the HotSpot JVM which uses native memory.
- Garbage Collection
The process of automatically reclaiming memory by removing objects that are no longer in use.
- Permanent Generation
The older memory space used for storing class metadata before Java 8, with limited size.
- OutOfMemoryError
An error thrown by the JVM when it cannot allocate an object due to insufficient memory.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
