Lagrangians and Euler Descriptions
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Fluid Descriptions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

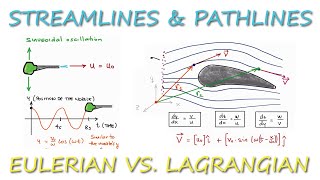
Today, we begin our discussion of fluid mechanics by examining the Lagrangian and Eulerian descriptions. Can anyone tell me what they think the main focus of the Lagrangian perspective might be?

Is it about following individual fluid particles as they move?

Exactly! The Lagrangian description tracks the motion of every fluid particle, examining their trajectories. Now, how does that differ from the Eulerian perspective?

It looks at specific points in space instead, right? Rather than individual particles?

Correct! In Eulerian, we analyze the velocity and pressure at fixed locations in space. This distinction is crucial in fluid mechanics.

To help remember, consider 'L' for Lagrangian as 'Location of individual particles' while 'E' for Eulerian as 'Everywhere in space.'

Got it! L for Locating particles and E for observing the entire field!

Well done! This foundational understanding paves the way for more complex discussions on fluid dynamics.
Applications of Lagrangian and Eulerian Descriptions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about practical applications of both descriptions. Can someone give an example where the Lagrangian perspective might be more beneficial?

Studying the motion of pollutants in a river? Tracking them would be crucial to see their effects.

Exactly! The Lagrangian approach is excellent for understanding the trajectory of particles, like pollutants. How about an example for Eulerian?

Maybe when analyzing weather patterns? Wind direction at certain locations?

Very good! The Eulerian framework allows us to analyze flow patterns in a broad area, useful in meteorology.

Remember, 'Lagrangian tracks' and 'Eulerian fields' can help you recall which method to apply in a given scenario.
Comparative Study of Lagrangian and Eulerian
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive deeper comparing both methods. What is a primary advantage of using the Lagrangian approach?

It allows for understanding particle-specific behaviors, like vortices.

Right! Following individual particles can provide insights into localized effects. And what about the Eulerian method?

It provides a comprehensive view of the field, allowing for large-scale flow analyses.

Exactly! Both perspectives are crucial, and knowing when to apply each one is essential for fluid mechanics.

As a memory aid, think; 'Lagrangian is granular, Eulerian is broad.'

That’s helpful! I can visualize the focus of each method now.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section provides an overview of the Lagrangian and Eulerian frameworks for analyzing fluid motion. It emphasizes how these two concepts model fluid behavior differently—Lagrangian focusing on individual particles and Eulerian focusing on specific points in space.
Detailed
Lagrangians and Euler Descriptions
This section discusses the two primary descriptions used in fluid mechanics: Lagrangian and Eulerian. Both frameworks provide distinct perspectives on fluid behavior and motion.
Lagrangian Description
- The Lagrangian approach focuses on individual fluid particles, tracking their motion through space as they move from one location to another over time. Each particle's position is expressed as a function of time, and the model captures the trajectory of each fluid element.
- This method is particularly useful for analyzing problems where the history of individual particles is crucial, such as in studying vortex formations, trajectories, and flow patterns.
Eulerian Description
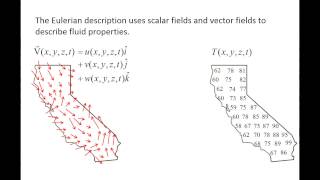
- The Eulerian approach, in contrast, observes fluid motion at fixed points in space. Here, the interest lies in the characteristics of the flow (like velocity and pressure) at specific locations rather than following individual fluid particles. The velocity field can be described as functions of spatial coordinates and time.
- This framework is especially effective for examining large-scale phenomena, such as flow rates and pressure distributions, where the behavior of the fluid as a whole is more relevant than tracking specific particles.
Key Differences and Applications
- One of the significant differences between the Lagrangian and Eulerian descriptions is the perspective: Lagrangian focuses on particles while Eulerian on fields.
- Both methods are essential in fluid mechanics; for example, Lagrangian is used in simulating particle dynamics while Eulerian is preferred for analyzing flow fields in computational fluid dynamics (CFD).
In summary, understanding both descriptions is critical for fluid mechanics, as they provide complementary insights into fluid behavior.
Youtube Videos
![Lagrangian Description and Eulerian Description [Fluid Mechanics]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/27m1I-DlOik/mqdefault.jpg)






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Lagrangian and Eulerian Descriptions
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Let us come back to our basic fluid mechanics okay, so as in the last class I talked about 2 types of descriptions; one is Eulerian frame of descriptions, another is Lagrangian frame of description.
Detailed Explanation
In fluid mechanics, there are two primary ways to describe fluid motion: the Eulerian approach and the Lagrangian approach. The Eulerian frame focuses on specific locations in the fluid field and observes how fluid properties change at those points over time. In contrast, the Lagrangian frame follows individual fluid particles as they move through the flow field, tracking their paths and experiences throughout the motion. This distinction is vital for understanding how to model and analyze fluid behavior in different scenarios.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine watching a river flow from a fixed point on the bank (Eulerian perspective) versus floating down the river in a canoe, noticing all the different currents and changes in flow around you (Lagrangian perspective). The former allows you to see the overall flow at one point in time, while the latter gives you a personal journey with continuous changes.
Fluid Elements and Motion Types
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
I have the fluid element which is you know in any of fluid mechanics book. They talk about the fluid element which is representing a certain space of the fluid particles which is much larger scale than the molecules levels or it is not that bigger scale to represent the flow process.
Detailed Explanation
Fluid elements represent larger groups of fluid particles, which is essential for studying their dynamics. A fluid element can undergo different types of motion, including translation (moving from one place to another), rotation (spinning about an axis), and deformation (changing its shape). Understanding these motions helps predict how a fluid will behave under different conditions. For instance, translation depends on the velocity of the fluid at the specific moment, while rotation is related to variations in velocity across the fluid, impacting how it flows.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a smoothie in a blender. The fruit chunks (fluid elements) can spin (rotate), move around (translate), or get squished (deform) as the blender mixes everything together. Observing these motions helps us understand how well the ingredients blend.
Displacement and Velocity Components
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The displacement is equal to velocity into ∆t. So, it is very easy concept that how much of displacement will be there, how much of translations will be there.
Detailed Explanation
Displacement in fluid mechanics is calculated using the simple formula: displacement equals velocity multiplied by the time interval (∆t). This means if we know the velocity of a fluid element and the time it travels, we can determine how far it moves. This principle is foundational in analyzing fluid flows, as it allows engineers to predict how fluid positions change over time.
Examples & Analogies
If you throw a ball with a certain speed, the distance it travels depends on how long the ball is in the air. If you can measure the speed (velocity) and the time it’s flying (∆t), you can easily calculate how far it goes. The same principle applies to fluid particles in motion!
Rate of Rotation and Angular Velocity
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Now, coming to the rate of rotations, which is called angular velocity. See if I take it this is the fluid element okay, it will have a this the velocity variations that means, if this is the u velocity is here at this point, you will have a v velocity here at this point.
Detailed Explanation
Angular velocity in fluid mechanics measures how quickly a fluid particle is rotating about an axis. This is critical because even when fluid elements are translating, they may also be rotating due to differences in velocity across the fluid. The rotational behavior can be analyzed using variations in the u and v velocities within the flow field, helping engineers understand how fluids behave in rotating systems or around obstacles.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a merry-go-round at a playground. Children sitting at the edge move quickly in a circular path (high angular velocity) as they spin around. The difference in speed between children closer to the center and those at the edges relates to how we might analyze fluid motion and rotation.
Key Concepts
-
Lagrangian Method: Focuses on the motion of individual fluid particles.
-
Eulerian Method: Examines the fluid motion at fixed points in space.
-
Velocity Field: A mapping of fluid velocities at different locations.
-
Trajectories: The route taken by fluid particles in motion.
-
Vortex: Circular motion patterns in fluids.
Examples & Applications
In environmental engineering, the Lagrangian approach is applied to model pollutant dispersion in water bodies, tracking the flow over time.
In meteorology, the Eulerian method is indispensable for understanding wind patterns and precipitation, providing insights into large-scale atmospheric phenomena.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Particles in the flow, Lagrangian you will know; Observing just the place, Eulerian sets the pace.
Stories
Imagine you're a river watching fish swim by—Lagrangian tracks each fish, while Eulerian sees the whole river's rush.
Memory Tools
Remember 'L' for Lonesome particles (Lagrangian) and 'E' for Everything in space (Eulerian).
Acronyms
LE for Learning
for Lagrangian tracking particles
for Eulerian observing fields.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Lagrangian Description
A framework in fluid mechanics that follows individual particles as they move through space.
- Eulerian Description
A method that observes fluid properties at fixed points in space instead of tracking individual particles.
- Velocity Field
A representation of the velocity of fluid at various points in space.
- Trajectories
The paths followed by moving fluid particles.
- Vortex
A flow pattern in fluids characterized by the movement of fluid in a circular motion.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
