Vorticity and Fluid Rotation
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Vorticity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we will start with the concept of vorticity. Vorticity measures the rotation of fluid particles. Can anyone tell me why it is important in fluid mechanics?

Isn't vorticity important for understanding airflow in cyclones and how storms develop?

Exactly! Vorticity helps us analyze the rotational behavior of fluids, especially in large-scale phenomena like cyclones. Remember, we can visualize vorticity as the 'twist' of the fluid.

How do we measure vorticity in real-life situations?

Great question! We can use Particle Image Velocimetry or PIV, which tracks the movement of particles in a fluid to calculate velocity fields and thus vorticity.

Does that mean we can visualize how cyclones form?

Yes! And this leads into our next topic on the practical applications of understanding fluid rotation. Let's dive deeper!
Types of Fluid Descriptions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's examine the two main approaches to describe fluid motion: Eulerian and Lagrangian. Who can summarize the difference?

Eulerian focuses on specific locations in the flow field, while Lagrangian follows individual fluid particles over time.

Correct! Eulerian is about 'where' the fluid is at a point, while Lagrangian focuses on 'what' happens to a particle as it moves. Can anyone think of an advantage of each method?

Eulerian is great for analyzing flows with a fixed reference point, while Lagrangian can provide detailed trajectory information of particles.

Exactly! Each method has its strengths depending on the context of fluid flow we are examining.
Rotational Motion and Angular Velocity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's now dive into the concept of rotational motion. Angular velocity is essential in describing how fluid elements rotate. Can anyone explain how it’s related to velocity fields?

Angular velocity is related to the gradient of the velocity components, right?

That's correct! The relative velocity differences across fluid elements lead to rotations within the fluid.

So, we use the curl of the velocity vector to find vorticity?

Yes! Vorticity is defined mathematically as the curl of the velocity field. It encapsulates how much and in which direction the fluid is rotating.
Strain Rates and Deformations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

We’ve talked about rotation, but what about deformation? Linear strain rates describe how the shape of fluid elements changes. What do you think causes these deformations?

Differences in velocity among fluid particles, right?

Exactly! When fluid particles with different velocities interact, it causes stretching or compression, which we measure as strain rates.

Are shear rates related to this as well?

Yes! Shear rates measure angular changes in shape and are equally significant when analyzing flow behavior.
Applications of Vorticity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s discuss the applications of our knowledge of vorticity. How might this knowledge be critical for predicting weather patterns?

Meteorologists can use vorticity to predict storm formations and forecasts!

Exactly! This principle is used in weather models to simulate atmospheric dynamics. Can anyone think of other fields where understanding fluid rotation is important?

Perhaps in civil engineering, where water flow impacts structural integrity?

Absolutely! Fluid dynamics is key in numerous engineering applications, highlighting the importance of vorticity in both natural and built environments.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Vorticity is a critical parameter that describes the rotation of fluid elements, influential in understanding fluid flow, turbulence, and vortex formation. The section discusses the fundamental principles of fluid rotation, experimental techniques used to measure vorticity, and the mathematical representations of these concepts.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
In this section, we explore the concept of vorticity, a measure of a fluid's rotation at a point. Vorticity is essential in fluid mechanics, helping to describe how fluid elements spin as they advect and interact. Understanding vorticity is crucial for analyzing phenomena like cyclones, where large-scale vortices form in the atmosphere, as exemplified by recent super cyclones in the Bay of Bengal.
Vorticity can be mathematically expressed through the curl of the velocity field, which quantifies the local rotation of fluid elements. The discussion moves to the different descriptions of fluid motion, particularly Eulerian and Lagrangian approaches, which offer varying perspectives on how fluid particles move and deform.
Experimental methodologies such as Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) are highlighted for measuring vorticity in real-time, showcasing how advancements in technology allow for detailed analysis of flow patterns and turbulence. Specific attention is given to the rotational motion of fluid elements and the relationship between velocity fields and angular rotations, elaborated through mathematical derivations.
The concepts of linear strain rates and shear rates are introduced as tools to analyze deformations within the fluid, ultimately linking these ideas back to vorticity and rotation. Understanding the dynamics of vorticity and fluid rotation not only aids in fundamental fluid mechanics but also has far-reaching implications for engineering, meteorology, and environmental science.
Youtube Videos
![What you need to know about Vorticity [Fluid Mechanics]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/Xu5IT4bL-v8/mqdefault.jpg)




![How To Calculate A Vorticity [Fluid Mechanics]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/wRQZz6VTWlY/mqdefault.jpg)

![Vorticity Explained Conceptually [Aero Fundamentals #67]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/X-hgPslzTcc/mqdefault.jpg)
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Fluid Elements
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Let us come back to our basic fluid mechanics okay, so as in the last class I talked about 2 types of descriptions; one is Eulerian frame of descriptions, another is Lagrangian frame of description... fluid balls that means, there will be a series of balls will be there, since there is a velocity gradients are there, so these balls will try to move these directions, these balls have try to move to these directions.
Detailed Explanation
In fluid mechanics, we often analyze fluids by considering them as small elements or 'balls'. These fluid elements can be thought of as collections of many fluid particles, allowing us to study how they behave as they move and interact with their surroundings. There are two primary ways to describe fluid motion: the Eulerian method, which focuses on specific locations in space (like a fixed observation point), and the Lagrangian method, which tracks individual particles as they move through the fluid. In this context, we think about how these fluid 'balls' respond to changes in velocity. When there are gradients in velocity, the balls may experience different rates of movement, which can lead to rotations and deformations within the fluid. The difference in velocity between various parts of the fluid causes these changes in motion, and this is crucial to understanding vorticity and rotation.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are watching a group of kids playing with a beach ball at a park. Each kid is moving in a different direction and some are faster than others. If we track one kid (Lagrangian perspective), we notice they sometimes have to catch up with the ball or move aside to avoid collisions. If we instead focus on a fixed spot in the park (Eulerian perspective), we observe how the ball moves through that space, sometimes spinning as it rolls. Just like those kids’ movements cause the ball to rotate and change direction, the velocity differences within a fluid cause it to rotate and form vortices.
Rate of Rotations and Angular Velocity
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Now, coming to the rate of rotations, which is called angular velocity okay, what could be the angular velocity of the fluid point... it will have a rotations along the z direction; along the z directions perpendicular to this surface.
Detailed Explanation
Angular velocity refers to how quickly a fluid element is rotating about a central point. When fluid particles within an element move at different velocities, the result is a rotational motion. For instance, if one side of the fluid element moves faster than the other side, this can cause the element to start rotating around an axis. In our analysis, we can calculate angular velocity by carefully examining how the velocity gradients affect each part of the fluid. The combination of velocities at different points provides a detailed picture of the angular motion and is essential for understanding how vortices form in fluids.
Examples & Analogies
Think about spinning a pizza dough in the air. As you stretch it out, different parts of the dough move at different speeds and directions – the outer edge moves faster than the center, which creates a rotational motion. This is similar to how fluid elements rotate when the particles at one end are moving faster than those at the other. The angular velocity is akin to how quickly your hands need to rotate to keep the dough balanced and not let it fall.
Shear Strain Rate and its Importance
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Now, coming to the very simple thing is called linear strain rate that means, what is the strain rate; rate of increase the length per unit length... whether the fluid is incompressible that means, the density does not change within the fluid flow domain.
Detailed Explanation
The linear strain rate represents how much a fluid element stretches or compresses when subjected to stress. In fluid mechanics, it is important to understand how these deformations occur over time, particularly in relation to the velocity of the fluid. When fluid flows through pipes or around objects, variations in velocity cause certain parts of the fluid to stretch or compress more than others. For instance, an incompressible fluid maintains a constant volume, meaning any change in shape leads to other dimensions adjusting to compensate. This interplay between strain rate and velocity is critical for predicting fluid behavior in various applications.
Examples & Analogies
A good analogy is a rubber band. When you pull on it (applying stress), it stretches and its length increases. The rate at which it stretches compared to its original size gives you the strain rate. Just like the rubber band, when fluid passes through narrower pathways, it experiences strain. If you think about squeezing the rubber band to make it smaller in diameter, that reflects how fluid elements behave as they pass through constrictions in their environment. They have to adapt to the spaces they move through, leading to stretching or compressing.
Understanding Vorticity
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
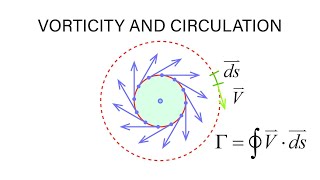
So, let us look at another component is called the vorticity or the rotationality, when you talk about a vorticity vectors, the basically we are representing as a vorticity vectors which actually the measures of rotations of a fluid particle...
Detailed Explanation
Vorticity is a vector quantity that describes the local spinning motion of a fluid at a point. It is mathematically defined as the curl of the velocity vector. Essentially, vorticity quantifies how much rotation is occurring within a tiny fluid element due to the various velocities acting at different points within the element. A high vorticity value indicates a strong rotational motion, and areas with significant vorticity are often where turbulence and complex fluid behaviors occur. Understanding vorticity is crucial for engineers and scientists as it helps predict how fluids behave in natural systems and engineering applications.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a whirlpool in a river. The water at the center spins rapidly while the outer edges flow outwards, creating a contrast in velocities. The whirlpool's ability to draw in surrounding water and create that vortex motion is a visual representation of high vorticity in action. Just as you can see the spinning motion of water, vorticity helps us understand where and how turbulence develops in various fluid flows.
Key Concepts
-
Vorticity: Defines the rotational characteristics of fluid flow and is vital for understanding many fluid dynamics scenarios.
-
Angular Velocity: Represents the speed of rotation and is closely tied to the concept of vorticity.
-
Eulerian vs. Lagrangian: Two different perspectives in fluid mechanics; one focuses on spatial properties while the other focuses on individual particle trajectories.
-
Linear Strain Rate: Measures the deformation of fluid elements due to velocity differences among them.
-
Shear Strain Rate: Describes the angular deformations that occur in a fluid, critical for analyzing flow behavior.
Examples & Applications
Cyclonic storms serve as practical examples of where understanding vorticity is crucial for weather prediction.
Engineering challenges such as calculating fluid stress in pipelines utilize vorticity and strain rates for design safety.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Vorticity twists and turns, in fluid flow it surely learns.
Stories
Imagine a dancer twirling in a stream of water; their spins represent the vorticity as they interact with the flows around them.
Memory Tools
E for Eulerian, L for Lagrangian - Remember both perspectives to understand fluid dynamics.
Acronyms
V.A.S. for Vorticity, Angular velocity, Strain rate - key concepts in fluid rotation.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Vorticity
A measure of the rotation of fluid particles in a flow field, represented mathematically as the curl of the velocity field.
- Angular Velocity
The rate of rotation of a fluid element, typically expressed in radians per unit time.
- Eulerian Description
A framework for analyzing fluid flow focused on specific locations within the fluid domain.
- Lagrangian Description
A framework for analyzing fluid flow by following individual fluid particles as they move through space.
- Strain Rate
A measure of the rate of deformation of a fluid element, relating to how velocities change within it.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
