Preparation of Bituminous Emulsions
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Overview of Bituminous Emulsion Preparation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will learn about the preparation of bituminous emulsions. Can anyone tell me what bituminous emulsions are used for in road construction?

They are used to improve the handling of bitumen without heating it!

Exactly! Now let’s explore how we prepare these emulsions. The first step involves heating the bitumen to reduce its viscosity.

Why do we need to reduce the viscosity?

Good question! Lower viscosity allows for easier mixing and dispersion in the next steps. Next, we prepare the water phase with an emulsifier.

What’s the role of an emulsifier?

An emulsifier stabilizes the mixture by keeping the bitumen droplets suspended in water. This is essential since bitumen and water can’t mix on their own. Let’s proceed to the mixing step.
Mechanical Shearing in the Colloidal Mill
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, can anyone explain what happens in the colloidal mill?

That’s where the heated bitumen meets the water phase, right?

That's correct! In the colloidal mill, the bitumen is mechanically sheared into tiny droplets to ensure even distribution. Why do you think that’s important?

It must help in forming a stable emulsion!

Yes! A stable emulsion ensures that we have uniform properties throughout. Finally, we store the emulsion in tanks while monitoring critical parameters.
Parameters for Stability in Bituminous Emulsions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss some important parameters that impact the stability of a bituminous emulsion. What do you think we should monitor?

Maybe the bitumen content?

Absolutely! Along with bitumen content, we also need to consider droplet size and pH. How might these factors affect the emulsion?

If the droplet size isn’t consistent, the emulsion might not be stable.

Correct! Consistent droplet size helps maintain separation of the phases, whereas pH affects the emulsifier's efficiency. As you see, controlling these factors is vital for effective emulsions.
Final Steps in Preparation and Storage
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up, can anyone summarize the steps we’ve discussed in preparing bituminous emulsions?

We heat the bitumen, prepare the water phase, mix them in a colloidal mill, and finally store them in tanks!

Well done! Remember that ensuring the right parameters are monitored leads to stable emulsions. This ensures better performance in construction applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The preparation of bituminous emulsions involves a series of steps including heating bitumen to reduce its viscosity, preparing the water phase with emulsifiers, and mixing them in a colloidal mill to achieve stable emulsions. Key parameters such as bitumen content, droplet size, and pH are crucial for ensuring the stability of the emulsion.
Detailed
Preparation of Bituminous Emulsions
Bituminous emulsions are crucial for road construction as they provide a practical solution to the challenges posed by high-viscosity bitumen. This section delineates the following key steps in their preparation:
- Heating of Bitumen: Initially, bitumen is heated to significantly reduce its viscosity, making it easier to process.
- Preparation of Water Phase: Concurrently, a water phase containing an emulsifying agent is prepared. This emulsifier plays a crucial role in stabilizing the mixture by preventing the separation of water and bitumen, which are otherwise immiscible.
- Mixing in a Colloidal Mill: The heated bitumen is then introduced into a colloidal mill. Here, it is mechanically sheared into smaller droplets, which facilitates an even distribution within the water phase, creating a stable emulsion.
- Storage: Finally, the emulsion is collected and stored in specialized tanks, with critical parameters such as bitumen content, droplet size, and pH monitored and adjusted to maintain stability.
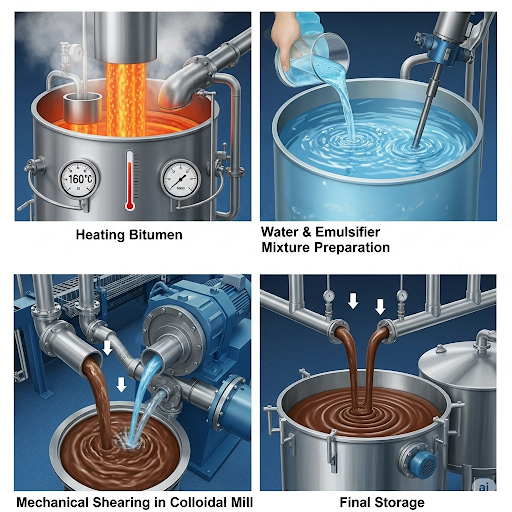
These steps are paramount for producing emulsions that can be effectively used in various applications in road maintenance and construction, ensuring their practicality and effectiveness.
Youtube Videos










Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Bituminous Emulsion Preparation
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Bituminous emulsions are manufactured using a colloidal mill where bitumen is mechanically sheared into small droplets and mixed with water containing the emulsifying agent.
Detailed Explanation
Bituminous emulsions are produced through a specific process that involves breaking down bitumen into very small droplets. This is done using a colloidal mill, which mixes these tiny droplets with water. The water also contains an emulsifying agent, a substance that helps stabilize the mixture. Since bitumen and water do not naturally mix well, the emulsifying agent plays a crucial role in creating a stable emulsion.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of the process like making a salad dressing. When you mix oil (which represents bitumen) and vinegar (which represents water), they don’t mix well on their own. However, if you add mustard (the emulsifying agent), it helps combine them into a stable dressing that can coat the salad evenly.
Steps in Preparation
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Steps in Preparation:
1. Heating of bitumen to reduce viscosity.
2. Preparation of water phase with emulsifier.
3. Introduction into the colloidal mill for mixing.
4. Collection and storage of the emulsion in tanks.
Detailed Explanation
The preparation of bituminous emulsions involves several key steps:
1. Heating of Bitumen: The bitumen is first heated to lower its viscosity. Lower viscosity means the bitumen is less thick and easier to shear into droplets.
2. Preparation of Water Phase: While the bitumen is heating, a water phase is prepared that includes the emulsifier. This mixture will help hold the bitumen droplets in suspension once they are created.
3. Mixing in Colloidal Mill: The heated bitumen is then introduced into the colloidal mill. In this mill, high shear forces cause the bitumen to break into small droplets which are then mixed with the water and emulsifier.
4. Collection and Storage: Once the mixing is complete, the emulsion is collected and transferred to storage tanks, where it must be kept stable until use.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine making a smoothie. You start by blending fruits (the bitumen) while warming them slightly to make them easier to blend. You prepare a mixture of yogurt (the emulsifier) and juice (the water) to help create a smooth texture. When you put everything in the blender (the colloidal mill), it mixes well, and you pour out a delicious smoothie (the emulsion) ready to drink.
Control of Important Parameters
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Important parameters such as bitumen content, droplet size, and pH are controlled to ensure emulsion stability.
Detailed Explanation
To create a high-quality bituminous emulsion, certain parameters must be carefully controlled during preparation:
- Bitumen Content: The proportion of bitumen in the emulsion is critical because it affects the adhesive properties and durability of the final product.
- Droplet Size: The size of the bitumen droplets influences how well the emulsion performs. Smaller droplets usually lead to a more stable emulsion and better application characteristics.
- pH Level: The pH of the emulsion can also affect its stability and performance. Maintaining the correct pH ensures that the emulsifying agent works effectively.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like baking a cake. If you don’t get the proportions of flour, sugar, and eggs (the bitumen, water, and emulsifier) just right, the cake (emulsion) might not rise or hold together properly. Similarly, if you use the wrong size of baking powder or mix at the wrong temperature, your cake can end up dense or uneven, just like an unstable emulsion.
Key Concepts
-
Heating Bitumen: Reduces viscosity to facilitate the mixing process.
-
Water Phase Preparation: Essential for creating a stable emulsion.
-
Colloidal Mill: A crucial tool that mechanically shears bitumen to create small droplets.
-
Stability Parameters: Factors like droplet size, bitumen content, and pH are monitored for effective emulsions.
Examples & Applications
In road maintenance, bituminous emulsions are used to apply a thin layer of asphalt on the road surface, enhancing durability.
In cold weather applications, bituminous emulsions allow for work without the need for heating the bitumen.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To mix hot and cold, just use an emulsifier bold; it keeps the droplets from breaking the mold.
Stories
Imagine a chef mixing oil and water; they need a strong whisk – that’s like the emulsifier in making emulsions!
Memory Tools
H-W-M-S: Heat bitumen, Water phase, Mix in colloidal mill, Store safely for stability.
Acronyms
B-W-M-S
Bitumen is heated
Water phase is prepared
Mixed in a mill
Stored for stability.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Bituminous Emulsion
A mixture where bitumen droplets are suspended in water with the aid of an emulsifying agent.
- Emulsifier
A surfactant that enables the formation and stabilization of emulsions by reducing surface tension between immiscible liquids.
- Colloidal Mill
A machine used to mechanically shear bitumen into small droplets, facilitating the creation of stable emulsions.
- Viscosity
A measure of a fluid's resistance to deformation; important in determining how easily a material can be mixed or applied.
- Stability
The ability of an emulsion to maintain its structure without separation of components over time.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
