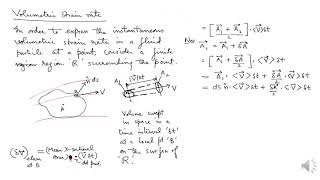
Volumetric Strain Rate
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Volumetric Strain Rate
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start with the basic definition of volumetric strain rate. Can anyone tell me what volumetric strain rate means?

Is it how much a fluid's volume changes in relation to its original volume?

Exactly! Volumetric strain rate is the change in volume per unit volume. It is crucial in understanding how fluids behave under various velocity gradients. Now, how do you think this relates to fluid motion?

It probably relates to how particles translate or rotate within the fluid.

Great observation! Translational movement and rotational motion both affect how fluid volumes change. Let’s dive deeper into those movements.
Translations and Rotations in Fluid Motion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

When we discuss fluid motion, we talk about translations and rotations. Can anyone give me an example of each?

Translations would be like a water jet moving forward, while rotations might be the flow around a vortex.

Spot on! In translational movement, particles travel from point A to point B, affecting distance and volume. Can anyone explain how rotations contribute to strain?

I think it's about how the velocity differences among particles cause them to twist or change angles.

Exactly! The differences in velocity create angular rotations, leading to shear and volumetric strains in the fluid.
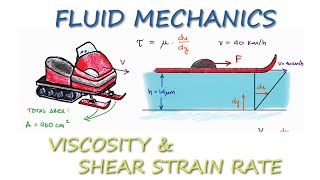
Linear and Shear Strain Rates
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know about translations and rotations, let's discuss linear and shear strains. How do we define linear strain rate?

It's the rate of change of length per unit length.

Correct! And shear strain rate is related to how angles between two lines change when shearing occurs. Can anyone illustrate this with an example?

When fluid flows from a larger pipe to a smaller one, parts of the fluid get stretched, and the angles change.

Exactly! Such changes lead to both linear and shear strains, crucial in practical applications. Let's summarize.
Vorticity and its Relation to Strain
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, we’ll explore the concept of vorticity. How would you define vorticity in the context of fluid mechanics?

It measures the rotation of fluid particles, right? Like how fast they’re spinning?

Yes! Vorticity relates directly to rotational strain within fluids. If there’s no rotation, what can we say about the vorticity?

It would be zero, indicating no turbulence or spinning.

Correct! Relating strain with motion helps us understand fluid dynamics better. Let's recap all that we've discussed.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section elaborates on volumetric strain rates, emphasizing the effects of fluid motions such as translations and rotations on deformation. The results establish a foundation for understanding shear rates and their applications in fluid mechanics, particularly in relation to vortices and fluid dynamics.
Detailed
Volumetric Strain Rate
Volumetric strain rate is a vital concept in fluid mechanics that refers to the rate of change of volume per unit volume in a fluid. It arises from fluid motion and deformation during flow, influenced by the velocity gradients within the fluid. This section begins with a foundational review of fluid elements, detailing how fluid flows involve translations and rotations, leading to various strain rates.
Understanding volumetric strain is crucial when analyzing incompressible flows where density remains constant, as it relates directly to the mass conservation equations. The section also introduces key definitions—linear strain rate, shear strain rate, and volumetric strain rate—specifically detailing methods to derive these rates from velocity components and the mathematical relationships involved.
Additionally, the concept of vorticity is introduced, measuring the directional rotation of fluid particles, and linking it to both volumetric and shear strain rates. The collapse of fluid columns and the shear strain development in pipes of varying diameters are examined as practical examples. This theoretical knowledge lays the groundwork for advanced study in fluid dynamics, particularly in applications involving turbulence and vortex formations.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Volumetric Strain Rate
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
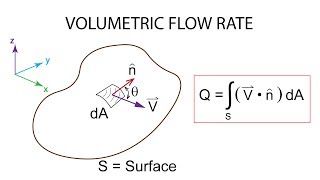
Volumetric strain rate is a measure of the change in volume per unit volume of fluid due to deformation. It is represented mathematically as:
\[ V_{rate} = \frac{1}{V} \frac{dV}{dt} \]\n
where \( V \) is the volume and \( dV \) is the change in volume over time \( dt \).
Detailed Explanation
Volumetric strain rate provides insight into how a fluid's volume changes under different influences, like pressure or temperature. It quantifies how much the volume of a fluid changes within a given time frame relative to its original volume. Understanding volumetric strain rates is crucial in fields like civil engineering and fluid mechanics since it helps predict material behavior under different loading conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you have a balloon. When you blow air into it, the volume of the balloon increases. The rate at which the size of the balloon increases in relation to its original size is analogous to volumetric strain rate. If you blew air faster, the volumetric strain rate would be higher, indicating a quicker change in volume.
Volumetric Strain Rate in Incompressible Flow
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In incompressible flow, the volumetric strain rate approaches zero, meaning the density of the fluid does not change as it flows. This condition holds true for most liquids where the volume remains consistent despite changes in pressure.
Detailed Explanation
For incompressible fluids, like water, we assume that its density stays constant regardless of the flow conditions. The implication is that as the fluid moves through a pipeline or any other medium, its volume does not expand or contract. If you consider a closed container with water, even if you apply pressure or increase velocity, the volume inside remains constant because the liquid cannot be compressed.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a water bottle. No matter how much you squeeze it, the water inside remains at the same volume because liquids are incompressible. Thus, in fluid flow scenarios, we treat water as having a volumetric strain rate of zero, meaning its density and volume do not change as it flows.
Mathematical Representation of Volumetric Strain Rate
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
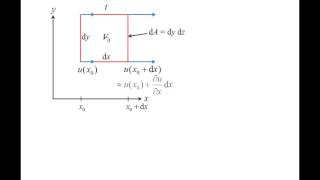
Mathematically, the volumetric strain rate can be expressed in Cartesian coordinates as follows:
\[ V_{rate} = \frac{\partial u}{\partial x} + \frac{\partial v}{\partial y} + \frac{\partial w}{\partial z} \]
where \( u, v, w \) are the velocity components in the x, y, and z directions respectively.
Detailed Explanation
This mathematical expression reflects how the changes in velocity in each spatial direction contribute to the overall volumetric strain rate. Each component (u, v, and w) signifies an aspect of how the fluid moves through space. If any of these components changes rapidly, it can suggest that the fluid is experiencing a significant volumetric change.
Examples & Analogies
Picture a river. The velocity increases when the river narrows due to terrain changes. The mathematical representation reflects how shifts in speed (velocity components) directly impact the water's overall volume as it flows, revealing potential changes in pressure, turbulence, or strain in the water mass.
Implications of Volumetric Strain Rate
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Understanding the volumetric strain rate is crucial for analyzing fluid systems, particularly when dealing with processes involving compressibility and expansion, such as gas flows and dynamic fluid interactions.
Detailed Explanation
The volumetric strain rate plays an essential role in engineering applications, particularly in understanding how different fluid behaviors affect system performance. High strain rates typically indicate rapid changes in flow conditions and can lead to turbulence or instability in designs. Engineers must consider these factors when designing systems, such as pipelines, chemical reactors, and hydraulic systems.
Examples & Analogies
Consider an automobile engine. The air and fuel mixture expand rapidly when ignited, creating pressure that forces the pistons down. Understanding the volumetric strain rate in this scenario helps engineers design engines that can withstand the immense forces generated during combustion.
Key Concepts
-
Volumetric Strain Rate: Change in volume per unit volume in fluid flow.
-
Linear Strain Rate: Rate of change of length per unit length in a fluid particle.
-
Shear Strain Rate: Rate of change in angle between two lines within fluids.
-
Vorticity: A measure of the rotation of fluid particles.
Examples & Applications
Example of volumetric strain includes the stretching of fluid between two points with different velocities.
Flow through a pipe changing diameter demonstrates both shear and volumetric strain effects.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When fluids flow, their volumes must grow, or sometimes shrink, when they go.
Stories
Imagine a river flowing. As it narrows between cliffs, the water speeds up, leading to stretch and swirl—that’s volumetric strain at work!
Memory Tools
VSL: Remember Volumetric = Stretching, Linear = Length, Shear = Slicing (angles).
Acronyms
VLS - Volumetric, Linear, Shear - these are the types of strain in fluids.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Volumetric Strain Rate
The rate of change in volume per unit volume of a fluid during flow.
- Linear Strain Rate
The rate of increase in length per unit length, indicating elongation or compression.
- Shear Strain Rate
The rate of change of the angle between two lines, indicative of angular deformation in fluids.
- Vorticity
A measure of the local rotation of fluid elements, related to angular velocity.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
