CMOS XOR Gate Truth Table
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to CMOS XOR Gate
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into the CMOS XOR gate. Does anyone know what an XOR gate does?

Isn't it a gate that gives a high output when inputs are different?

Exactly! The XOR gate outputs a high value when the inputs differ. Can someone give me an example of input combinations?

How about 0 and 1? That gives us an output of 1.

Right! And what about the case when both inputs are the same?

If both are 0 or both are 1, the output will be 0.

Perfect! Remember, this behavior is crucial for many digital applications. Let’s keep that in mind!
XOR Truth Table
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s analyze the truth table for the CMOS XOR gate. Can anyone summarize how it’s structured?

It shows all combinations of two inputs, A and B, and the resulting output!

Exactly! Here’s what it looks like: when both inputs are 0, the output is 0; when they are different, the output is 1! Let's visualize it.

So, just to be sure, when A and B are both 1, the output is also 0?

Correct! It’s like the gate is saying, 'I only care about different inputs!' Keep this table in mind as it has many applications in real-world circuits!
Applications of the XOR Gate
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss the applications of the CMOS XOR gate. Any thoughts?

I think it's used in arithmetic operations, right?

Absolutely! The XOR gate is essential for binary addition. It helps in determining whether there's a carry or not. Any other applications?

I heard it’s also used for parity checks in error detection.

Great point! The exclusivity of the XOR gate makes it ideal for checking parity. It can help ensure data integrity. Fantastic connections to real-world systems!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The truth table for the CMOS XOR gate reveals its operational characteristics, where the output is high only when the inputs differ. A detailed exploration of this truth table is essential for understanding its role in digital logic.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of CMOS XOR Gate Truth Table
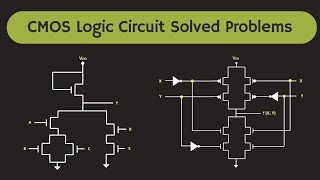
The CMOS XOR gate, or Exclusive OR gate, is a vital component in digital circuits utilized for various applications, including arithmetic operations and parity checks. The essence of an XOR gate lies in its ability to produce a high output (
1
) when an odd number of its inputs are high. In this case, with two inputs, the output will be high only when one input is high (1) while the other is low (0).
Truth Table of the CMOS XOR Gate
The truth table for a CMOS XOR gate can be defined as follows:
| Input A | Input B | Output (Vout) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Key Points:
- Output Characteristics: The output is high (1) for inputs that differ (0,1) or (1,0), showing the exclusive nature of the gate.
- Significance: XOR gates are crucial in digital systems where operations require differentiation between states, such as in arithmetic functions like addition.
Understanding this truth table is fundamental in analyzing the performance and application of CMOS technology in digital logic design.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Input Combinations for the XOR Gate
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
| Input | Input | Output |
|---|---|---|
| A | B | Vout |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Detailed Explanation
This table represents the behavior of the XOR gate. The XOR gate has two inputs, A and B, and produces an output Vout based on the values of these inputs. The table shows all the possible combinations of A and B and the corresponding output:
- When both inputs A and B are 0, the output Vout is also 0.
- When A is 0 and B is 1, Vout becomes 1.
- When A is 1 and B is 0, Vout is again 1.
- When both inputs are 1, the output Vout returns to 0.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the XOR gate like a light switch controlled by two different people. If they both want the light off (both are 0), the light is off (0). If only one person turns their switch on (one is 1 and the other is 0), the light turns on (1). But if both decide to turn it on (both are 1), the light is off (0) again. This scenario shows how XOR outputs high (1) only when the inputs are different.
Behavior of the XOR Gate
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The output of the XOR gate behaves as follows:
- It produces a high output (1) when an odd number of inputs are high.
- It produces a low output (0) when the inputs are the same.
Detailed Explanation
The XOR gate is unique because it outputs a high signal only when the inputs differ. In simpler terms:
- If one input is high (1) and the other is low (0), the output is high (1).
- If both inputs are the same (both high or both low), the output is low (0). This characteristic makes the XOR gate very useful in digital circuits, particularly in operations like error detection and odd parity checking.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a voting system where two friends can vote for pizza toppings. If one votes for pineapple and the other for pepperoni, they agree on a topping (output is high). But if both vote for pineapple or both vote for pepperoni, they cannot agree on a unique topping (output is low). This reflects how the XOR gate operates with its inputs.
Key Concepts
-
XOR Gate: Outputs high when one input is high, and the other is low.
-
Truth Table: Represents all possible inputs and the corresponding outputs for a logic gate.
Examples & Applications
Example: With inputs A=1 and B=0, the output of the XOR gate is 1, illustrating the gate's exclusivity.
Example: In a parity check, an XOR gate compares bits and determines if the number of ones in the input is odd.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
XOR is quite a clever gate, it only likes to differentiate.
Stories
Think of two friends at a party. If one is dancing and the other is not, they're having fun; if both stay still or both dance, it's a quiet night.
Memory Tools
For XOR, think 'Odd one out': it turns on for the odd combination.
Acronyms
XOR
'Xcept One's Right' signifies the exclusivity of the gate.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- CMOS
Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor, a technology for constructing integrated circuits.
- XOR Gate
A digital logic gate that outputs true or high only when an odd number of inputs are true.
- Truth Table
A mathematical table used to represent the output of a logic gate for all possible input combinations.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
