Budget Set and Budget Line
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding the Budget Set
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing the budget set. Who can tell me what a 'budget set' is?

Is it the collection of bundles a consumer can afford?

Exactly! It's all the combinations of goods that a consumer can purchase with their income at present prices.

And how do we mathematically represent that?

Great question! We use the equation p1*x1 + p2*x2 ≤ M, where p1 and p2 are the prices and M is the total income.

So, if I have Rs 100 and bananas cost Rs 5 while mangoes cost Rs 10, can I figure out my budget set?

Yes! You would find all combinations of bananas and mangoes that keep your spending within Rs 100.

Let’s summarize: the budget set consists of all bundles that a consumer can purchase with their income. This includes combinations that cost less than or equal to the budget.
Introducing the Budget Line
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s shift focus to the budget line. Who can define what a budget line is?

Is it the line that represents all the combinations of goods that exactly spends the entire income?

That’s correct! The budget line is plotted on a graph where each point shows a different combination of the two goods that exhausts the consumer's income.

How is that different from the budget set?

The budget set includes all bundles costing less than or equal to the income, while the budget line only includes those that spend all of it.

And what does a change in income do to the budget line?

If income increases, the budget line shifts outward, allowing more combinations. If it decreases, the line shifts inward.

Remember, the slope of the budget line also represents the rate at which one good can be substituted for another.
Interpreting Changes in the Budget Line
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's explore how changes in prices affect our budget line. Can someone give an example based on price change?

If the price of bananas increases, would the budget line become steeper?

Exactly! If the price of one good increases, consumers will have to sacrifice more of the other good to maintain their quantity purchased.

And if the price decreases?

Then yes, the budget line flattens as they can now buy more of that good without sacrificing as much of the other.

To conclude, it’s vital to understand that changes in prices and income alter what consumers can afford. Always visualize these changes on a graph!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The budget set refers to the collection of consumption bundles a consumer can afford given their income and the prices of goods, while the budget line represents all combinations of goods that exhaust the consumer's income. Together, they shape the consumer's choice in the marketplace, constrained by their financial limits.
Detailed
In consumer theory, the budget set is the collection of all possible consumption bundles that a consumer can purchase with a fixed income at given prices of goods. The equation defining this relationship is the budget constraint: p1x1 + p2x2 ≤ M, where p1 and p2 are the prices of goods 1 and 2, respectively, and M is the total income. Graphically, the budget line is a straight line representing all combinations that exhaust the consumer's entire income (p1x1 + p2x2 = M). Shifts in the budget line can occur due to changes in income or prices, affecting the affordable combinations of goods and thereby influencing consumer choices.
Youtube Videos


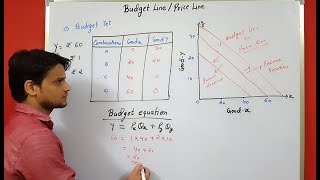

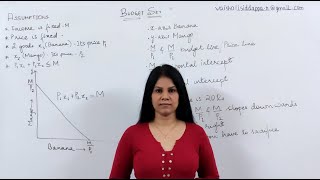


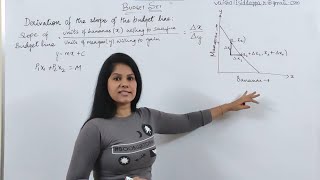

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding the Budget Set
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Suppose the income of the consumer is M and the prices of bananas and mangoes are p and p respectively. If the consumer wants to buy x quantities of bananas, she will have to spend p_x amount of money. Similarly, if the consumer wants to buy x quantities of mangoes, she will have to spend p_x amount of money. Therefore, if the consumer wants to buy the bundle consisting of x quantities of bananas and x quantities of mangoes, she will have to spend p_x + p_x amount of money. She can buy this bundle only if she has at least p_x + p_x amount of money. Given the prices of the goods and the income of a consumer, she can choose any bundle as long as it costs less than or equal to her income.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk explains that a consumer's budget set is determined by their income and the prices of the goods they want to buy. If the consumer's total expenditures on bananas and mangoes do not exceed their income, they can afford that bundle. The equation captures the idea that the consumer has a fixed budget (M) to spend on two goods, where each good has its own price. The consumer must balance the quantities of each good so that the total spending does not exceed M.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you have a monthly budget of $100 for groceries. If bananas are $2 each and mangoes are $3 each, you can buy various combinations of these fruits as long as the total cost is $100 or less. For instance, you could buy 30 bananas (at $2 each) and 0 mangoes, or 0 bananas and around 33 mangoes, or any combination that fits within your budget.
Budget Constraint Equation
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In other words, the consumer can buy any bundle (x_1, x_2) such that p_1 × x_1 + p_2 × x_2 ≤ M (2.1). The inequality (2.1) is called the consumer’s budget constraint. The set of bundles available to the consumer is called the budget set.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk introduces the budget constraint equation, which is a mathematical representation of the affordability condition for the consumer. It shows that the total expenditure on the two goods (bananas and mangoes) cannot exceed the consumer's income (M). This condition helps to determine the set of combinations that the consumer can choose from, which is referred to as the budget set.
Examples & Analogies
Continuing with the grocery budget example, if you were to create a list of combinations based on your budget, you could write down all the different amounts of bananas and mangoes you could buy without exceeding $100. The budget constraint equation helps you see limits on your purchases and guides your shopping decisions.
The Budget Line
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The equation of the line is p_x1 + p_x2 = M (2.2). The line consists of all bundles which cost exactly equal to M. This line is called the budget line. Points below or on the budget line represent bundles which cost strictly less than M.
Detailed Explanation
The budget line is a graphical representation that shows all possible combinations of two goods that a consumer can purchase if they spend their entire income (M). When plotted on a graph, the budget line illustrates the trade-off between the two goods: the slope indicates the relative prices of the goods compared to each other. Points below the line indicate bundles that are affordable with some remaining income, while points on the line depict combinations that just exhaust the consumer's budget.
Examples & Analogies
Picture a graph where the X-axis is the number of bananas and the Y-axis is the number of mangoes. The budget line will show all the combinations you can buy if you spend every dollar you have. If you try to buy a combination that sits above this line, it indicates you are trying to spend more than your budget allows, which is not feasible.
Changes in the Budget Set
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The set of available bundles depends on the prices of the two goods and the income of the consumer. When the price of either of the goods or the consumer’s income changes, the set of available bundles is also likely to change.
Detailed Explanation
In this chunk, the impact of changes in income and prices on the budget set is explained. If a consumer’s income increases or the price of one good decreases, the budget set expands, allowing more combinations of goods to be purchased. Conversely, if income decreases or prices increase, the budget set contracts, limiting the combinations the consumer can afford.
Examples & Analogies
Consider if you get a raise at work and your grocery budget increases to $150. You can now include more options in your shopping list. On the other hand, if the price of bananas doubles, your ability to purchase them decreases, affecting your choices. These changes can significantly affect your shopping experience and food variety.
Key Concepts
-
Budget Set: Represents all possible combinations of goods that the consumer can afford.
-
Budget Line: The specific combinations of goods that exactly use up the entire income.
-
Consumption Bundles: Different combinations of two products that illustrate consumer choice.
-
Income: The financial resources available to the consumer to purchase goods.
-
Price: The monetary cost of acquiring a good.
Examples & Applications
If a consumer has Rs 50 and wants to buy bananas at Rs 10 each and mangoes at Rs 5 each, using the budget constraint, they can determine how many of each they can buy without exceeding Rs 50.
With an income of Rs 100, if the price of bananas decreases from Rs 10 to Rs 5, the consumer can afford double the quantity of bananas.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Budget line, oh so fine, shows what we can buy and line up our treasures.
Stories
Imagine a shopper, Sam, with Rs 50, deciding how many bananas and mangoes to buy, creating various combinations, all while staying within budget – that’s the budget line story!
Memory Tools
Remember 'Buy Limits' for Budget Set = Buying Limits based on income and prices.
Acronyms
BUBBLE
Budget = Understanding Buying Limits By Earning.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Budget Set
The collection of all consumption bundles that a consumer can afford given their income and market prices.
- Budget Line
The graphical representation of all combinations of goods that exhaust the consumer's income.
- Consumption Bundle
A specific combination of quantities of two goods.
- Income
The total monetary resources available to a consumer for purchasing goods.
- Prices
The amount of money required to acquire a unit of goods.
- Budget Constraint
An inequality that represents the limitations of a consumer's available resources.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
