Introduction
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Bitumen
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing why bitumen is essential in road construction. Can anyone tell me about its key properties?

It’s adhesive and waterproof, right?

That's correct! These properties make bitumen a great binder for roads. However, what challenges do you think we face when using bitumen in colder ambient temperatures?

It might be too thick to apply without heating.

Exactly! That high viscosity can indeed pose a problem. To tackle this, we have bituminous emulsions and cutbacks. Can anyone guess how they might help us?
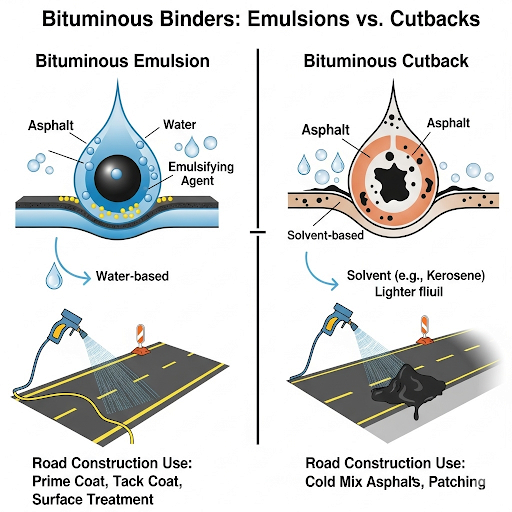
Bituminous Emulsions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Bituminous emulsions are a mixture of bitumen droplets in water with the aid of an emulsifying agent. Why do you think this could be advantageous?

Maybe it helps with the viscosity issue?

Exactly! This emulsification allows for easier application and better penetration into road materials. What do you think might be a typical use for these emulsions?

They could be used for maintenance, especially in cold weather.

Great point! We'll explore their specific uses in more depth in upcoming sections.
Bituminous Cutbacks
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's shift our focus to bituminous cutbacks. They are created by dissolving bitumen in volatile solvents. Does anyone know why we would want to do this?

To make bitumen easier to apply, I guess?

That's right! This method reduces the viscosity of bitumen to enhance fluidity at ambient temperatures. What happens to the solvent after the application?

It evaporates, leaving behind a bituminous film.

Exactly! And this evaporation is crucial to the curing process of the material. Let’s think about how cutbacks compare to emulsions.
Applications in Road Construction
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Both bituminous emulsions and cutbacks have diverse applications in road construction. Can anyone name a few?

They’re used for tack coats and surface dressing!

Correct! Emulsions are often used in surface dressing while cutbacks may be used as prime coats. Can any of you think of situations where one might be preferred over the other?

Maybe emulsions are better in wet conditions?

Absolutely! That's a significant advantage of emulsions. Let’s also consider their environmental impacts.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In road construction, while bitumen is prized for its adhesive and waterproofing qualities, its viscosity and need for heating can complicate its use. This section presents bituminous emulsions and cutbacks as practical alternatives that allow for easier application, better penetration, and energy savings. The upcoming chapters will delve into their preparation, classification, characteristics, uses, and testing.
Detailed
Introduction to Bituminous Emulsions and Cutbacks
In road construction, bitumen is the material of choice primarily because of its excellent adhesive and waterproof properties. However, using bitumen directly can pose significant challenges, especially when applied at ambient temperatures due to its high viscosity, which often necessitates heating. To overcome these obstacles, bituminous emulsions and cutbacks are employed as modified forms of bitumen that facilitate easier handling, improved penetration, and energy savings.
This section serves as an introductory overview of the topic, setting the stage for a more detailed exploration of the following key areas:
- Preparation - The methods by which bituminous emulsions and cutbacks are created.
- Classification - How these materials are categorized based on certain criteria.
- Characteristics - The properties that define these modified materials.
- Uses - Practical applications found in road construction and maintenance.
- Testing - Methods employed to evaluate their quality and effectiveness.
Through this chapter, we will gain a deeper understanding of how these alternatives to traditional bitumen can enhance efficiency and performance in road construction.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Importance of Bitumen in Road Construction
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In road construction, bitumen is widely used as a binder due to its excellent adhesive and waterproofing properties.
Detailed Explanation
Bitumen serves a critical role in road construction as it acts like glue, holding together various materials like stones and aggregates. This ability to stick together is crucial for ensuring that the road surface is durable and resistant to water damage. Because of its waterproofing properties, bitumen helps protect the road from rain and moisture, which can weaken the structure over time.
Examples & Analogies
Think of bitumen like the glue used in a craft project that holds all the pieces together firmly, preventing them from falling apart, even when exposed to water. Just like a well-glued project withstands wear and tear, a road made with bitumen remains strong and intact under the stresses of traffic and weather.
Challenges with Bitumen Application
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
However, the application of bitumen at ambient temperatures can be challenging due to its high viscosity and requirement for heating.
Detailed Explanation
Bitumen has a thick and sticky consistency (high viscosity) when it is at room temperature, which makes it difficult to work with. To make it easier to handle, it typically needs to be heated to a higher temperature, which can complicate the application process and require additional equipment and safety measures.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to spread cold honey on toast; it's thick and difficult to spread. But if you warm it up, it becomes much easier to pour and spread. In the same way, heating bitumen makes it easier to use for road construction, but it requires careful handling to avoid burns or accidents.
Alternatives to Bitumen
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
To address this, bituminous emulsions and cutbacks are used as alternatives. These modified forms allow for easier handling, better penetration, and energy savings.
Detailed Explanation
Bituminous emulsions and cutbacks are modified forms of bitumen that help overcome the challenges of working with pure bitumen. Emulsions allow bitumen to be mixed with water, making it easier to apply at lower temperatures without the need for heating. Cutbacks, on the other hand, involve dissolving bitumen in solvents, reducing its viscosity to enhance flow and application ease, especially in colder conditions. Using these alternatives not only simplifies the application but can also save energy because less heating is needed.
Examples & Analogies
Think of bituminous emulsions like a smoothie made with fruits and yogurt instead of eating solid fruits one by one. The smoothie is easier to drink and digest, just as emulsions and cutbacks make it easier to apply bitumen compared to using it straight from the can. This saves time and effort in road construction, making the process more efficient.
Overview of the Chapter
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This chapter discusses the preparation, classification, characteristics, uses, and testing of bituminous emulsions and cutbacks.
Detailed Explanation
The chapter provides a comprehensive exploration of both bituminous emulsions and cutbacks, detailing how they are made (preparation), the different types available (classification), their properties (characteristics), their practical applications (uses), and how they are evaluated for quality and performance (testing). This structured approach helps readers understand each aspect of these materials and their significance in road construction.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine if we were learning how to bake a cake; we would start by preparing the ingredients, then classify different types of cakes (like chocolate or vanilla), understand the characteristics, know how to use them in a recipe, and finally, test the cake to see if it’s done; this chapter does the same for bituminous emulsions and cutbacks, providing a complete guide for learners.
Key Concepts
-
Bitumen: The key binder used in road construction for its adhesive and waterproof properties.
-
Emulsions: Mixtures of bitumen and water requiring an emulsifying agent, useful for easier application.
-
Cutbacks: Prepared by dissolving bitumen in solvents to reduce viscosity, facilitating use at ambient temperatures.
-
Viscosity: A crucial property influencing the handling of bitumen in various temperatures.
Examples & Applications
Using emulsions for surface dressing in wet conditions to achieve better bonding.
Using cutbacks for prime coats applied directly onto unpaved roads to stabilize the surface.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When the cold will freeze the day, bitumen's hard, it won't play. But emulsions and cutbacks lead the way, paving roads without delay.
Stories
Imagine a construction site where a thick, heavy material like bitumen almost refuses to move due to the cold. The workers are struggling until they find a magical potion (the emulsifying agent) that allows the bitumen to dance smoothly onto the road!
Memory Tools
Remember 'E.C. Cut' for Emulsions, Cold, and Cutbacks – three solutions for colder applications.
Acronyms
B.E.C.
Bitumen
Emulsions
Cutbacks – remembering the road construction essentials.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Bitumen
A viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum used as a binder in road construction.
- Emulsion
A mixture of two immiscible liquids, typically bitumen and water, stabilized by an emulsifying agent.
- Cutback
A form of bitumen dissolved in a volatile solvent to reduce viscosity for easier application.
- Emulsifying Agent
A surfactant that stabilizes the mixture of bitumen and water in an emulsion.
- Viscosity
A measure of a fluid's resistance to flow, crucial to understanding the application of bitumen.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
