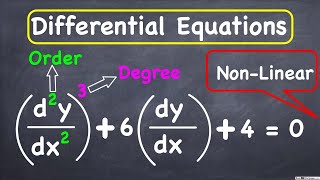
Order and Degree
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Order
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss the concept of order in differential equations. The order is defined as the highest derivative in the equation. Can someone give me an example?

Is it the highest number of d's in the equation?

Exactly! If an equation includes \( \frac{d^2y}{dx^2} \), \( \frac{dy}{dx} \), and y, the order is 2 because of the second derivative. This is crucial for classifying the equation.

Why does the order matter?

Great question! The order helps us determine which methods to use for solving the equation later. Remember: Higher order usually means more complex behavior!

In summary, the order is the highest derivative present, and it defines the complexity of the differential equation.
Understanding Degree
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's move on to the degree of a differential equation. The degree is the power of the highest derivative. How does this differ from order?

So, the degree could be higher than the order if the powers are different?

Good observation! For example, in \( \left(\frac{dy}{dx}\right)^4 + 2y = 1 \), the order is 1 but the degree is 4. The degree indicates how many times the highest derivative is multiplied by itself.

Does it mean that if the degree is high, the equation could be more difficult to solve?

Precisely! Higher degree indicates increased difficulty, and it can also dictate the solvable methods. Remember: Order tells us the complexity level while degree tells us the polynomial nature.

To summarize, the order is the highest derivative present, while the degree is the power of this derivative.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In linear differential equations, the order refers to the highest derivative present, while the degree is the power of that highest derivative. Understanding these concepts is essential for applying appropriate solution methods to differential equations.
Detailed
Order and Degree
This section describes two critical characteristics of differential equations: order and degree. The order of a differential equation indicates the highest derivative that appears in the equation. For example, in the equation \( \frac{d^2y}{dx^2} + P(x)y = Q(x) \), the order is 2 since the highest derivative is the second derivative \( \frac{d^2y}{dx^2} \).
The degree of a differential equation is defined as the power of the highest derivative, given that the equation is polynomial in derivatives. This means that if you have an equation like \( \left(\frac{dy}{dx}\right)^3 + y = 0 \), the degree is 3 because the highest derivative \( \frac{dy}{dx} \) is raised to the power of 3.
These definitions are foundational for later classifications and solutions of linear differential equations, emphasizing their utility in mathematical modeling within engineering contexts.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Order
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Order: The highest derivative present in the equation.
Detailed Explanation
The 'order' of a differential equation refers to the highest order derivative that appears in the equation. For example, if we have a differential equation that involves derivatives like dx/dt or d²y/dx², the order of the equation is determined by the highest derivative that is present. So, in an equation that contains d²y/dx², like d²y/dx² + 3dy/dx = 5, the order is 2 because the highest derivative is the second derivative d²y/dx².
Examples & Analogies
Think of order like the highest level of command in an organization. The CEO might make decisions that affect the entire company, while managers (represented by lower order derivatives) act on those decisions. In the same way, the highest derivative (or order) in a differential equation represents the most significant change that influences the behavior defined by that equation.
Understanding Degree
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Degree: The power of the highest derivative (provided the equation is polynomial in derivatives).
Detailed Explanation
The 'degree' of a differential equation refers to the exponent of the highest derivative, given that the equation is polynomial in its derivatives. For example, if we have an equation like (d³y/dx³)² + 5(dy/dx) - 2 = 0, the degree is 2 because the highest derivative, d³y/dx³, is raised to the power of 2. It's important to note that if the equation involves non-polynomial terms (like trigonometric functions or logarithms of the derivatives), the degree is not defined.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a basketball player shooting hoops. The degree can be thought of as how high they jump to make the shot; a higher jump (higher degree) can lead to more impressive shots (solutions) if executed well. Just as the height matters in a jump, the power of the highest derivative matters in determining the nature of the solutions to a differential equation.
Key Concepts
-
Order: The highest derivative in a differential equation determines its classification.
-
Degree: The power of the highest derivative, providing insights into the equation's complexity.
-
Differential Equation: A mathematical statement involving a function and its derivatives.
Examples & Applications
In the equation dy/dx + 3y = x, the order is 1 and the degree is 1.
In the equation (d^2y/dx^2)^2 + dy/dx + 4y = 0, the order is 2, but the degree is 2 because of the highest derivative squared.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Order's the highest, degree's its flair, in derivatives, with math, you must be aware.
Stories
Once upon a time in a differential land, the Order was mighty, and Degree took a stand. They worked together to solve all despair, finding solutions with utmost care.
Memory Tools
Remember O for Order, D for Degree, highest and power, that's the key!
Acronyms
O.D. represents Order and Degree, remember these terms, they're fundamental, you see!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Order
The highest derivative present in a differential equation.
- Degree
The power of the highest derivative in a differential equation, assuming the equation is polynomial in its derivatives.
- Differential Equation
An equation involving an unknown function and its derivatives.
- Linear Differential Equation
A differential equation where the dependent variable and its derivatives appear only to the first power and are not multiplied together.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
