Interconnects
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Interconnects
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we are discussing interconnects in FinFET devices. Can anyone tell me what interconnects are and why they are important?

Are they the wiring connections that link different parts of a circuit?

Exactly! Interconnects are crucial for connecting various circuit components. They ensure signals travel efficiently across the device. Let's explore how they are formed.
Metal Layer Creation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Interconnects involve creating metal layers for wiring, often using processes like damascene. Student_2, can you describe what damascene means?

I think it’s a process that embeds metal within a dielectric layer?

Exactly right! This method helps reduce resistance. Now, what about the dual-damascene process? Student_3?

Isn't that a technique to create multiple interconnect levels more efficiently?

Yes! It significantly enhances circuit density. Great job!
Advanced Techniques in Interconnects
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about advanced techniques used in interconnects. Who can name a few innovations that improve accuracy in fabrication?

I remember hearing about self-aligned patterning!

Correct! Self-aligned patterning helps reduce manufacturing variations. It’s crucial for scaling devices as we reach smaller nodes. Can anyone mention why this is important?

Because smaller nodes help improve device performance?

Absolutely! As technology advances to 10 nm and smaller, reliable interconnects are key to maintaining performance.
Summary of Key Points
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s summarize what we’ve covered about interconnects. What are the main methods used for creating them?

We talked about damascene and dual-damascene processes!

Correct! And what’s the significance of using advanced techniques in this context?

It helps minimize variations and improve accuracy!

Exactly! Excellent participation, everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section elaborates on the crucial step of establishing interconnects in FinFET devices, focusing on the methods employed to create metal layers for effective wiring. The use of advanced techniques, such as damascene or dual-damascene processes, is highlighted to improve performance in circuit design.
Detailed
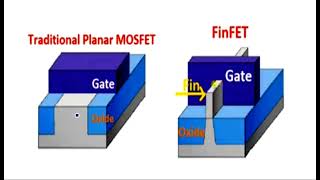
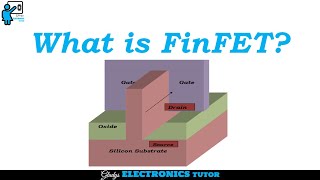
Understanding Interconnects in FinFET Technology
Interconnects are vital components in FinFET device fabrication, facilitating communication between different circuit elements. In the fabrication process, once the FinFET structure is established, creating reliable and efficient wiring becomes essential for device performance.
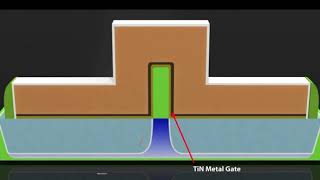
1. Metal Layer Creation: The interconnects are formed using metal layers, commonly employing damascene or dual-damascene processes.
2. Damascene Process: This technique involves embedding metal (like copper) within a dielectric layer to form interconnects while ensuring minimal resistance and maximal reliability.
3. Dual-Damascene Process: This more advanced technique allows for creating multiple levels of interconnects efficiently, streamlining the wiring process to enhance circuit density.
4. Advanced Techniques: The adoption of self-aligned patterning and gate-last processing in advanced nodes aids in achieving better accuracy and reduced manufacturing variations.
The importance of interconnects cannot be overstated, as they are pivotal in ensuring that FinFET devices operate efficiently and effectively at reduced sizes, particularly as they scale down towards smaller nodes such as 10 nm and beyond.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Creating Metal Layers for Wiring
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Create metal layers for wiring using damascene or dual-damascene processes.
Detailed Explanation
In this chunk, we learn about how metal layers are created for wiring in FinFET devices. There are two primary methods used for this: the damascene process and the dual-damascene process. Both methods are effective for integrating metal interconnects into the chip design. In a damascene process, metal is deposited into already etched patterns in an insulating layer, which creates a pathway for electrical signals. The dual-damascene process is a bit more complex; it involves two separate layers where the first layer includes vias (vertical connections) to connect different metal layers. This allows for more compact designs and reduces the electrical resistance, enhancing performance.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the city layout where roads are like metal layers in a chip. Just as you interconnect various parts of a city using roads and bridges, in a chip, we use metal wiring to connect different components, allowing data and power to flow seamlessly. Using a damascene process is akin to paving roads into a planned map, whereas the dual-damascene process is like building multilayered highways where cars can travel vertically as well as horizontally.
Advancements in Interconnect Techniques
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Advanced nodes may use self-aligned patterning, gate-last processing, or EUV lithography to improve accuracy and reduce variation.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk highlights several advanced techniques used in modern interconnect development for FinFETs. Self-aligned patterning allows for better alignment of features on a chip. Gate-last processing is a fabrication method where the gate is created after finishing the Fin structure, which can lead to enhanced performance. Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) lithography is a cutting-edge technique that uses shorter wavelengths of light to create more precise patterns, reducing errors due to fabrication variations. These advancements are crucial, particularly as the technology nodes continue to shrink in size.
Examples & Analogies
Think of building a precision model of a city where every detail matters and mistakes can ruin the design. Using techniques like self-aligned patterning is like having a laser-guided system for placing each building perfectly. Similarly, EUV lithography acts like using a high-definition map that allows you to see every minute detail without distortion, ensuring that the intricate parts of the model fit together exactly as planned.
Key Concepts
-
Interconnects: Essential wiring in FinFET devices for connecting components.
-
Damascene Process: A method for embedding metal into dielectric layers.
-
Dual-Damascene Process: An advanced technique for creating multiple interconnect levels.
-
Self-Aligned Patterning: A technique that reduces variations and improves accuracy in IC fabrication.
Examples & Applications
The use of copper in the damascene process ensures low resistance in interconnections.
Dual-damascene methods allow for increased circuit complexity in modern IC designs.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Connect with metal, be it single or dual, flows in circuits like water in a pool.
Stories
Imagine a city where each building needs roads to connect. The roads represent interconnects in a FinFET, allowing the city (the circuit) to operate smoothly.
Memory Tools
D for Damascene, D for Dual - remember these processes are smart and cool.
Acronyms
DIE
'Dual Interconnect Embedding' is a way to recall dual-damascene as a technique for multiple layers.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Interconnects
Wiring connections in integrated circuits that connect different components.
- Damascene Process
A technique to embed metal within a dielectric layer, reducing resistance in interconnects.
- DualDamascene Process
An advanced method that allows the creation of multiple interconnect levels efficiently.
- SelfAligned Patterning
A fabrication technique minimizing variations in dimensions of circuit components.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
