Definition - 1.1
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Workability
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing a key concept in concrete known as 'workability.' Can anyone tell me what workability means in the context of fresh concrete?

Isn't it how easily the concrete can be mixed and poured?

That's correct! Workability refers to the ease of mixing, placing, compacting, and finishing concrete without segregation. Think of it as how 'friendly' the concrete is to work with. A simple way to remember it is the '4 Cs' - Mixing, Placing, Compacting, and Finishing.

What happens if the workability is too low?

Great question! Low workability can lead to issues like poor compaction and a higher likelihood of cracks. It might not fill all the corners of the formwork properly, resulting in weak spots.

So, how is workability measured?

Workability is typically measured using tests like the slump test, which observes how much concrete settles under its own weight. Remember the acronym 'SCAFT' - Slump, Compacting Factor, Vee-Bee, and Flow Table tests for the various methods.

Thanks for the acronym! That makes it easier to remember.

To summarize, workability is crucial for proper concrete placement and quality. Keep in mind the 4 Cs and the measurement tests 'SCAFT'.
Factors Affecting Workability
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's dive deeper into what affects workability. Who can name one factor?

Water content!

Absolutely! More water typically increases workability, but what’s a downside of adding too much?

It can reduce the strength of concrete!

Exactly! Next, let's talk about aggregate. Student_3, can you tell me how aggregate size affects workability?

Larger, rounded aggregates make it easier to mix and work with, right?

That's spot on! While angular aggregates can hinder workability. Remember, we want a good balance. Think of the phrase 'SAGR' for Size, Aggregate shape, Grading, and Ratio of water and cement which all impact workability.

I like that! It summarizes the factors really well.

To wrap up, we’ve gone over how water, aggregate properties, and ratios affect workability. Try to keep these factors in mind when discussing or working with concrete!
Testing Workability
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s focus on how we test for workability. Who knows about one of the tests?

The slump test is one of them!

Exactly! The slump test measures the vertical settlement of concrete. And what does a higher slump indicate?

Higher workability?

Right again! Next is the compacting factor test. Student_3, can you explain why this one matters?

It tells us how much concrete can be compacted in standard conditions, which helps understand how well it's going to perform.

Well said! Additionally, we have the Vee-Bee test and flow table test for very fluid mixes. Keep in mind the acronym 'SVF' for Slump, Vee-Bee, and Flow Table.

That’s helpful! Testing sounds vital for ensuring quality control.

Exactly! To conclude, testing workability through methods like the slump test is essential in helping maintain concrete quality. Remember 'SVF'!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Workability is a critical property of fresh concrete that affects its performance. It is influenced by factors such as water content, aggregate properties, and admixtures, and can be measured using various tests. Understanding and controlling workability is essential for achieving durable and high-quality concrete structures.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Workability in Fresh Concrete
Workability refers to the ease with which concrete can be mixed, placed, compacted, and finished without signs of segregation or bleeding. It is one of the most critical properties of fresh concrete, as it directly impacts the quality of the finished product. Factors influencing workability include:
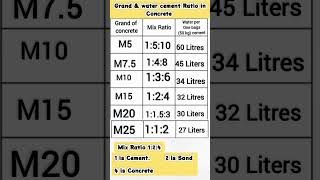
- Water Content: An increase in water raises workability but may compromise concrete strength.
- Aggregate Size and Shape: Rounded aggregates enhance workability while angular aggregates decrease it.
- Grading: Well-graded aggregates promote better workability.
- Cement Content: Higher cement content improves workability by enhancing lubrication within the mix.
- Admixtures: The addition of plasticizers and superplasticizers can boost workability without altering the water-cement ratio.
- Environmental Conditions: Time delays in placing concrete and high temperatures can negatively affect workability due to rapid setting.
Measuring workability can be performed through several tests, including the slump test, compacting factor test, Vee-Bee consistometer test, and flow table test. Understanding workability is pivotal for engineers and construction managers to ensure that concrete reaches its design requirements effectively.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Workability
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Workability is the ease with which concrete can be mixed, placed, compacted, and finished without segregation or bleeding.
Detailed Explanation
Workability refers to how easily concrete can be manipulated during the construction process. This means that the concrete should be mixed well, placed in its final position without difficulty, compacted properly to eliminate air gaps, and finished smoothly. Good workability ensures that the concrete maintains its homogeneity and does not separate into different components, which can happen if not handled properly.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine making a smoothie. If the ingredients blend smoothly without any lumps, it's easy to pour into a glass. However, if the fruits weren't blended well and separated into chunks, it would be difficult to pour and wouldn't have the desired texture. Similarly, concrete with good workability acts like a well-blended smoothie, flowing easily into molds without separation.
Importance of Workability
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
It is one of the most important properties of fresh concrete.
Detailed Explanation
Workability is crucial because it directly affects the quality and durability of the finished concrete. If the concrete is too stiff (low workability), it may be difficult to place and may result in voids or honeycombing, leading to weaker structures. Conversely, overly fluid concrete (high workability) can lead to segregation and bleeding, where the concrete components separate, compromising its integrity. Therefore, achieving the right level of workability is essential for successful concrete placement.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a cake batter. If it's too thick, you might struggle to pour it into the pan, risking uneven baking. If it’s too runny, it can spill over and lose shape. Just like achieving the perfect cake batter balance impacts the final product, having the right workability in concrete is essential for strong and durable structures.
Key Concepts
-
Workability: The ease of mixing, placing, compacting, and finishing concrete without segregation.
-
Factors Affecting Workability: Include water content, aggregate size and shape, grading, cement content, and environmental conditions.
-
Tests for Workability: Various tests like the slump test, compacting factor test, and flow table test are used to measure workability.
Examples & Applications
Example 1: High water content increases workability, allowing for ease in placing concrete but may compromise strength.
Example 2: Using rounded aggregates improves workability compared to angular aggregates which may reduce it.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Workability's the name of the game, with 4 Cs to remember the same: Mixing, Placing, Compacting, Finishing, do it right for quality; that's our mission!
Stories
Imagine a builder with a bucket of concrete. The easier it is to mix and pour without trouble, the happier the builder is. If the mix is too thick or too runny, it becomes a challenge, but with just the right amount of water, it's magic!
Memory Tools
For evaluating workability, remember 'SCAFT': Slump, Compacting Factor, Vee-Bee, Flow Table, all key to know the state.
Acronyms
To remember the factors affecting workability, use 'SAGR' - Size, Aggregate Shape, Grading, Ratio.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Workability
The ease with which fresh concrete can be mixed, placed, compacted, and finished without segregation or bleeding.
- Segregation
The separation of coarse aggregates from the cement paste or mortar during handling, leading to non-uniform concrete.
- Bleeding
The movement of water to the surface of freshly placed concrete, potentially causing weak surface layers.
- Slump Test
A test that measures the vertical settlement of concrete under its own weight.
- Admixtures
Substances added to concrete to enhance its properties, such as workability or setting time.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
