Pseudo-Inverse (Moore-Penrose)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Pseudo-Inverse and its Need
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're going to explore the concept of the pseudo-inverse, which is especially important when dealing with non-square matrices or systems that do not have a unique solution.

What exactly is a pseudo-inverse?

Good question! The pseudo-inverse, or Moore-Penrose inverse, is a generalization of the matrix inverse. It's used to find solutions to linear equations that might not have a direct solution.

When do we actually need to use it?

You would typically use the pseudo-inverse when you have an overdetermined system where the number of equations exceeds the number of unknowns. For instance, in data fitting, where we're trying to model data that doesn’t exactly fit a line.

So, it helps when direct solving isn't feasible?

Exactly! It minimizes the error instead of looking for an exact solution. Let's remember that A⁺ helps us find the best possible solution to Ax = b when direct methods fail.

Can we see an example of how this works?

Sure! We will get to that in future sessions, but remember, the formula x = A⁺b will be central to our solutions.
How to Calculate the Pseudo-Inverse
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s dive into how to actually calculate the pseudo-inverse of a matrix.

Are there specific methods for calculating it?

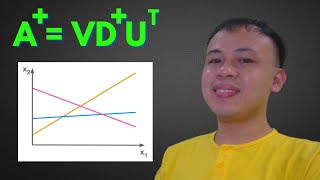
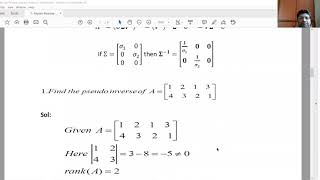
Yes! One common method is to use the Singular Value Decomposition, or SVD. It decomposes A into three matrices, allowing us to easily compute the pseudo-inverse.

And what are the conditions where it’s valid to use?

The pseudo-inverse exists for any matrix, but the computation becomes particularly insightful with full rank matrices. SVD helps ensure we handle cases of rank deficiency correctly.

Can you break down what SVD involves?

Certainly! SVD expresses A as UΣV*, where U and V are orthogonal matrices and Σ contains the singular values. This structure helps us calculate A⁺ effectively!

Sounds complex! Any tips for remembering SVD?

Try this: 'Unique Singular Vectors'. Each matrix plays a unique role in restructuring A!
Applications of the Pseudo-Inverse in Engineering
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss how the pseudo-inverse is applied in civil engineering.

Are there specific examples where this is particularly useful?

Absolutely! In civil surveying and sensor networks, for instance, we often encounter overdetermined systems that require least squares approaches.

What about in structural analysis?

Great point! It helps model relationships in structural feedback systems where precise solutions aren't available.

So it’s valuable in achieving realistic outcomes?

Exactly! The pseudo-inverse bridges the gap when precision isn't attainable, which is crucial in systems where conditions change.

I see! This makes sense for optimizing design solutions.

Yes! Remember that its value lies in error minimization across various applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In cases where a matrix is either non-square or singular, the pseudo-inverse, denoted as A⁺, provides a method to approximate solutions for Ax = b by minimizing the least squares error. This is particularly useful in applications where an exact solution is either not available or requires a different approach.
Detailed
Pseudo-Inverse (Moore-Penrose)
The pseudo-inverse, also known as the Moore-Penrose inverse, is a useful mathematical tool in linear algebra, especially when dealing with systems of equations that may not have a unique or straightforward solution. Given a matrix A that is not square or is singular (not invertible), we can find an approximate solution to the system of linear equations Ax = b. The solution is expressed as:
Formula:
x = A⁺b
Here, A⁺ represents the pseudo-inverse of matrix A. The significance of using the pseudo-inverse lies in its ability to minimize the residual error in the least-squares sense, thereby enabling the best approximate solution even when the traditional inverse cannot be computed. This method is pivotal in various engineering applications, particularly when designing systems or conducting data analysis where an optimal solution is necessary.
Youtube Videos





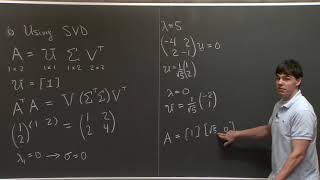

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding the Pseudo-Inverse
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
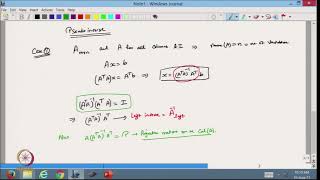
If A is not square or not invertible:
x=A+¿b¿
Where A+¿¿ is the pseudo-inverse of A.
Detailed Explanation
In linear algebra, when we're working with matrices, we often encounter scenarios where the matrix A is either not square (meaning it has a different number of rows compared to columns) or not invertible (meaning its determinant is zero, which makes it impossible to find a traditional inverse). In such cases, we can't directly apply the usual methods to solve equations of the form Ax = b.
Instead, we use the pseudo-inverse of A, denoted as A⁺. The equation x = A⁺b provides us with an approximate solution to the equation Ax = b, minimizing the least squares error. This is especially useful in cases where the system of equations has no exact solution, like in overdetermined systems where there are more equations than unknowns.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are trying to fit a straight line (representing A) through several data points (b) on a graph. If you have more data points than parameters for the line (as with an overdetermined system), it's unlikely that a single straight line can pass through all points perfectly. The pseudo-inverse helps find the best-fitting line, meaning that while the line may not pass through every point, it minimizes the overall distance to all points, providing a practical solution to a complex problem.
Key Concepts
-
Pseudo-Inverse: A generalized inverse for solving linear systems involving non-square or singular matrices.
-
Moore-Penrose Conditions: A set of properties that define the pseudo-inverse.
-
SVD: A method used to compute the pseudo-inverse, critical for handling rank-deficient matrices.
Examples & Applications
Using the pseudo-inverse to fit a regression line to an overdetermined data set.
Applying the pseudo-inverse in sensor calibration problems to minimize measurement error.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a system where solutions can't be found, the pseudo-inverse turns the error around.
Stories
Imagine a bridge engineer trying to fit data points from various sensors to model a bridge. The direct paths are tangled, leading to noise; here, the pseudo-inverse provides clarity, finding the best fit through the chaos.
Memory Tools
Remember SVD as 'Separate Values Diagonally' - each part plays a role in revealing the structure of the matrix.
Acronyms
P.I.N. for Pseudo-Inverse Necessity - P for Pseudo, I for Inverse, N for Necessity.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- PseudoInverse
A generalization of the matrix inverse used to find solutions to linear equations when the matrix is not square or invertible.
- MoorePenrose Inverse
Another name for the pseudo-inverse; it satisfies specific properties defined by the Moore-Penrose conditions.
- Singular Value Decomposition (SVD)
A method that factors a matrix into three components, facilitating the computation of the pseudo-inverse.
- Least Squares Minimization
A statistical method used to minimize the differences between observed and predicted values in data fitting.
- Rank Deficiency
A situation where the rank of the matrix is less than the number of its rows or columns, hindering inversion.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
