CMOS XOR Gate
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to CMOS Logic
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to focus on the CMOS XOR gate. Can anyone tell me what a logical XOR operation does?

I think it gives a high output only when one input is high and the other is low.

Exactly! The output is high when inputs are different. Let's take a closer look at how the CMOS XOR gate is structured. Who can tell me why we use both NMOS and PMOS transistors?

It's to ensure efficient power consumption and to control the output based on the input states.

Correct! That complementary action minimizes power loss. Now, who can summarize the truth table for the XOR gate?

The truth table shows that the output is high when inputs are different. So, 0,1 gives 1, 1,0 gives 1, and 0,0 or 1,1 gives 0.

Very well summarized! To remember this, you can think of XOR as 'eXclusive OR'—it only 'wins' when the inputs are different. Great job!
Truth Table and Applications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss the applications of the XOR gate. Can anyone give an example where XOR might be used?

I think it's used in error detection, like in parity bits.

Exactly! XOR is crucial for detecting error states in data transmission. Now, let’s go over the truth table together. What do we see?

It confirms what we learned! 0,0 is 0, 0,1 is 1, 1,0 is 1, and 1,1 is 0.

Great! Remembering the truth table can help you quickly understand how this gate operates in larger circuits. Now, why do you think XOR gates are more complex than NAND and NOR gates?

I think it’s because they need multiple gates to be configured together.

Right! The complexity arises from how we want to achieve that exclusive behavior. Excellent discussion today, let’s keep building on these concepts.
Practical Applications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s think about where we find XOR gates in practical circuits. Can anyone suggest a scenario?

They can be found in arithmetic circuits, like in adders.

Great point! XOR gates are fundamental in full adders. They help decide whether a carry is generated. Now, let’s consider how this impacts circuit design. What challenges might arise?

Maybe the propagation delay increases because of the added complexity?

Exactly! The propagation delay can affect speed. That’s a key consideration in circuit design. Remember, understanding these functions helps us design better logic solutions!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section details the construction and operation of the CMOS XOR gate, explaining how it utilizes complementary transistor configurations to deliver a high output when the inputs differ. The section provides insights into the truth table and application in digital circuits.
Detailed
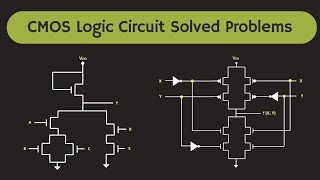
CMOS XOR Gate
The CMOS XOR (exclusive OR) gate is a vital component in digital circuits, particularly for applications requiring parity checks, error detection, and arithmetic functions. Characteristically, the XOR gate produces a high output (1) when an odd number of its inputs are high, specifically when one input is high and the other is low. Conversely, its output is low (0) when the inputs are equal (both low or both high).
Key Concepts:
- Construction: The XOR gate is constructed by combining multiple NAND and NOR gates, leveraging the complementary nature of NMOS and PMOS transistors to achieve the desired logical output.
- Operation: The output mechanism of the XOR gate is such that it provides logical correctness for varying binary input configurations, making it essential for tasks requiring logical decisions based on binary values.
Significance:
Understanding the operation of the CMOS XOR gate provides foundational knowledge for more complex circuit design and digital logic applications, thereby forming a bridge between fundamental transistor logic and advanced digital processing.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
CMOS XOR Gate Overview
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The CMOS XOR gate can be constructed by combining several NAND and NOR gates. It produces a high output (1) when an odd number of inputs are high.
Detailed Explanation
The CMOS XOR gate is a type of digital logic gate that performs the exclusive OR operation. It is built by interlinking multiple NAND and NOR gates to achieve its functionality. The main feature of this gate is its ability to output a high signal, represented as '1', when an odd number of its inputs is set to high. This means that if either one of its two inputs is high, the output will be high; however, if both inputs are high or both are low, the output will be low.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a situation where two friends are deciding to go out based on their schedules. They decide to go out if either one of them is free, but not if both are busy or both are free. This situation mirrors the behavior of the XOR gate - they go out only when there’s an odd scenario about their availability.
Operation of the CMOS XOR Gate
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Operation:
○ The output is high (1) when the inputs are different (i.e., one input is high and the other is low).
○ The output is low (0) when both inputs are the same (both high or both low).
Detailed Explanation
The operation of the CMOS XOR gate is defined by its ability to consider the states of its two inputs. The output will be high, or '1', when the inputs differ. For example, if input A is high and input B is low, the output will be high. Conversely, the output will be low, or '0', when both inputs share the same state; hence, if both are high or both are low, the output remains low.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a light switch that only turns on if one switch is flipped but not both. If you have two switches controlling a single light, only when one switch is flipped will the light turn on, similar to how the XOR gate functions with its inputs.
Key Concepts
-
Construction: The XOR gate is constructed by combining multiple NAND and NOR gates, leveraging the complementary nature of NMOS and PMOS transistors to achieve the desired logical output.
-
Operation: The output mechanism of the XOR gate is such that it provides logical correctness for varying binary input configurations, making it essential for tasks requiring logical decisions based on binary values.
-
Significance:
-
Understanding the operation of the CMOS XOR gate provides foundational knowledge for more complex circuit design and digital logic applications, thereby forming a bridge between fundamental transistor logic and advanced digital processing.
Examples & Applications
Example of an XOR gate in a full adder that adds binary numbers while considering carry bit.
Use of XOR gates in parity checking to detect errors in data transmission.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When one is high, the other's low, XOR gate turns the output glow!
Stories
Imagine two miners digging. Only if they're at different sites can they find gold. That’s how XOR works—only when inputs differ, they produce results!
Memory Tools
O-R = Odd Result; XOR gives a result only when one is high.
Acronyms
XOR
eXclusive OR - for outputs that are exclusive of each other!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- CMOS
Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor, a technology for constructing integrated circuits.
- XOR Gate
A digital logic gate that outputs true or high only when the number of true inputs is odd.
- Truth Table
A table that summarizes the output of a logical operation for all possible input combinations.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
