Conclusion
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
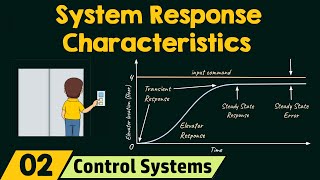
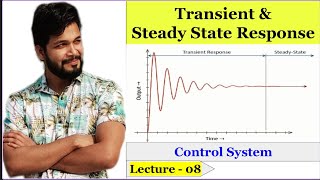
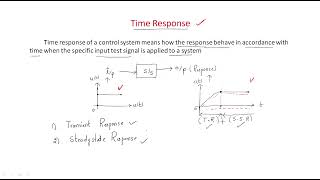
Transitory vs. Steady-State Responses
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In control systems, we analyze two key responses: the transient and steady-state responses. Can anyone explain what a transient response is?

The transient response is how the system initially reacts to a change in input?

Exactly! It's all about the system's initial behavior after a disturbance. Now, can someone tell me what we mean by steady-state response?

That's when the system settles down and behaves consistently over time!

Well done! Remember: transient leads to steady-state. Think of it as the 'temporary chaos before calm'.
Key Parameters of Each Response
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s dive deeper into transient responses. What key parameters can we measure?

Rise time, settling time, and overshoot?

Fantastic! Which of these helps us understand how quickly the system responds?

The rise time!

Correct! And what about the steady-state response? What does it tell us?

It shows us the accuracy of the system and the steady-state error.

Great job! Remember: accuracy and stability are the hallmarks of a well-designed system.
Application of Analysis Methods
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

How do engineers analyze transient and steady-state responses? Any thoughts on the methods used?

We can use time-domain and frequency-domain methods, right?

Exactly! Time-domain methods involve solving differential equations, while frequency-domain uses Bode plots. Why do both matter?

Both approaches help us optimize system performance under different conditions!

That's correct! Remember that both types of analysis ensure our systems are stable and reliable.
Importance of Understanding Responses
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

So, after all this discussion, why is it crucial to understand both transient and steady-state responses?

It helps engineers design systems that are both fast and accurate!

Exactly! The sooner we understand behavior through analysis, the better our system designs will be. Remember: speed, accuracy, stability!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The conclusion emphasizes that understanding both transient and steady-state responses is key for engineers to design stable, accurate, and high-performance control systems. It consolidates key insights into system behaviors and their analysis methods to optimize performance.
Detailed
Conclusion
In this chapter, we examined both the transient and steady-state responses of control systems. The transient response provides insight into the system's behavior during the transition from one state to another, while the steady-state response describes the system's behavior once it has settled. Engineers use various time-domain and frequency-domain methods to analyze these responses, allowing them to design systems with optimal performance in terms of speed, accuracy, and stability. The key takeaways include:
- The transient response comprises rise time, overshoot, settling time, and damping effects.
- The steady-state response reflects the system’s accuracy and error characteristics, which can be quantified using error constants.
- Understanding and analyzing both transient and steady-state responses is crucial for ensuring a control system meets its performance requirements.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of System Responses
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In this chapter, we examined both the transient and steady-state responses of control systems. The transient response provides insight into the system's behavior during the transition from one state to another, while the steady-state response describes the system's behavior once it has settled.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk summarizes the primary focus of the chapter, which is the two essential phases of system responses: transient and steady-state. The transient response helps understand how the system behaves initially when a change occurs, reflecting its immediate reactions. In contrast, the steady-state response explains how the system behaves when it reaches a constant condition after any disturbances have settled down.
Examples & Analogies
Think about how water boils. Initially, when you turn on the heat, the water temperature rises (this is the transient phase). Eventually, once the water reaches boiling point, it maintains that temperature consistently (this is the steady-state phase).
Engineers' Analysis Methods
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Engineers use various time-domain and frequency-domain methods to analyze these responses, allowing them to design systems with optimal performance in terms of speed, accuracy, and stability.
Detailed Explanation
In this part, we learn that engineers have tools at their disposal to study how systems respond over time and at different frequencies. Time-domain methods often involve solving differential equations, while frequency-domain methods include techniques like Bode plots. Understanding these methods is crucial for designing systems that meet specific performance criteria such as being fast and accurate.
Examples & Analogies
Consider that when tuning a musical instrument (like a guitar), you may check the tension of the strings (time-domain) and also assess the sound frequency (frequency-domain) to ensure it plays the right notes cleanly and accurately.
Key Takeaways
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Key takeaways include:
- The transient response includes rise time, overshoot, settling time, and damping effects.
- The steady-state response reflects the system’s accuracy and error characteristics, which can be quantified using error constants.
- Both responses are critical for evaluating and designing control systems.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk lists essential points to remember. The transient response has specific characteristics that help in understanding how quickly and effectively the system can adapt to changes. Meanwhile, the steady-state response illustrates how reliable the system is once it stabilizes. Recognizing these two sets of behaviors is vital for engineers when creating and assessing the efficiency of control systems.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine driving a car. During sudden acceleration or braking, your car's engine and brakes respond quickly (the transient response), but once you're cruising at a constant speed on the highway, your driving stabilizes (the steady-state response). Understanding both phases is essential for safe driving!
Importance of Analyzing System Responses
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Understanding and analyzing both transient and steady-state responses is crucial for ensuring a control system meets its performance requirements.
Detailed Explanation
This final chunk emphasizes why studying both responses is important. For a control system to function effectively, it must be able to handle both immediate changes (transient effects) and maintain excellent performance over time (steady-state). Both analyses are foundational for meeting the operational goals set by engineers.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a roller coaster. The initial steep drops and quick turns must be thrilling yet safe (transient response), while the thrill should continue smoothly throughout the ride without unexpected stops or jitters (steady-state response) to be enjoyable.
Key Concepts
-
Transient Response: Immediate system behavior post-input change.
-
Steady-State Response: Long-term system behavior after settling.
-
Error Constants: Key parameters for assessing steady-state accuracy.
-
Damping Ratio: Affects speed and oscillations in transient behavior.
Examples & Applications
For a system that takes 2 seconds to rise from 10% to 90% output, its rise time would be 2 seconds.
If a system overshoots its final output by 15% before settling, this indicates an overshoot of 15%.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
From chaos to calm, the system behaves, Transient to steady, its stability paves.
Stories
Imagine a tightrope walker. At first, they sway (transient), but soon they find balance (steady-state).
Memory Tools
SOS: Speed, Overshoot, Settle summarizes key transient measures!
Acronyms
POSS
Parameters of Steady-State
Flash Cards
Glossary
- SteadyState Response
The behavior of a system after it has settled and reached equilibrium, reflecting its long-term stability and accuracy.
- Rise Time
The time taken for a system's output to rise from 10% to 90% of its final value.
- Settling Time
The time required for the output to remain within a specified percentage of the final value after a disturbance.
- Overshoot
The extent to which a system exceeds its final steady-state value during a transient response.
- Error Constants
Factors used to evaluate the steady-state error in response to different types of inputs.
- Damping Ratio
A measure of how oscillations in a system decay over time; affects overshoot and settling behavior.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
