Silicidation and Contacts
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Silicidation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re focusing on silicidation and its importance in FinFETs. Can anyone tell me what silicidation is?

Is it when metal is used to enhance electrical conductivity in silicon?

Exactly! Silicidation involves reacting metal with silicon to form metal silicide, reducing contact resistance. Why is this important?

Because lower resistance means better performance in the circuit, right?

Correct! Lower contact resistance enhances the drive current and overall efficiency in FinFETs.

How do we achieve this silicidation?

Great question! It typically involves depositing a metal layer on the source and drain regions and then performing thermal annealing.

What metals are typically used?

Commonly used metals include cobalt and nickel, as they form stable silicides with silicon.

To summarize, silicidation is critical for reducing contact resistance in FinFETs, which directly affects device performance.
Importance of Low-Resistance Contacts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss why low-resistance contacts are vital in FinFETs. What would happen if the contact resistance is high?

It could limit the current that flows through the device, right?

Exactly! High contact resistance can lead to significant voltage drops, limiting the overall performance. Can anyone think of a consequence of this limitation?

Maybe it would affect the switching speed?

Precisely! Slower switching speeds can drastically affect the performance of digital circuits. What’s the ideal outcome we’re trying to achieve here?

We want to minimize the contact resistance to maximize current flow and improve switching speeds.

That’s correct! A focus on low-resistance contacts is key to enhancing the efficiency of FinFET devices.

In conclusion, we’ve established that achieving low-resistance contacts through silicidation is crucial for device performance.
Fabrication Steps of Silicidation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s look at how we integrate silicidation into the FinFET fabrication process. What do you think is the first step?

Isn’t it about preparing the surface of the silicon?

That’s a good start! First, we need to ensure that the silicon surface is clean and properly treated for optimal silicidation. What would come next?

Depositing a layer of metal?

Correct! We deposit a thin metal layer, usually cobalt or nickel, on the source and drain areas. Then what comes after that?

Thermal annealing, to form silicide?

Yes! Thermal annealing facilitates the reaction between metal and silicon to create low-resistance silicide. Can someone summarize the entire silicidation process?

Prepare the silicon, deposit metal, then anneal, forming the silicide?

Absolutely! That summarizes it perfectly. This process is key for effective contact formation.
Challenges of Silicidation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s explore potential challenges with the silicidation process. What issues might arise?

Maybe silicide formation could be inconsistent?

Yes, inconsistency in silicide formation can lead to variations in contact resistance. What could cause this inconsistency?

Perhaps impurities on the silicon surface?

Correct! Impurities and surface roughness can affect the quality of the silicide. What’s a potential solution to mitigate these issues?

Maybe more rigorous cleaning before deposition?

Absolutely! Enhanced surface preparation is crucial. To conclude, understanding and overcoming these challenges in silicidation improve the reliability of FinFETs.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we delve into the silicidation process, which involves forming metal silicide to create low-resistance contacts for FinFETs. The significance of this process in reducing contact resistance and ensuring efficient electrical performance of the device is highlighted, along with the steps involved in integrating silicidation in FinFET fabrication.
Detailed
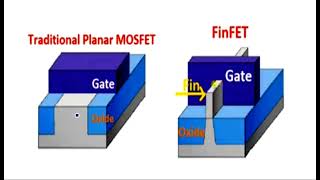
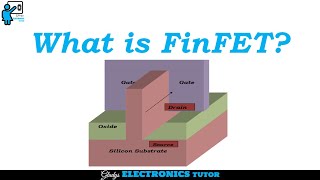
Silicidation and Contacts in FinFETs
In FinFET device fabrication, silicidation plays a critical role in enabling low-resistance contacts, which are essential for optimal device performance. This process involves the reaction of metal with silicon to form metal silicide, enhancing the electrical connectivity between the source/drain regions and the interconnect wiring. Lower contact resistance is crucial, as it significantly impacts the drive current and overall device performance. Effective silicidation techniques are vital to maintain the integrity and performance of FinFET devices as they are scaled down to advanced technology nodes. In this context, understanding the implementation of silicidation is fundamental for integrating FinFETs in modern semiconductor applications.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Silicidation
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
○ Form low-resistance contacts using metal silicide.
Detailed Explanation
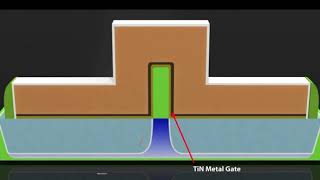
Silicidation is a crucial process in FinFET fabrication where a metal silicide is formed to create low-resistance electrical contacts. Metal silicide is created by reacting metal with silicon at elevated temperatures. This technique minimizes the resistance at the contact points, allowing for more efficient current flow in the transistor.
Examples & Analogies
Think of silicidation like applying a conductive glue between two electronic components. Just like the glue ensures a strong bond that allows electricity to flow easily between them, metal silicide helps ensure that the electrical contacts at the ends of the fin have low resistance, improving the overall efficiency of the FinFET.
Importance of Low-Resistance Contacts
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Low-resistance contacts are vital for improving the overall performance of FinFET devices.
Detailed Explanation
Low-resistance contacts reduce the amount of energy lost as heat when current passes through the FinFET. This is important because high resistance can lead to power loss, decreased performance, and can even affect the longevity of the device. In modern electronic circuits, efficient performance is critical, especially as devices operate at lower voltages and higher frequencies.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to push a heavy cart across a bumpy surface versus a smooth surface. On the bumpy surface, the cart encounters more friction and resistance, making it hard to move. Similarly, low-resistance contacts smooth the pathway for electrons, allowing for easier and more efficient flow, making the FinFET work more effectively.
Key Concepts
-
Silicidation: A process forming metal silicide to enhance electrical contact.
-
Low-Resistance Contacts: Essential for optimal FinFET performance, reducing contact resistance.
-
Thermal Annealing: A step in the silicidation process that facilitates silicide formation.
Examples & Applications
Cobalt Silicide: Often used in silicidation due to its favorable properties for achieving low resistance contacts.
Nickel Silicide: Commonly employed in semiconductor manufacturing for its effective performance in forming stable silicide.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Cobalt and Nickel do the trick,
Stories
Imagine a tiny race car on a track—if the track is smooth and clear, the car goes faster (just like a silicon surface). Now imagine adding a slick coating (silicide) on the tires. This reduces friction and helps the car zoom ahead, representing how low-resistance contacts allow electrical currents to flow swiftly.
Memory Tools
Remember Smooth Metal Silicide (SMS) to recall the steps: Surface cleaning, Metal deposition, Silicide formation!
Acronyms
LRC - Low Resistance Contacts
Keep this in mind as key to enhance FinFET performance.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Silicidation
The process of forming metal silicide from a reaction between silicon and metal, used to achieve low-resistance contacts.
- Metal Silicide
A compound formed when a metal reacts with silicon, which improves electrical conductivity and reduces contact resistance.
- Contact Resistance
The resistance encountered at the interface between metal contacts and semiconductor materials, which affects overall device performance.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
