Setting Time of Concrete
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Defining Setting Time
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss setting time in concrete. Can anyone tell me what setting time refers to?

Is it the time it takes for the concrete to harden?

Exactly! Setting time is the duration it takes for concrete to transition from a plastic to a hardened state. Great answer! Now, who can describe the two phases of setting time?

There's initial setting time and final setting time, right?

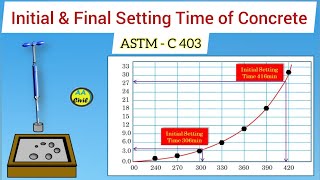
Correct! The initial setting time is when the concrete starts to lose plasticity, and the final setting time is when it's hard enough to resist pressure. Remember: Initial signifies the beginning, and final signifies completion.
Factors Influencing Setting Time
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's explore what factors can influence the setting time of concrete. Can anyone give me an example?

I think the temperature can affect it.

Absolutely! Higher temperatures generally speed up the setting time. Can anyone think of other factors?

What about the type of cement used?

Excellent point! Different types of cement, like rapid-hardening cement, will have different setting times. Water-cement ratio is also key; a higher ratio can delay setting time. Let's remember the acronym WCT for Water and Cement interactions.
Understanding Admixtures' Role
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let's talk about admixtures. How do they affect setting times?

I think accelerators make it set faster, right?

Yes! Accelerators indeed speed up the process, whereas retarders extend it. Remember: 'Accelerate to hasten, Retard to delay.' Can anyone tell me how these might be used in construction?

We might use retarders in hot weather to prevent quick setting.

Exactly! Using retarders helps in managing temperature effects and setting times effectively. Well done everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section covers the concept of setting time in concrete, which is the duration required for concrete to transition from a plastic to a hardened state. It defines initial and final setting times and explores various factors affecting these times, such as type of cement, temperature, water-cement ratio, and the use of admixtures.
Detailed
Setting Time of Concrete
Setting time is a crucial property of fresh concrete, denoting how long it takes for the concrete to transition from a plastic to a hardened state. This phase is essential for ensuring proper handling, placement, and quality of concrete structures.
Initial and Final Setting Times
- Initial Setting Time: This marks the moment when concrete starts to lose its plasticity and begins to set.
- Final Setting Time: This is the point at which concrete has hardened enough to withstand certain pressures without deformation.
Factors Affecting Setting Time
Several elements can influence the setting time of concrete:
- Type of Cement: Different cement types, such as rapid hardening cement, have varying setting characteristics.
- Temperature: Higher temperatures can accelerate the setting process.
- Water-Cement Ratio: A higher water-cement ratio may extend the setting time, while a lower ratio can lead to quicker setting.
- Admixtures: The use of accelerators can speed up the setting time, whereas retarders prolong it.
Understanding these factors is crucial for construction professionals, as they must adjust the concrete mix to match environmental conditions and project requirements.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Setting Time
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Time required for concrete to transition from a plastic to a hardened state.
Detailed Explanation
Setting time refers to the period during which freshly mixed concrete transitions from a fluid or 'plastic' state, where it can be easily shaped and molded, to a solid and 'hardened' state, where it gains its strength. This is an important phase as it affects how the concrete can be handled and what methods can be used during construction.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine baking a cake. When you mix the ingredients, the batter is like plastic concrete - it can be poured and shaped. Once you bake it, it hardens into a cake. Just as cake has a specific time in the oven to set properly, concrete also has a specific time to set before it becomes too hard to work with.
Initial and Final Setting Times
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Initial Setting Time: Time when concrete starts losing its plasticity.
• Final Setting Time: Time when concrete hardens enough to resist certain pressure.
Detailed Explanation
The initial setting time is the first phase in the setting process, marked by the concrete beginning to stiffen. At this point, it's still usable but has started to lose its plasticity. The final setting time is when the concrete has hardened enough to withstand certain pressures, meaning forms and support structures can be removed. Understanding these times is crucial for planning construction activities, ensuring the right timing for placement and finishing.
Examples & Analogies
Think of setting a jelly. Initially, it's still liquid, and you can stir it. However, after some time, it starts to thicken and loses its fluidity (initial setting). Finally, when it's fully set, it holds its shape and you can slice it (final setting). Just as you must wait for the jelly to set properly before serving, builders need to wait for concrete to reach its final setting time before removing molds.
Factors Affecting Setting Time
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Type of cement (e.g., rapid hardening, ordinary Portland).
• Temperature: Higher temperatures accelerate setting.
• Water-cement ratio: High w/c ratio delays setting.
• Admixtures: Accelerators decrease, retarders increase setting time.
Detailed Explanation
Several factors influence how quickly concrete sets. The type of cement chosen will dictate its setting properties, with some designed for rapid hardening while others take longer. Temperature plays a significant role; higher temperatures accelerate the setting process, while lower temperatures can slow it down. The water-cement ratio also matters - a higher ratio will delay setting because it increases the amount of water relative to cement. Finally, admixtures can be added to adjust setting times: accelerators speed up the process, while retarders slow it down.
Examples & Analogies
Consider cooking rice. The type of rice and the heat level affect how quickly it cooks. If you use too much water or keep it on low heat, the rice might take longer to cook. Similarly, in concrete, the right amount of water and the right temperature can greatly impact how quickly it sets, just like a good cook adjusts the ingredients and heat to get the perfect rice.
Key Concepts
-
Setting Time: The crucial duration for transitioning from plastic to hardened concrete.
-
Initial vs Final Setting Time: The phases of concrete's setting process.
-
Factors Affecting Setting Time: Key influencers include temperature, type of cement, water-cement ratio, and admixtures.
-
Role of Admixtures: Admixtures affect both initial and final setting times.
Examples & Applications
If a concrete batch is mixed using rapid-hardening cement, the initial setting time might be significantly lower compared to conventional Portland cement.
In hot weather, using water-reducing admixtures can help control the setting time and prevent early hardening.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When the cement starts to meld, that's when the initial setting's held.
Stories
Imagine a race, where concrete is a runner; the setting time is the distance it needs to run before it can compete.
Memory Tools
S.I.F.A.: Setting, Initial, Final, Admixture – remember the key aspects of setting time!
Acronyms
WCT
Water-Cement for mix transitions in time.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Setting Time
The period required for concrete to transition from a plastic to a hardened state.
- Initial Setting Time
The time when concrete begins to lose its plasticity.
- Final Setting Time
The time when concrete has sufficiently hardened to resist pressure.
- Admixtures
Substances added to the concrete mix to modify its properties, including setting times.
- WaterCement Ratio
The ratio of the mass of water to the mass of cement in a concrete mix, influencing strength and setting time.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
