Fault Simulation
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
What is Fault Simulation?
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss fault simulation. Can anyone tell me what you think fault simulation is?

I think it's about testing circuits to see how they react to faults.

Exactly! Fault simulation applies specific fault models to circuit designs to simulate potential failures.

What kind of faults are we looking for?

Great question! We typically evaluate conditions like stuck-at faults or timing issues. These simulations help engineers catch issues before actual hardware testing.

So it’s cheaper than physical testing, right?

Yes! By using simulations, we can save time and costs associated with manufacturing physical prototypes. That's very important in our design process!

To summarize, fault simulation lets us virtually test how circuits behave under various failures, enhancing reliability before building physical versions.
Types of Fault Simulation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's discuss the two main types of fault simulation: Boolean Fault Simulation and Timing Fault Simulation. Has anyone heard of these?

I think I've heard about Boolean Fault Simulation, but I don’t know much about it.

Let's dive into it! Boolean Fault Simulation applies stuck-at fault models to check if a logic circuit can detect faults like being stuck at high or low.

What about timing fault simulation?

Good question! Timing Fault Simulation checks for delay faults, which are critical for ensuring signals propagate through circuits within the correct timing window.

Can you give us an example of a delay fault?

Sure! Imagine a flip-flop where the data doesn't change output fast enough when the input changes—this can cause a timing violation.

To wrap up, Boolean Fault Simulation looks for logic errors, while Timing Fault Simulation focuses on timing-related issues. Both are crucial for reliable circuit design.
Importance of Fault Simulation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Why do you think fault simulation is important in electronic design?

It helps find problems before we build anything!

Exactly! Early detection of faults saves time and money. Can anyone think of other benefits of fault simulation?

It must help improve the test coverage too, right?

That’s correct! Fault simulation allows engineers to analyze fault coverage, ensuring the design can handle a variety of faults.

So, it basically strengthens our designs?

Yes! By ensuring reliability through simulation, we can develop better electronic systems. Never forget: simulate to innovate!

To sum up, fault simulation is essential for early fault detection, improving test coverage, and enhancing overall design reliability.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses fault simulation, a crucial aspect of fault detection that allows engineers to assess the behavior of circuit designs under different fault conditions. It covers the types of fault simulation, including Boolean fault simulation and timing fault simulation, highlighting their significance in ensuring robust electronic designs.
Detailed
Fault Simulation
Fault simulation is a vital process in analyzing electronic circuit designs. It leverages fault models to evaluate how faults affect system behavior. The two primary types of fault simulation are: 1. Boolean Fault Simulation, which applies the stuck-at fault model to logic circuits to check for detectable faults, and 2. Timing Fault Simulation, designed to identify delay faults by analyzing the timing of signal propagation in circuits. Both methods are crucial for ensuring circuits can withstand real-world errors and operate correctly under potential fault conditions.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Fault Simulation
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Fault simulation involves applying fault models to a circuit design and running simulations to observe how the faults impact the system’s behavior. There are two primary types of fault simulation:
Detailed Explanation
Fault simulation is a critical process where engineers takes predefined fault models and apply them to a digital circuit design. The purpose is to understand how these faults affect the overall performance of the circuit. This means that engineers can predict possible failures and identify issues without needing to fabricate the physical device first. By running simulations, they can visualize the changes in behavior due to specific faults.
Examples & Analogies
Think of fault simulation like a virtual safety test for a car. Before making the car, the designers use computer simulations to see how the car responds in a crash test scenario. Similarly, in fault simulation, before finalizing a circuit design, engineers can see how it reacts under potential fault conditions.
Boolean Fault Simulation
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
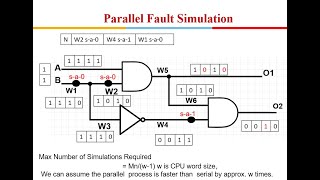
● Boolean Fault Simulation: This type of simulation applies the stuck-at fault model to logic circuits. It checks whether a fault, such as a stuck-at-1 or stuck-at-0 condition, is detectable with the given test vectors.
Detailed Explanation
Boolean Fault Simulation specifically focuses on digital logic circuits using the stuck-at fault model. A stuck-at-1 fault means that a wire in the circuit is permanently held high (1), while a stuck-at-0 fault means it's held low (0). The simulation checks whether these faults are detectable by the existing test cases (test vectors) that are used to test the circuit's functionality. Essentially, it checks if the circuit can recognize there's a problem if one of its signals doesn’t change as expected.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a light switch in your home that is supposed to toggle the light on and off. If the switch is stuck in the 'on' position, the light will always be bright, regardless of how many times you flip the switch. Boolean Fault Simulation is like testing whether all your light switches can still control the lights correctly after one switch gets stuck.
Timing Fault Simulation
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Timing Fault Simulation: This type of simulation is used to detect delay faults by simulating the timing of signals as they propagate through the circuit. Timing fault simulation tools can detect whether signals meet timing constraints and identify any violations.
Detailed Explanation
Timing Fault Simulation is crucial for identifying delay faults where signals take longer to travel through the circuit than anticipated. This delay can lead to timing violations, meaning that signals might not arrive at their destination on time. Through this simulation, engineers can examine the timing of each signal transition and determine if all timing requirements are met, ensuring the circuit functions correctly at the intended speeds.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a relay race where each runner must pass the baton to the next runner within a specific timeframe. If one runner is delayed, it could affect the whole team’s performance. Similarly, Timing Fault Simulation checks if signals in a circuit can pass through their 'batons' (connections) quickly enough to keep the whole system running smoothly.
Key Concepts
-
Fault Simulation: The testing process that applies fault models to predict circuit behavior under faults.
-
Boolean Fault Simulation: Checks for detectability of logic faults via stuck-at models.
-
Timing Fault Simulation: Detects delay faults by analyzing signal timing.
Examples & Applications
Example of a Stuck-At Fault: A logic gate that continuously outputs a high signal despite the input condition indicating otherwise.
Example of a Delay Fault: A flip-flop where the output does not change in response to input changes within the required time frame.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a circuit where faults stay, simulate to keep them at bay.
Stories
Once upon a time, engineers designed a circuit but faced issues because they didn't simulate. After learning about fault simulation and its types, they caught many faults, making their final product much more reliable.
Memory Tools
Remember 'STF' for types of Fault simulation: Stuck-at and Timing Fault Simulation.
Acronyms
Use the acronym 'BD' for Boolean and Delay to recall the major fault simulation types.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Fault Simulation
The process of applying fault models to test circuit designs and observe how faults impact system behavior.
- Boolean Fault Simulation
A type of fault simulation that uses the stuck-at fault model to check detectability of faults in logic circuits.
- Timing Fault Simulation
A fault simulation method focused on detecting delay faults by analyzing signal timing in circuits.
- StuckAt Fault
A common fault model where a logic gate or signal line is fixed at a high (1) or low (0) state, regardless of input.
- Delay Fault
A fault that occurs when the propagation delay of a signal exceeds the expected duration, leading to timing violations.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
