Application of Fourier Series in PDE Solutions
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Eigenfunctions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore the concept of eigenfunctions in the context of Partial Differential Equations. Who can remind us what eigenfunctions are?

Aren't they the functions we find after applying the method of separation of variables?

Exactly! They often take the form of sine or cosine functions. These eigenfunctions form a complete set, allowing us to express complex solutions. Think of them as the 'building blocks' for our solutions. Can anyone illustrate how we use these eigenfunctions?

I think we use them in Fourier series expansion, like how we break down initial conditions.

Great point! The coefficients in these expansions are derived from the initial conditions. Now, let's move to how these coefficients are calculated.
Fourier Series Coefficients
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Once we have our eigenfunctions, how do we determine the coefficients for our Fourier series?

We integrate the initial condition function with our eigenfunctions, right?

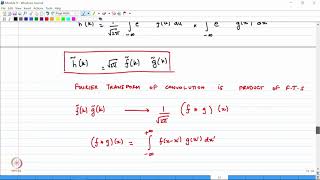
Exactly! We use the formula: \[ C_n = \frac{2}{L} \int_{0}^{L} f(x) \sin\left(\frac{n\pi x}{L}\right) dx \]. This integration gives us each coefficient which weights the eigenfunction to fit the initial condition.

So, if we have a specific temperature distribution as an initial condition, we can express it as a Fourier series?

Exactly! This lets us capture the behavior of the system over time. This is particularly useful in civil engineering applications like heat transfer. Now, what would happen as t approaches infinity?
Applications in Civil Engineering
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's take a step back and consider how we apply Fourier series in civil engineering. Can anyone give an example where we might use this?

We use it in heat transfer, for temperature distribution in walls!

Exactly! It’s also used in vibration analysis of structures and fluid flow problems. By expressing the initial conditions as Fourier series, we can analyze these complex scenarios effectively.

What about the constraints of using Fourier series?

A great question! Under certain conditions, like linearity and homogeneous boundaries, Fourier series work exceptionally well. Let's summarize what we’ve learned today.

We discussed eigenfunctions and how to calculate Fourier coefficients. We also saw their applications in civil engineering. Understanding these concepts is crucial as they form the foundation for solving PDEs effectively.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, the application of Fourier series in the context of partial differential equations (PDEs) is discussed, highlighting how eigenfunctions derived from the separation of variables facilitate the expression of complex initial conditions. This method enables engineers to address various physical phenomena within the realm of civil engineering.
Detailed
Application of Fourier Series in PDE Solutions
The section focuses on how Fourier series play a crucial role in solving partial differential equations (PDEs) by enabling the determination of unknown coefficients, specifically when initial conditions are provided. This process begins after eigenfunctions have been found through the method of separation of variables, typically taking the form of sine or cosine functions.
Key Points:
- Eigenfunctions: The solutions derived from separating variables are often sine and cosine terms. These functions form the basis of Fourier series.
- Determining Coefficients: Coefficients for these Fourier series are obtained from the initial condition function, expressed as follows: $$ C_n = rac{2}{L} \int_{0}^{L} f(x) \sin\left(\frac{n\pi x}{L}\right) dx $$
This equation allows the expression of any initial condition (like temperature distribution in a material) as a weighted sum of these eigenfunctions, facilitating solution formulation.
In summary, the application of Fourier series significantly aids in structuring solutions to PDEs encountered in various civil engineering problems, including heat transfer, vibrations, and stress analysis.
Youtube Videos




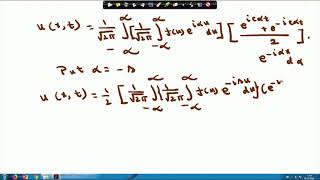

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Determining Coefficients in Fourier Expansion
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Once the eigenfunctions from the separation of variables are found (usually sine or cosine terms), the unknown coefficients C are determined using the initial condition via Fourier expansion:
C_n = \frac{2}{L} \int_0^L f(x) \sin\left(\frac{n\pi x}{L}\right) dx
Detailed Explanation
In this step, we take the eigenfunctions that we derived earlier, which are often sine or cosine functions, and we need to determine the coefficients that will help us form a complete solution to our PDE. The coefficients, represented as C_n, reflect how much each eigenfunction contributes to the overall solution. We find these coefficients by integrating the product of the initial condition function f(x) (which describes the state of the system at the starting point) and the appropriate sine function over the interval from 0 to L. This integration essentially helps us to project the initial condition onto our eigenfunctions, thus giving us the weighted sums of these functions that can describe the system at any time.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like mixing colors to get a specific shade. If you want a specific color (like hitting the initial temperature distribution), you need to know how much of each primary color you need to mix together (the contributions of each eigenfunction, represented by C_n, to the overall solution). Just like in mixing colors, the right combination will help you create the exact shade you want.
Expressing the Initial State in Terms of Eigenfunctions
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This allows expressing any arbitrary initial state (e.g., temperature distribution) as a weighted sum of the eigenfunctions.
Detailed Explanation
After determining the coefficients using Fourier expansion, we combine these coefficients with their corresponding eigenfunctions to express our initial condition as a series. This means that we can represent complex initial states, such as the temperature distribution in a solid, as an infinite series of simpler functions (the eigenfunctions). Each term in the series represents a different oscillation mode of the system, and their combination provides a comprehensive description of how the system behaves over time.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a musical performance where each instrument plays a different melody (the eigenfunctions). The overall harmony (the full solution of the PDE) is achieved by combining these melodies in specific ratios (the coefficients C_n). Just as a conductor blends these sounds to create a beautiful orchestral piece, engineers use these weighted sums to model complex behaviors like heat distribution in materials.
Key Concepts
-
Eigenfunctions: Fundamental solutions resulting from separation of variables in PDEs.
-
Fourier Series: Technique to express functions as sums of sine and cosine terms.
-
Coefficients: Derived from initial conditions to weight eigenfunctions in solutions.
Examples & Applications
Using Fourier series to express the temperature distribution in a concrete slab.
Applying Fourier series to analyze vibration modes in structural engineering.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In Fourier's way, we find our sway, eigenfunctions lead the way, coefficients at play.
Stories
Imagine a civil engineer standing before a wall, unable to predict heat flow. With Fourier's series, they uncover hidden patterns and coefficients, discovering how hot or cold each section feels over time.
Memory Tools
F-E-C: Fourier helps with Eigenfunctions, Coefficients for conditions.
Acronyms
PDE
Predicting Disturbance Events through Fourier methods.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Eigenfunctions
Functions obtained from the separation of variables used in Fourier series to represent solutions of PDEs.
- Fourier Series
A representation of a periodic function as a sum of sine and cosine functions, often used to solve differential equations.
- PDE (Partial Differential Equation)
An equation involving partial derivatives of a multivariable function.
- Coefficients
Constants in the Fourier series that determine the weight of each eigenfunction in expressing a function.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
