Linear Differential Equations
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Linear Differential Equations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome class! Today, we'll dive into linear differential equations, a fundamental topic in engineering. Can anyone tell me what a differential equation is?

Isn't it an equation involving a function and its derivative?

Exactly! A differential equation involves an unknown function and its derivatives. Now, what makes a differential equation linear?

It means the dependent variable and its derivatives are to the first power, right?

Correct! Here’s a memory aid: think of L for Linear, like a line — no curves or higher powers. Let’s now explore first-order linear differential equations.
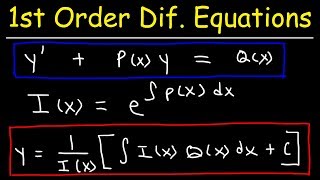
First-Order Linear Differential Equations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

First-order linear DEs have the format dy/dx + P(x)y = Q(x). Who can recall the solution method?

I remember it involves using an integrating factor!

Great! The integrating factor is μ(x) = e^(∫P(x)dx). This helps transform the equation into a solvable form. Let’s walk through an example of this method.

Can you show us the steps clearly, please?

Of course! First, identify P(x) and calculate the integrating factor. Then multiply both sides by μ(x) and integrate. This process is crucial for solving many engineering problems.
Second-Order Linear Differential Equations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s move to second-order linear differential equations. Who can share the general form?

Isn’t it d²y/dx² + P(x)dy/dx + Q(x)y = R(x)?

That's right! We can categorize these equations as homogeneous or non-homogeneous depending on whether R(x) equals zero. Can anyone think of applications of these in civil engineering?

Maybe something related to beam deflection or vibrations in structures?

Precisely! Understanding these equations is vital for analyzing structural integrity. Let's explore how we can solve for complementary functions and particular solutions.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section covers the fundamental concepts of linear differential equations, including their classifications, solution methods, and applications in civil engineering. It introduces first-order and second-order linear differential equations and demonstrates how to solve them using techniques like integrating factors and auxiliary equations.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Linear differential equations are pivotal in mathematical modeling within civil engineering. They allow for the analysis of how quantities change over time or space, making them essential for various applications such as fluid dynamics and structural analysis. This section provides a comprehensive introduction to the key aspects of linear differential equations, which are characterized by having the dependent variable and its derivatives to the first power, thus ensuring they do not multiply each other.
The section begins with definitions of crucial terms such as differential equations, order, and degree. A specific focus is placed on first-order linear differential equations, which can be solved using the method of integrating factors. A structured approach to solving these equations is detailed, along with an example for practical understanding. The discussion transitions to second-order linear differential equations, both homogeneous and non-homogeneous, and introduces solution methods that include finding complementary and particular functions. The methods such as undetermined coefficients and variation of parameters are discussed to find particular solutions for non-homogeneous equations. Throughout the section, the significance of these equations in civil engineering applications is emphasized, providing students with context as they learn the solutions to complex engineering problems.
Youtube Videos
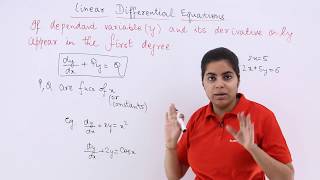





![Ordinary Differential Equations 25 | Example for Non-Diagonalizable Matrix [dark version]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/aPcCF1a21IU/mqdefault.jpg)


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Linear Differential Equations
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In the field of Civil Engineering, mathematical models are crucial to analyze structures, predict physical behaviors, and solve engineering problems. One of the most powerful tools in this modeling is Differential Equations, particularly Linear Differential Equations, which describe how a particular quantity changes over time or space. From analyzing fluid flow in pipelines, heat conduction in concrete, to deflection in beams and vibrations in structures, these equations form the foundation of mathematical simulation in engineering. This chapter introduces first-order and second-order linear differential equations, their classifications, standard methods of solution, and their application in engineering problems.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk introduces Linear Differential Equations and their significance in Civil Engineering. It emphasizes the role of mathematical models in analyzing and predicting various engineering phenomena, such as fluid flow and structural behavior. Linear Differential Equations are highlighted as powerful tools that translate real-world changes—like temperature or pressure changes—into mathematical language that can be analyzed and solved.
Examples & Analogies
Think of Linear Differential Equations as a set of instructions in a recipe. Just as a recipe guides you through the steps of combining ingredients to create a dish, linear differential equations guide engineers through understanding and predicting how different factors—like the weight on a bridge or water flow—change within a structure over time.
Basics of Differential Equations
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A differential equation is an equation that involves an unknown function and its derivatives.
Order: The highest derivative present in the equation.
Degree: The power of the highest derivative (provided the equation is polynomial in derivatives).
A differential equation is said to be linear if the dependent variable and its derivatives appear to the first power and are not multiplied together.
For example:
• First-order linear DE:
dy/dx + P(x)y = Q(x)
• Second-order linear DE:
d²y/dx² + P(x)d y/dx + Q(x)y = R(x)
Detailed Explanation
This chunk defines key concepts related to differential equations. It explains what a differential equation is, highlighting that it connects an unknown function with its derivatives. The concepts of order and degree are introduced, explaining how the order refers to the highest derivative in an equation and degree refers to its highest power. It also discusses linear differential equations, providing examples of the first-order and second-order forms.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a car’s speed as a function of time. The speed can change based on various factors like acceleration, represented mathematically by derivatives. A differential equation is like a speed limit sign; it tells you the maximum speed (the function) at any given time (the variable), while the order of the equation reflects how steep or gradual that speed change can be (its derivatives).
First-Order Linear Differential Equations
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
General Form:
dy/dx + P(x)y = Q(x)
Solution Method: Integrating Factor (IF)
1. Multiply both sides by an integrating factor:
µ(x) = e^(∫P(x)dx)
2. This transforms the equation into:
d/dx[µ(x)y] = µ(x)Q(x)
3. Integrate both sides:
y = (1/µ(x)) ∫[µ(x)Q(x)dx] + C
Detailed Explanation
This chunk introduces the general form of a first-order linear differential equation and outlines the standard method for solving it using the integrating factor. The process involves multiplying the equation by an integrating factor, which simplifies the equation into a form that can be integrated. The final step is to integrate and rearrange to solve for the unknown function.
Examples & Analogies
Think of solving a first-order linear differential equation like making a smoothie. The integrating factor is similar to a blender that mixes all the ingredients together. Just as you use the blender to create a smooth mixture from solid fruits, applying the integrating factor helps combine all the parts of the differential equation into a single, manageable equation that you can work with to find your final result.
Example of First-Order Linear Differential Equations
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Solve:
dy/dx + 2y = e^(-x)
Solution:
• P(x) = 2, so µ(x) = e^(∫2dx) = e^(2x)
• Multiply both sides:
e^(2x)dy/dx + 2e^(2x)y = e^(x) ⇒ d/dx[e^(2x)y] = e^(x)
• Integrate:
e^(2x)y = ∫e^(xdx) + C ⇒ y = e^(-x) + Ce^(-2x)
Detailed Explanation
This chunk presents a worked-out example of solving a first-order linear differential equation using the integrating factor method. It walks through the steps of determining the integrating factor, rewriting the equation, and then integrating to find the general solution. By applying the integrating factor and rearranging, students can see how to arrive at the solution in a systematic way.
Examples & Analogies
Think of this example as tuning a musical instrument. You start with a rough sound (the equation) and apply certain steps (the integrating factor) to gradually adjust the pitch. Each step—finding the right factor, adjusting the equation, and finally integrating—helps you refine the sound until it’s just right (the final solution).
Key Concepts
-
Linear Differential Equations: Differentiated equations characterized by first power terms.
-
First-Order Linear DE: Form dy/dx + P(x)y = Q(x).
-
Second-Order Linear DE: Form d²y/dx² + P(x)dy/dx + Q(x)y = R(x).
-
Complementary Function: Solution to the homogeneous part of the differential equation.
-
Particular Solutions: Specific solutions derived from non-homogeneous equations.
Examples & Applications
Example of solving a first-order linear differential equation using integrating factors.
Example demonstrating the application of second-order linear differential equations in structural analysis.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To solve a DE with ease, use an integrating factor, please!
Stories
Imagine a bridge flexing under weight; that’s how engineers predict with differential states!
Memory Tools
‘FLOP’ for first-order linear: Find, Multiply, Organize, and Process.
Acronyms
RAPID
Reality of Analysis using PDEs.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Differential Equation
An equation that involves an unknown function and its derivatives.
- Order
The highest derivative present in the equation.
- Degree
The power of the highest derivative, provided the equation is polynomial in derivatives.
- Linear Differential Equation
A differential equation where the dependent variable and its derivatives appear to the first power and are not multiplied together.
- Integrating Factor
A function used to simplify differential equations to facilitate their solution.
- Homogeneous Equation
A second-order linear differential equation where R(x)=0.
- NonHomogeneous Equation
A second-order linear differential equation where R(x) is not zero.
- Complementary Function
The solution to the homogeneous part of a differential equation.
- Particular Solution
A specific solution to a non-homogeneous differential equation.
- Auxiliary Equation
An algebraic equation derived from a differential equation used to find characteristic roots.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
