Types of Bituminous Cutbacks
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Bituminous Cutbacks
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll explore bituminous cutbacks. To start, can anyone tell me what a bituminous cutback is?

Is it a type of asphalt?

Good guess! A bituminous cutback is created by dissolving bitumen in a volatile solvent to reduce its viscosity and enhance fluidity. This makes it easier to apply at ambient temperatures.

So, it helps the bitumen flow better?

Exactly! And once applied, the solvent evaporates, leaving behind a bituminous film.

What are the solvents typically used?

Common solvents include naphtha and kerosene. They are crucial for determining the cutback type.

To help you remember, think of cutbacks as 'cutting' down viscosity with 'back'ing solvents!
Types of Bituminous Cutbacks
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's dive into the types of bituminous cutbacks. Who can define Rapid Curing?

Is that the one that evaporates quickly?

Correct! Rapid Curing uses highly volatile solvents, making it ideal for quick applications like surface treatments.

What about Medium Curing?

Medium Curing uses moderately volatile solvents and is often used in premixing with coarse aggregates. It has an intermediate evaporation rate.

And Slow Curing?

Slow Curing, made with low volatility oils, has a very slow evaporation rate, suitable for applications requiring a longer working time like prime coats.

Remember, for each type: RC for Rapid usage, MC for Medium mixing, and SC for Slow stabilization.
Applications of Bituminous Cutbacks
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Can anyone suggest where we might use these different types of cutbacks?

I think Rapid Curing would be used for quick repairs.

Exactly! RC is often used for surface treatments like spray applications. What about Medium Curing?

That's for mixing with aggregates, right?

Yes! It's great for premixing. And Slow Curing?

For stabilizing roads?

Very good! Slow Curing is often used for prime coats or other stabilization projects. Great job everyone!
Conclusion and Review
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's quickly recap what we've learned today about bituminous cutbacks. Who can summarize the three types?

We have Rapid Curing for quick applications, Medium Curing for premixing, and Slow Curing for stabilization.

Exactly! And remember how the choice of solvent affects the curing type. Knowing this will help us choose the right materials for our projects.

So, if I need something quick to apply, I should select Rapid Curing?

Correct! Choosing the right type is essential for effective road construction and maintenance.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section categorizes bituminous cutbacks into three main types—Rapid, Medium, and Slow Curing—based on their evaporation rates which are determined by the volatility of the solvents used. Each type serves specific applications in road construction and maintenance.
Detailed
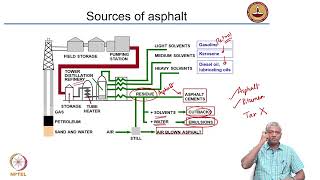
Types of Bituminous Cutbacks
Bituminous cutbacks are categorized based on their curing times, which are influenced by the type of solvent used during their preparation. The following types are discussed in detail:
- Rapid Curing (RC): Made with highly volatile solvents, RC cutbacks evaporate quickly and are ideal for applications requiring immediate adhesion, such as surface treatments performed via spray application.
- Medium Curing (MC): Utilizing moderately volatile solvents, MC cutbacks have an intermediate evaporation rate, making them suitable for premixing with coarse aggregates.
- Slow Curing (SC): Prepared with lower volatility oils, SC cutbacks evaporate slowly, and are typically used for applications such as prime coats or stabilization where a longer working time is necessary.

Understanding these types is essential for selecting the appropriate cutback for various applications in road construction and maintenance.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Rapid Curing (RC) Bituminous Cutbacks
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Rapid Curing (RC):
- Uses highly volatile solvents like gasoline.
- Quick evaporation.
- Used for surface treatments like spray application.
Detailed Explanation
Rapid curing bituminous cutbacks are designed to evaporate quickly after application. They utilize solvents such as gasoline, which have a high volatility. This means that once the cutback is applied to a surface, the solvent evaporates almost immediately, allowing the bitumen to form a solid film on the surface. This type of cutback is primarily useful in surface treatments where quick setting is required, such as during spray applications. The rapid evaporation helps to avoid issues with moisture or other environmental factors that could affect the adhesion of the bitumen.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine applying a light layer of hair gel that dries instantly, giving your hair a firm hold. Just as the gel sets quickly, RC cutbacks allow for rapid formation of a protective layer on roads after application, ensuring that the surface can be used almost immediately without the risk of the bitumen blending with moisture or debris.
Medium Curing (MC) Bituminous Cutbacks
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Medium Curing (MC):
- Uses moderately volatile solvents like kerosene.
- Intermediate rate of evaporation.
- Used for premix with coarse aggregates.
Detailed Explanation
Medium curing bituminous cutbacks use solvents that evaporate at a moderate rate, such as kerosene. This property makes them suitable for applications where a controlled curing time is necessary. The medium evaporation rate allows the cutback to be mixed with coarse aggregates before application, providing a stable, workable mixture. This balance helps in achieving the desired consistency and ensures effective bonding between the bitumen and the aggregates once the solvent has evaporated.
Examples & Analogies
Think of making a cake batter. You want certain ingredients to combine at the right pace. If you mix too quickly, it might not set well. Similarly, MC cutbacks allow for a careful blend of bitumen and aggregates, ensuring the mixture holds together before setting completely, much like waiting for the cake to rise properly before taking it out of the oven.
Slow Curing (SC) Bituminous Cutbacks
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Slow Curing (SC):
- Uses low volatility oils.
- Very slow evaporation.
- Suitable for prime coats or stabilization.
Detailed Explanation
Slow curing bituminous cutbacks employ low volatility solvents that evaporate much slower than RC and MC cutbacks. This slow evaporation rate means that they remain workable for a longer period after application. As a result, SC cutbacks are particularly effective for applications requiring extended time frames, such as prime coats or soil stabilization. They allow for better adherence and integration with the materials on site, making them an ideal choice for specific road construction and maintenance applications.
Examples & Analogies
Consider slow-cooking a stew. The longer cooking time allows flavors to meld beautifully, creating a rich dish. In the same way, slow curing bituminous cutbacks take their time to evaporate, ensuring that the bitumen properly bonds and enhances the stability of the surface it is applied to.
Key Concepts
-
Cutbacks: Mixtures of bitumen and volatile solvents used to decrease viscosity.
-
Rapid Curing: Fast-evaporating cutbacks suitable for quick applications.
-
Medium Curing: Cutbacks with intermediate evaporation for premix applications.
-
Slow Curing: Gradually evaporating cutbacks ideal for stabilizing surfaces.
Examples & Applications
A road maintenance team uses Rapid Curing cutback for a quick fill-in of potholes.
A highway contractor uses Medium Curing cutback to mix with coarse aggregates for better performance.
A construction site applies Slow Curing cutback as a prime coat before laying new asphalt.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Cutbacks make it flow so fast, RC is first, MC's mid-range cast; SC slows down, it's built to last.
Stories
Imagine a maintenance team at a busy crossroads: they need to fix a pothole quickly. They grab their Rapid Curing cutback, spray it, and it evaporates, allowing cars to drive smoothly again. For larger repairs, they might use Medium Curing, while for long-term fixes like prime coats, Slow Curing does the job.
Memory Tools
Remember the acronym 'RMS' for Rapid, Medium, Slow to keep the cutbacks in order.
Acronyms
RC for Rapid, MC for Mediocre timing, SC for Slow going; this helps you remember their evaporation rates.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Bituminous Cutback
A mixture of bitumen and a volatile solvent to reduce viscosity and enhance fluidity for easy application.
- Rapid Curing (RC)
A type of cutback that uses highly volatile solvents for quick evaporation.
- Medium Curing (MC)
A cutback type that utilizes moderately volatile solvents for an intermediate evaporation rate.
- Slow Curing (SC)
Uses low volatility oils resulting in a slow evaporation rate, suitable for prime coats.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
