Sampling and Frequency
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Importance of Sampling in Fresh Concrete
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Hello everyone! Today we're discussing the significance of sampling in fresh concrete. Can anyone tell me why they think sampling is crucial?

I think it helps in testing the quality of the concrete.

Exactly! Sampling allows us to verify the quality and consistency of the concrete mix. It's essential for ensuring that it meets the required standards for strength and durability.

How do we decide how much to sample, though?

Good question! The guidelines suggest taking one sample for every 5 cubic meters of concrete or per batch for smaller projects. This helps ensure adequate representation of the entire mix.

What happens if we don’t sample properly?

Failure to sample correctly could lead to undetected quality issues. If something goes wrong, it becomes harder to trace back the source of the problem.

So, keeping records is important too?

Absolutely! Maintaining sampling records not only supports quality assurance but also aids in compliance with professional standards.

In summary, proper sampling and record-keeping are essential for ensuring the quality and safety of fresh concrete used in construction projects.
Standards and Regulations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's delve into the standards we follow, specifically IS 4926 and IS 456:2000. Can someone remind us what these standards provide guidelines for?

They provide guidelines for concrete quality control.

Correct! These standards outline how to properly sample and analyze fresh concrete mixes.

Why is it important to follow these specific standards?

Following established standards ensures that there's a clear method for sampling, which can be replicated across different projects. This consistency helps in maintaining overall quality and safety.

Can you explain what IS 4926 actually states about sampling?

Certainly! IS 4926 states that you should take samples based on the volume of concrete produced, ensuring that each sample is representative of the entire batch.

This sounds like it helps avoid any potential issues down the line!

Exactly! By adhering to these regulations, we minimize the chances of quality-related issues during and after construction.

In summary, adhering to IS standards for sampling and frequency is crucial in maintaining quality assurance across construction projects.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section discusses how to sample fresh concrete according to IS standards, presenting guidelines on the frequency of sampling based on the volume of concrete produced or for batches. It emphasizes the importance of maintaining sampling records for ensuring traceability and quality control on construction sites.
Detailed
Sampling and Frequency in Fresh Concrete
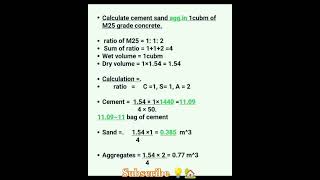
The quality of fresh concrete is crucial for achieving the desired properties in the hardened state. As per standards like IS 4926 and IS 456:2000, this section on sampling and frequency provides guidelines essential for ensuring quality control during the construction process. It stipulates that for every 5 m³ of concrete or per batch for smaller projects, one sample should be taken. This systematic approach to sampling establishes a traceable record of the concrete used, offering insights into quality and consistency. Maintaining these records is not merely procedural; it serves multiple purposes, such as ensuring compliance with standards, facilitating quality audits, and tracing any issues that may arise with the concrete's performance.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Sampling Guidelines
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• As per IS 4926 and IS 456:2000.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk outlines the standards for sampling fresh concrete. IS 4926 and IS 456:2000 are specific Indian Standards that provide guidelines on the quality of concrete. They ensure that the fresh concrete’s characteristics are adequately assessed for quality control.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine baking a cake where you want to ensure that the ingredients are perfect. Just as you would taste a spoonful of batter to see if the flavors are right, concrete samples are taken to check if the concrete mix is correct and meets necessary standards.
Frequency of Sampling
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• One sample per 5 m3 or per batch for small projects.
Detailed Explanation
This guideline indicates how often you should collect samples of concrete for testing. For larger projects, it's recommended to take one sample for every 5 cubic meters of concrete poured. For smaller projects, a sample should be collected from each batch, ensuring every mix is evaluated.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a painter dipping their brush into paint to test the color before applying it to the canvas. By sampling every batch or at regular intervals, you ensure the quality of the concrete mix is consistent, just like ensuring that the paint color matches your vision before continuing to paint.
Importance of Record Keeping
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Maintain sampling records for traceability.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk emphasizes the importance of maintaining records of each sample taken. Keeping track of samples allows you to trace back any issues that arise, ensuring accountability and the ability to verify whether the concrete meets the necessary specifications.
Examples & Analogies
It's similar to how a chef keeps a recipe book. If a dish turned out great, they can refer back to their notes to recreate the magic. In concrete production, records help you identify what worked well or what went wrong, allowing you to replicate success or correct mistakes in future batches.
Key Concepts
-
Sampling Frequency: Refers to how often samples should be taken to ensure quality control.
-
Quality Assurance: Procedures put in place to ensure concrete meets defined standards.
-
Traceability: The process in which the history of the concrete batch is documented for future references.
Examples & Applications
A construction site produces 15 m³ of concrete; following guidelines, three samples should be taken to ensure proper quality checks.
In a project involving multiple small batches of concrete, one sample is taken per batch to maintain traceability.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For every five cubic, a sample's a must, to keep our concrete sturdy and robust.
Stories
Imagine a builder who samples sand and stone, checking quality first so that the building stands alone.
Memory Tools
S.A.F.E.: Sampling Always For Excellence in concrete.
Acronyms
S.Q.R.
Sampling
Quality
Records for concrete safety.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Sampling
The process of taking a portion of concrete from a batch for testing its quality.
- IS 4926
An Indian Standard for ready-mixed concrete providing guidelines for quality control.
- Quality Control
The procedure of ensuring that a product meets specified standards, particularly related to quality.
- Traceability
The ability to verify the history, location, or application of an item by means of documented recorded identification.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
