Software Design
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Software Design in EMS
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome, students! Today, we are going to discuss the critical role of software design in developing our Employee Management System. Can anyone tell me why software design is so important?

I think it helps to organize the code better and makes it easier to work on.

Exactly! A good design helps organize code, making it easier to read, maintain, and scale. Now, let’s explore the different elements we need to consider for our design.

What elements do we need to design for the EMS?

Great question! We will define classes such as `Employee`, `Manager`, and more. It’s also crucial to utilize design patterns. Can anyone mention some design patterns that might be useful?

Singleton and Factory pattern, right?

Correct! The Singleton pattern helps ensure a single database connection. Now, who can summarize what we've discussed?

We talked about why software design is important and mentioned some classes and design patterns we'll use.

Well done! Let's move to the next session.
Understanding Design Patterns
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss the design patterns we’ll use—specifically Singleton, Factory, and DAO. Who can explain what the Singleton pattern is?

The Singleton pattern makes sure that a class has only one instance, and provides a global point of access to it.

Exactly! The Singleton pattern is ideal for managing database connections in our EMS. Now, how does the Factory pattern differ?

It helps in creating objects without specifying the exact class of object that will be created.

Spot on! The Factory pattern gives us flexibility in object creation. Lastly, can anyone summarize the DAO pattern?

The DAO pattern abstracts the data access layer, making the code cleaner and easier to maintain.

Great job everyone! These patterns will help us structure our code effectively. Let’s ensure we remember them while designing our software.
Creating Class Diagrams
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, we’ll talk about class diagrams. Who can explain why we use class diagrams in software design?

They help visualize the relationships and structures between different classes.

That's right! Let’s outline the classes we need for the EMS. Can someone name a class we should include?

We definitely need an `Employee` class.

Good! The `Employee` class will hold all relevant data about employees. What other classes are important?

A `Manager` class and maybe a `DatabaseHandler`?

Exactly! And don't forget about `ReportGenerator`. Class diagrams are essential for visualizing how these classes interact. Let’s recap the classes we’ve defined.

We talked about `Employee`, `Manager`, `DatabaseHandler`, and `ReportGenerator`.

Excellent! This visual structure will guide our implementation. Let's move on to explore coding these classes!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore software design principles critical for developing programs, particularly using design patterns like Singleton, Factory, and DAO. We also define key classes necessary for the employee management system and advocate for modular design to enhance code maintainability and scalability.
Detailed
Software Design
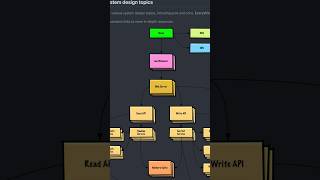
Software design is a pivotal step in developing any advanced software application. In the context of creating an Employee Management System (EMS), employing well-established design patterns and a modular design approach is essential. This section highlights how to effectively use class diagrams to outline components such as Employee, Manager, DatabaseHandler, and ReportGenerator.
Key Design Patterns Discussed:
- Singleton: Ensures that only one instance of the database connection exists, providing a global point of access to that instance.
- Factory: Centralizes object creation, allowing for easier management and flexibility to adapt the creation process.
- DAO (Data Access Object): Abstracts the data access layer, promoting separation of concerns and enhancing code maintainability.
These design choices are crucial for implementing an efficient, scalable, and maintainable system, aligning with the principles outlined in this chapter.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Class Diagrams Overview
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Class Diagrams: Define Employee, Manager, DatabaseHandler, ReportGenerator.
Detailed Explanation
Class diagrams are visual representations of the classes in a system and how they interact with one another. In this case, we're defining the main entities involved in our Employee Management System (EMS). The key classes include: 1. Employee: Represents an employee's data, such as their ID, name, department, and salary. 2. Manager: This may represent operations or methods related to managing multiple employees. 3. DatabaseHandler: Responsible for managing data access, such as connecting to a database and executing queries. 4. ReportGenerator: Generates reports based on employees' data, such as salary reports or departmental summaries.
Examples & Analogies
Think of this like creating an organizational chart for a company. Each box represents an individual role (Employee, Manager, etc.) and shows how these roles are interconnected. Just as a company needs a clear structure to function efficiently, our software needs a clear diagram to define how the various components correlate.
Utilizing Design Patterns
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Design Patterns Used: Singleton (for DB connection), Factory (for object creation), DAO (for data access abstraction).
Detailed Explanation
Design patterns are best practices that denote tried-and-true solutions to common problems in software design. In our EMS implementation: 1. Singleton Pattern: This pattern ensures that there is only one instance of a Database connection throughout the application. This prevents multiple connections and allows for efficient resource management. 2. Factory Pattern: This pattern is used for creating objects without specifying the exact class of object that will be created. For instance, different types of employees (like full-time or part-time) can be instantiated through the factory without needing to know the specifics each time. 3. Data Access Object (DAO) Pattern: This abstracts the interaction with the database, allowing us to manage the database's data operations easily without exposing the underlying database implementation to the rest of the application.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of design patterns like building blocks or toolkits that programmers keep in their back pocket. Just as a seasoned chef has favorite recipes that streamline meal preparation, programmers use design patterns to avoid reinventing the wheel, ensuring they have the best solutions at their fingertips, tailored for efficient coding.
Key Concepts
-
Software Design: The blueprint for constructing a program using structured methodologies.
-
Design Patterns: Reusable solutions to common problems encountered in software design.
-
Class Diagrams: Visual tools to represent the relationships and structure between different components in an application.
Examples & Applications
Using the Singleton pattern, we ensure that only one instance of the database connection is created to manage data effectively.
Applying the Factory pattern allows us to create different types of employees without hardcoding the employee classes.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Singleton stays alone, Factory makes them clone.
Stories
Imagine a librarian (Singleton) who manages a single library, while multiple students (Factory) come to borrow various books (objects) from the library.
Memory Tools
Sculptor Artfully Crafts Designs - Singleton, Abstract Factory, Class Diagram.
Acronyms
SDF - Singleton, Design patterns, Factory.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Singleton
A design pattern ensuring a class has only one instance and provides a global point of access.
- Factory Pattern
A design pattern that allows for creating objects without specifying their exact class.
- DAO (Data Access Object)
A design pattern that provides an abstract interface to some type of database or other persistent storage.
- Class Diagram
A type of static structure diagram that describes the structure of a system by showing the system's classes, their attributes, and the relationships between the classes.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
