Partial Differential Equations (PDEs) and their Types
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to PDEs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we’re going to discuss Partial Differential Equations, or PDEs for short. Can anyone tell me what a PDE involves?

I think it involves multiple variables and their derivatives.

Exactly! PDEs involve the partial derivatives of multivariable functions. They’re crucial for modeling real-world phenomena. Can anyone think of an area in civil engineering where we might use PDEs?

Maybe in heat conduction or fluid flow?

Yes! Those are perfect examples. Now, let’s dive into the three main types of second-order PDEs.
Types of PDEs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

The first type we’ll look at is the elliptic PDE. Can someone explain what it’s used for?

It’s used for steady-state problems, like heat distribution.

Correct! An example is Laplace’s equation. Now, how about parabolic PDEs?

Those are related to time-dependent problems like the heat equation, right?

Exactly! And finally, can anyone describe hyperbolic PDEs?

They relate to wave propagation, like the wave equation.

Good job! Remembering these three types is crucial; let’s create a mnemonic: 'Ewe Ponders Hard' for Elliptic, Parabolic, and Hyperbolic.
Applications of PDEs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, can anyone highlight how we apply these types of PDEs in civil engineering?

We can determine how heat is transferred in structures using elliptic PDEs.

And parabolic PDEs can help us find out how heat changes over time?

Exactly! And hyperbolic PDEs help in analyzing vibrations in structures. These applications demonstrate why mastering PDEs is fundamental to our field. Remember: Elliptic for steady, Parabolic for transient, and Hyperbolic for dynamic problems.
Review and Summary
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s review what we learned today. What are the three types of second-order PDEs?

Elliptic, Parabolic, and Hyperbolic!

Great! Can anyone provide a quick detail about each?

Elliptic is for steady state, Parabolic for time-dependent heat, and Hyperbolic for wave propagation.

Excellent! This classification is key for applying the Method of Separation of Variables as we move forward. Keep practicing these concepts!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore the fundamental types of Partial Differential Equations (PDEs) encountered in civil engineering, namely ellipses, parabolas, and hyperbolas. Each type is linked to specific physical phenomena like heat conduction and wave propagation, establishing the groundwork for the later introduction of methods to solve these equations.
Detailed
Exploration of Partial Differential Equations (PDEs)
In civil engineering, the analysis of various physical phenomena often leads to solving Partial Differential Equations (PDEs). These equations involve partial derivatives of functions with several variables and play a crucial role in modeling complex systems.
This section categorizes the second-order PDEs specifically into three significant types:
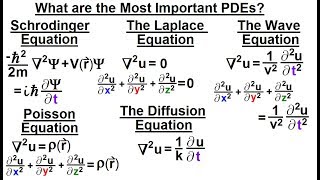
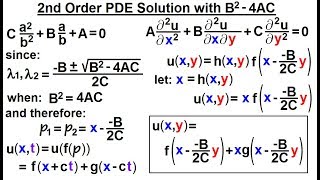
- Elliptic PDEs: These equations appear in scenarios such as steady-state heat distribution or potential flow, represented by Laplace’s equation. They are characterized by the absence of time dependence and typically describe static situations.
- Parabolic PDEs: This category includes equations like the heat equation, which is used for time-dependent heat conduction problems. Parabolic PDEs characterize how a quantity evolves over time and space, directly involving temporal changes.
- Hyperbolic PDEs: Representing phenomena such as wave propagation or vibrations in structures, hyperbolic PDEs like the wave equation describe systems where wave dynamics are significant and involve both space and time dependencies.
Understanding these classifications not only facilitates the selection of appropriate solution techniques, like the Method of Separation of Variables, but also establishes a framework for applying mathematical tools like Fourier series to address boundary and initial conditions.
Youtube Videos
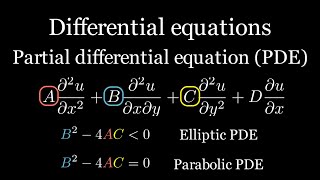




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Partial Differential Equations (PDEs)
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
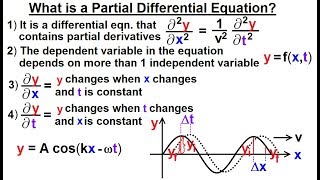
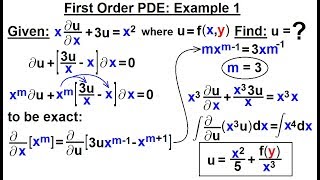
A partial differential equation involves partial derivatives of a multivariable function.
Detailed Explanation
A partial differential equation (PDE) is an equation that relates a function of multiple variables to its partial derivatives. This means that in a PDE, the function depends on more than one independent variable, and we are concerned with how the function changes with respect to these variables. For example, in heat conduction, we might be looking at how temperature changes over time and space, which involves two variables: time and position.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a weather map where temperatures vary across different geographic locations and also change throughout the day. The temperature at any point can be seen as a function of both location and time, making the temperature distribution a problem that can be described using a partial differential equation.
Types of PDEs in Civil Engineering
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The three classical types of second-order PDEs relevant to civil engineering problems are:
- Elliptic PDEs: e.g., Laplace’s equation, for steady-state heat distribution or potential flow.
- Parabolic PDEs: e.g., Heat equation, for time-dependent heat conduction problems.
- Hyperbolic PDEs: e.g., Wave equation, for vibration of structures or wave propagation.
Detailed Explanation
In civil engineering, we encounter three main types of second-order partial differential equations:
- Elliptic PDEs: These equations, such as Laplace's equation, are used in scenarios where we seek a steady-state condition, like how heat distributes evenly throughout a wall. The system doesn't change over time.
- Parabolic PDEs: These equations, exemplified by the heat equation, describe time-dependent processes such as heat conduction where the temperature can change over time as well as position.
- Hyperbolic PDEs: These equations, like the wave equation, are used in scenarios involving waves and vibrations, such as the analysis of how structures respond to dynamic loads or vibrations over time.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a water drum being tapped. As the drum is struck, waves propagate through the drum skin - this can be modeled using hyperbolic PDEs. If you were to heat one side of the drum, the temperature would gradually even out across the surface over time, which would be modeled with a parabolic PDE.
Key Concepts
-
Partial Differential Equation (PDE): An equation with partial derivatives of multiple variables.
-
Elliptic PDE: Used for static problems; example includes Laplace's equation.
-
Parabolic PDE: Represents time-dependent scenarios; example includes the heat equation.
-
Hyperbolic PDE: Describes wave phenomena; includes the wave equation.
Examples & Applications
Example of an elliptic PDE: Laplace's equation, used for analyzing heat distribution in a stationary medium.
Example of a parabolic PDE: The heat equation, used for studying the distribution of heat over time.
Example of a hyperbolic PDE: The wave equation, which models vibrations in a structure.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Elliptic for static, parabolic for time, hyperbolic's for waves – isn’t that just fine?
Stories
Imagine a river (elliptic) flowing steadily; think of logs (parabolic) drifting down stream but curved; finally, hear the waves (hyperbolic) crashing on the shore.
Memory Tools
Use 'EPH' to remember Elliptic, Parabolic, Hyperbolic.
Acronyms
Remember
'EPPH' - Elliptic for steady
Parabolic for time
Hyperbolic for waves.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Partial Differential Equation (PDE)
An equation that involves partial derivatives of a multivariable function.
- Elliptic PDE
A type of PDE such as Laplace’s equation used for steady-state problems.
- Parabolic PDE
A type of PDE like the heat equation that models time-dependent processes.
- Hyperbolic PDE
A PDE model used for wave propagation phenomena.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
