Understanding Sequential Circuits
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Sequential Circuits
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today's topic is Sequential Circuits. Can anyone tell me how these circuits differ from combinational circuits?

Sequential circuits depend on past states, while combinational circuits only depend on current inputs.

Exactly! Sequential circuits have memory elements, allowing them to store information over time. Can anyone give examples of sequential circuits?

Flip-flops and counters!

Great! Flip-flops help in storing bits, while counters can keep track of the number of occurrences. What makes these components crucial in digital systems?

They allow devices to perform tasks like counting and timing.

That's correct! These tasks are indispensable in most technological applications.
Understanding Memory in Sequential Circuits
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's explore why memory is essential in sequential circuits. Can someone explain the role of memory in these circuits?

Memory allows the circuit to remember past inputs and provide outputs accordingly.

Correct! This capability is what makes sequential circuits flexible for many applications. Can anyone think of instances where we heavily rely on this functionality?

Yes, in digital clocks, they need to keep track of time!

Excellent example! Digital clocks are indeed one use case. Another is in computer processors that need to remember states during operations.
Types of Sequential Circuits
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive into types of sequential circuits. What are the main types that we should be aware of?

There are flip-flops, counters, and finite state machines.

Good memory! Flip-flops store bits, counters measure events, and FSMs define states. What kind of applications might use FSMs?

Traffic light controllers!

Exactly! FSMs manage transitions between states, such as between red, green, and yellow lights.
Designing Sequential Circuits Using VHDL
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now we will look at how to design a sequential circuit using VHDL. Who can outline the steps involved in describing a D Flip-Flop?

We need to declare the entity, define ports, and then describe the architecture with a process that triggers on the clock edge!

Perfect! That’s the core approach. Would you like to see an example code for a D Flip-Flop in VHDL?

Yes, that would help a lot!

Alright, here’s a simple VHDL code snippet for a D Flip-Flop: (then presents the code). Remember, defining behavior is key!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section delves into the functionality and importance of sequential circuits, emphasizing their capacity to store information, making them ideal for applications such as counters and state machines. It outlines different types of sequential circuits and the fundamentals of designing them with VHDL and Verilog.
Detailed
Understanding Sequential Circuits
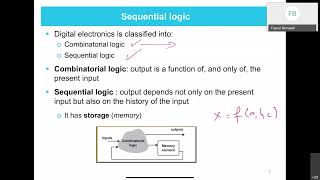
Sequential circuits are a vital component in digital systems, primarily because they have memory elements that allow their outputs to depend not only on the current inputs but also on previous states. This feature enables them to store data and maintain state information over time, which is essential for operations like counting, storing data, and managing states in various digital applications.
Key examples of sequential circuits include flip-flops, used for storage in registers; counters, which increment over time; and finite state machines (FSMs), critical for decision-making processes in control systems.
Types of Sequential Circuits
- Flip-flops: Devices like D Flip-flops, JK Flip-flops, and SR Flip-flops are commonly utilized to store binary data.
- Counters: These include binary and decade counters that count pulses based on clock signals.
- Registers: Temporary storage points for data in computational processes.
- Finite State Machines (FSMs): Complex logical systems that manage varying states based on defined inputs.
The design aspect of sequential circuits is typically done through hardware description languages (HDLs) such as VHDL and Verilog, allowing engineers to define intricate behaviors and states through coding.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Sequential Circuits
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Sequential circuits have memory elements, meaning that their outputs depend on both the current inputs and the past inputs (or states).
Detailed Explanation
Sequential circuits are unique in that they can store past information, which distinguishes them from combinational circuits that only rely on current inputs. This stored information is crucial in applications where the system needs to remember previous actions or states. For example, if you're keeping track of a game score, the score depends on both the current round's points and previous rounds' scores.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a sequential circuit like a diary. Just as you write down events that happen over time and can refer back to them later, a sequential circuit remembers the inputs it received in the past, affecting its current output.
Applications of Sequential Circuits
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
These circuits store information about previous events, which makes them suitable for applications like counters, registers, and state machines.
Detailed Explanation
Sequential circuits are used in various applications where remembering the past is essential. Counters use sequential circuits to keep track of the number of events (like how many times a button is pressed). Registers are storage locations used to hold data temporarily. State machines can change states based on both the current input and the state they were in previously, which is crucial for controlling systems like traffic lights or vending machines.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a counter as a turnstile at a concert. Each time someone passes through, the turnstile records this by increasing its count. It remembers how many people have entered, just like a sequential circuit remembers previous inputs.
Examples of Sequential Circuits
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Basic Examples of Sequential Circuits:
● Flip-flops (D flip-flop, JK flip-flop, SR flip-flop)
● Counters (Binary counters, Decade counters)
● Registers
● Finite State Machines (FSMs)
Detailed Explanation
Some common examples of sequential circuits include flip-flops, which are the basic building blocks for storing binary data. Counters can count up or down, and registers temporarily hold data during processing. Finite State Machines manage multiple states in applications like traffic signal control, where the state changes based on time and input conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a flip-flop like a light switch that stays on or off based on your last action. If you turn it on, it remembers to stay on until you turn it off, similar to how a flip-flop retains a binary value until it's changed.
Key Concepts
-
Memory Elements: Components that retain past input values for processing current outputs.
-
Circuits Examples: Essential types of sequential circuits such as flip-flops, counters, and FSMs.
Examples & Applications
A D Flip-Flop stores the value of input D during the clock's rising edge.
A binary counter increments its value with each clock pulse received.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a flip-flop’s warm embrace, past and now both hold their space.
Stories
Imagine a digital clock that can remember the last second and adjust accordingly. This is what flip-flops provide: a memory of time in circuits.
Memory Tools
FCCA - Flip-flops, Counters, Code . These are key types of sequential circuits.
Acronyms
SCM - Sequential, Current, Memory help remember the nature of these circuits.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Sequential Circuit
A type of digital circuit whose output depends on both current inputs and past states.
- FlipFlop
A memory element that can store one bit of data.
- Counter
A sequential circuit that counts pulses or events.
- Finite State Machine (FSM)
A model that transitions between a finite number of states based on input.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
