Uses of Bituminous Emulsions
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Bituminous Emulsion Uses
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re going to discuss the uses of bituminous emulsions. Can anyone tell me what they think an emulsion is?

Isn't it a mixture of bitumen and water?

Exactly! And the emulsifying agent helps this mixture stay stable. Now, let’s talk about its applications. One primary use is as a tack coat. What do you think a tack coat does?

I think it helps bond the layers of the pavement together.

Correct! It ensures strong adhesion between the layers. We can remember this with the acronym 'TACK'—Ties All Coatings Kinetically.

That’s a great way to remember it!

Let’s summarize: Tack coats bond layers of pavement. Now, what about prime coats? What purpose might they serve?
Understanding Prime Coats and Surface Dressing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Prime coats are used on low-strength subgrades. Why do you think they are important?

Maybe to strengthen the layer before adding more pavement?

Exactly! They create a strong binding layer. Now, let’s transition to surface dressing. Who can explain its role?

I believe it’s used for maintaining existing roads?

Good point! Surface dressing renews the surface and improves durability. Remember the mnemonic 'DRESS'—Durability Residing in the Emulsion's Surface Seal.

That's a clever way to remember it!
Exploring Cold Mixes and Soil Stabilization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Cold mixes are very useful. Can anyone guess why?

They can be applied without heating?

Exactly! This is crucial in colder regions. Now, what about using emulsions for dust control?

Isn’t that to stop particulates from blowing away?

Great observation! This application also helps stabilize the soil. We can use the mnemonic 'DUST'—Dust Unification via Stable Treatment.
Recap and Importance of Key Uses
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's recap what we’ve learned about bituminous emulsions. What are the main uses we discussed?

Tack coats, prime coats, surface dressing, cold mixes, and dust control!

Well done! Remember, these uses highlight the versatility of bituminous emulsions. They ensure our roads are safe, durable, and maintained without complicated procedures.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Bituminous emulsions serve several critical functions in road construction, including as tack coats, prime coats, and in dust control. Their ability to be applied without heating makes them especially useful in cold weather and for maintenance tasks.
Detailed
Uses of Bituminous Emulsions
Bituminous emulsions have a variety of significant applications in road construction due to their unique properties. The key uses include:
- Tack Coat: Used to bond different layers of pavement, ensuring strong cohesion between new and existing surfaces.
- Prime Coat: Ideal for low-strength subgrades where a binding layer is necessary to improve stability.
- Surface Dressing: Essential for maintaining existing road surfaces, providing waterproofing and renewing skid resistance.
- Slurry Seal and Microsurfacing: Techniques that utilize emulsions for sealing road surfaces to prevent moisture penetration and extend life.
- Cold Mixes: Useful in regions where heating facilities are unavailable, allowing for effective application in unfavorable conditions.
- Dust Control and Soil Stabilization: Emulsions help control dust and stabilize the soil, contributing to improved road conditions.
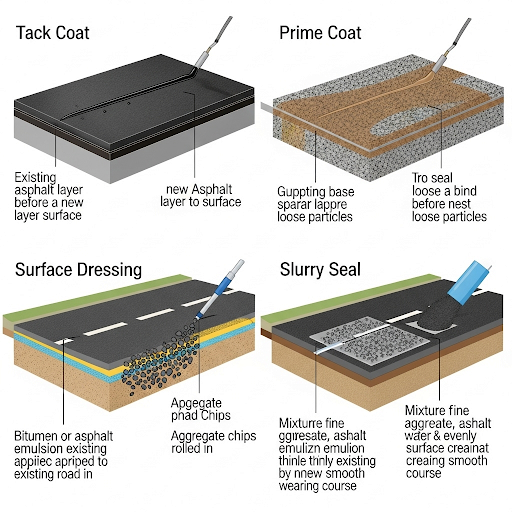
Overall, the use of bituminous emulsions is critical for modern highway maintenance and construction, offering convenience and performance without the need for high-temperature application.
Youtube Videos










Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Tack Coat
Chapter 1 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Tack Coat: For bonding between layers.
Detailed Explanation
A tack coat is a thin layer of bituminous emulsion that is applied to an existing surface before laying a new layer of asphalt. Its primary function is to create a strong bond between the two layers, ensuring that they adhere properly and work together as a unit. Tack coats are essential for preventing delamination or separation of the asphalt layers over time.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a tack coat like glue for paper. When you glue two sheets of paper together, it helps them stick and stay attached. If you don't use glue, the papers can easily peel apart. Similarly, a tack coat ensures that new asphalt stays firmly attached to the old surface, preventing any separation as vehicles pass over.
Prime Coat
Chapter 2 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Prime Coat: For low-strength subgrades.
Detailed Explanation
A prime coat is also a type of bituminous emulsion applied to low-strength subgrades (the layer of soil or base that supports a road). Its purpose is to penetrate the surface and seal it while also providing a better bonding surface for the subsequent layers of asphalt. It helps to stabilize the subgrade and minimizes the absorption of the subsequent asphalt layers.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a sponge soaking up water. If you pour water directly onto it, it absorbs quickly, losing strength. However, if you first seal the sponge with a thin layer of oil, it won't absorb as much, allowing for better control over how it handles the moisture. The prime coat functions similarly by sealing the subgrade, improving the strength and stability of the road.
Surface Dressing
Chapter 3 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Surface Dressing: For maintenance of existing roads.
Detailed Explanation
Surface dressing involves applying a layer of bituminous emulsion mixed with aggregates onto an existing road surface. This process refreshes the road, provides water resistance, and extends its life span. It is particularly useful for repaving old roads without extensive reconstruction.
Examples & Analogies
Consider surface dressing like putting a new coat of paint on an old fence. The paint helps protect the wood from the elements like rain and sun, making it last longer. In a similar way, surface dressing protects roads and makes them last longer by providing a new, resilient layer.
Slurry Seal and Microsurfacing
Chapter 4 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Slurry Seal and Microsurfacing.
Detailed Explanation
Slurry seal is a mixture of bituminous emulsion, aggregates, water, and additives, designed to repair and maintain road surfaces by sealing cracks and providing a new layer that enhances skid resistance. Microsurfacing is similar but allows for a thicker application and includes additional materials for better performance. Both methods are effective for extending the life of a roadway and improving its safety.
Examples & Analogies
Think of slurry sealing like spreading icing on a cake. Just as icing provides a protective layer and makes the cake look appealing, slurry seal coats the road, protecting it from damage and improving its appearance. Microsurfacing is like adding a thicker layer of frosting for a richer finish.
Cold Mixes
Chapter 5 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Cold Mixes: In areas without heating facilities.
Detailed Explanation
Cold mixes refer to bituminous emulsion mixtures that can be applied without heating. This is particularly useful in areas where heating facilities are not available or where temperatures are low. Cold mixes are ideal for patch repairs and surface treatments, providing flexibility in application while maintaining performance.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you have to make a cold salad instead of a hot casserole. Just like using fresh ingredients allows you to create a dish without cooking it, cold mixes allow road workers to repair roads without needing to heat bitumen, making it practical for various situations.
Dust Control and Soil Stabilization
Chapter 6 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Dust Control and Soil Stabilization.
Detailed Explanation
Bituminous emulsions are also used in dust control applications, especially on unpaved roads. They help to bind and stabilize the soil, reducing dust and improving road conditions. This application is crucial in rural areas where dust can create health hazards and reduce visibility.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're in a sandy area, and every time a vehicle passes, dust flies everywhere, making it hard to see and breathe. Applying bituminous emulsion is like laying down a wet cloth over the sand to keep it in place; it binds the particles together, preventing dust from spreading and making the environment much cleaner and safer.
Key Concepts
-
Tack Coat: A material used for bonding layers in road construction.
-
Prime Coat: An initial application on a subgrade to improve adhesion.
-
Surface Dressing: A maintenance technique to renew road surfaces.
-
Cold Mix: Emulsions used without heating, ideal for cold weather.
-
Soil Stabilization: The process to enhance soil strength for construction.
Examples & Applications
Using a tack coat improves the bond between new asphalt layers, ensuring longevity.
When applying a prime coat, workers enhance the performance of low-strength subgrades, making them suitable for road construction.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Tack coats help layers to cling, like glue for roads, it’s a good thing.
Stories
Imagine a road construction team using emulsions. Each worker applies a tack coat, bonding layers like friends holding hands, firm and united.
Memory Tools
DUST—Dust Unification via Stable Treatment.
Acronyms
TACK—Ties All Coatings Kinetically.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Tack Coat
A thin layer of emulsion used to bond layers of pavement.
- Prime Coat
An initial layer applied to untreated subgrade to enhance adhesion.
- Surface Dressing
A technique to renew the surface and improve road durability.
- Cold Mix
A type of bituminous emulsion mix that can be applied at ambient temperatures.
- Soil Stabilization
The process of improving soil properties to support construction.
- Dust Control
Methods to minimize dust generation from road surfaces.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
