Types of Class Loaders
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Class Loaders
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Class loaders play a crucial role in the Java Virtual Machine by loading class files into memory. Can anyone tell me the importance of class loaders in the JVM?

They help load classes at runtime so that Java applications can use them.

Exactly, they load classes on demand. Let's break down what happens when the JVM needs a class: it delegates the responsibility to one of three types of class loaders.

What are those class loaders?

Great question! We have the Bootstrap ClassLoader, Extension ClassLoader, and Application ClassLoader. Let's talk about each one.
Bootstrap ClassLoader
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

First up is the Bootstrap ClassLoader. It loads the core Java classes from `rt.jar`. Can anyone tell me why this loader is significant?

Is it because it loads the foundational classes that all Java applications rely on?

Precisely! It is written in native code and is the backbone of the Java platform. Remember, it handles the crucial task of loading essential classes.

So, if the Bootstrap ClassLoader fails, does that mean Java cannot run?

Exactly! If it can't load core classes, the entire execution could fail.
Extension ClassLoader
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s move onto the Extension ClassLoader. Who can tell me where it loads classes from?

From the `lib/ext` directory, right?

Yes! It allows you to extend the Java platform. Why do you think this is useful?

It helps in adding libraries that multiple applications can share.

Correct! It promotes reusability of classes across different applications.
Application ClassLoader
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, we have the Application ClassLoader. This one loads classes based on the application’s classpath. Why do you think it is called 'Application'?

Because it serves the specific needs of the application we're running?

That's exactly it! It is dynamic and adapts to the application's requirements. Is it clear how these class loaders work together?

Yes, they form a hierarchy to manage loading efficiently.

Excellent summary! Remembering the hierarchy and roles of these loaders helps grasp how Java manages resources efficiently.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section explains the Bootstrap ClassLoader, Extension ClassLoader, and Application ClassLoader, detailing their responsibilities in the class loading process within the JVM. Each loader serves a specific purpose, contributing to Java’s runtime flexibility and modular architecture.
Detailed
Types of Class Loaders
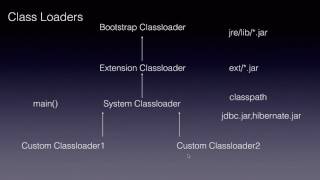
In the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), class loaders are essential components responsible for loading classes into memory. There are three main types of class loaders:
-
Bootstrap ClassLoader: This is the most fundamental class loader and is part of the core Java platform. It is responsible for loading core Java classes found in the
rt.jarfile or modules such asjava.base. It is written in native code and is crucial for the Java execution environment. -
Extension ClassLoader: This loader is tasked with loading classes from the Java Extensions directory, specifically from the
lib/extfolder. It allows developers to extend the Java platform with additional libraries that can be shared across different applications. - Application ClassLoader: This is the default class loader. It loads classes from the application’s classpath, which consists of directories and .jar files specified at runtime. This loader is crucial for loading user-defined classes and libraries necessary for application functionality.
Together, these class loaders create a hierarchy, enabling the JVM to manage classes efficiently and securely, allowing for modularity and comprehensive class loading strategies.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Bootstrap ClassLoader
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Bootstrap ClassLoader
Loads core Java classes fromrt.jaror modules likejava.base.
Detailed Explanation
The Bootstrap ClassLoader is the first and most fundamental class loader in Java. It is responsible for loading the core Java classes required by the Java platform itself, such as the classes found in the rt.jar file or within the java.base module. Since it's the first step in the class loading process, it has access to essential classes that are necessary for the entire Java ecosystem to function correctly.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the Bootstrap ClassLoader as the foundation of a building. Just as a strong foundation is essential for the stability of the entire structure, the Bootstrap ClassLoader provides the essential building blocks that support all other Java class loaders and applications.
Extension ClassLoader
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Extension ClassLoader
Loads classes from theextdirectory (lib/ext).
Detailed Explanation
The Extension ClassLoader is responsible for loading classes from the extension directory, which is typically located at lib/ext in the Java installation. This class loader serves as a bridge to incorporate additional functionality and libraries that can be utilized by Java applications. By allowing applications to leverage external libraries without modifying the core Java classes, it enhances the modularity and extensibility of Java applications.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the Extension ClassLoader as a library annex that provides additional books (or resources) that aren't part of the main library collection. It allows readers (Java applications) to access supplementary materials, expanding their knowledge (functionality) without altering the original library (core Java classes).
Application ClassLoader
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Application ClassLoader
Loads classes from the classpath.
Detailed Explanation
The Application ClassLoader, sometimes referred to as the System ClassLoader, is responsible for loading application-level classes that are specified on the classpath. This class loader operates at a higher level than the Bootstrap and Extension ClassLoaders, as it loads the classes that make up the applications you write. It is primarily concerned with loading user-defined classes, which might include your business logic and other components necessary for your application to function.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of the Application ClassLoader as a manager at a restaurant who oversees the preparation of menu items (application classes). This manager ensures that the chefs (Java virtual machine) have access to all the recipes (classes in the classpath) they need to fulfill customer orders (run the application) effectively.
Key Concepts
-
Bootstrap ClassLoader: Loads core Java classes essential for JVM functionality.
-
Extension ClassLoader: Loads classes from the Java Extensions directory for shared libraries.
-
Application ClassLoader: Loads classes from user-specified classpath, essential for application execution.
Examples & Applications
When starting a Java application, the Bootstrap ClassLoader initializes the process by loading foundational libraries such as java.lang.String.
The Application ClassLoader loads user-defined classes from the project directory as specified in the classpath during execution.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Bootstrap starts where all begins, core classes loaded for our wins.
Stories
Imagine three friends: Boot, Exten, and App. Boot loads essentials from the foundation, Exten gathers tools from everywhere, and App pulls in the bags of tricks we made - together, they build the Java world.
Memory Tools
B.E.A. - Bootstrap for essentials, Extension for extras, Application for the local stuff.
Acronyms
C.L.A. - Class Loaders
Core
Libraries
Application.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Bootstrap ClassLoader
The fundamental class loader that loads core Java classes from rt.jar.
- Extension ClassLoader
Class loader responsible for loading classes from the Java Extensions directory (lib/ext).
- Application ClassLoader
The default class loader that loads classes from the application’s classpath.
- Class File
A compiled Java source file that contains bytecode.
- JVM
Java Virtual Machine, the engine that runs Java applications and manages memory and execution.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
