Changes During Germination
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Water Absorption
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing how seeds begin to germinate. The first crucial step is water absorption through a small opening called the micropyle. Can anyone tell me what the micropyle does?

It allows water to enter the seed!

Yes, that's correct! Water activates enzymes within the seed. Think of it as waking up the seed after its long sleep. How do you all think the seed feels when it gets its first drink of water?

Maybe it feels refreshed and ready to grow!

Great analogy! Remember the phrase: 'Water wakes the seeds!' This will help you recall the importance of water in germination. Let's move on to what happens next.
Enzyme Activity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Once the seed absorbs water and wakes up, what do you think happens next?

The seed starts to grow?

Not quite just yet! First, enzymes start to convert the stored food into a form the embryo can use. Can anyone name some of the nutrients that might be involved?

Like carbohydrates and proteins?

Exactly! These nutrients provide energy for growth. Remember the acronym FENC – Food Enzymes Nurture Growth. Now, let’s talk about how the embryo starts to grow.
Radicle and Plumule Emergence
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Once the food is converted, the embryo starts growing. Which part do you think comes out first, the radicle or the plumule?

The radicle, because roots are important for stability!

That’s correct! The radicle emerges first to form the root. Then, soon after, the plumule appears and grows into the shoot. Here’s a funny way to remember: 'Roots first to explore, then shoots up for more!' When we think about plants, we want to remember which direction they grow!
Breaking of Seed Coat
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s discuss what happens when the radicle and plumule grow large enough to break the seed coat. Why do you think this is an important step?

Because the plant needs to get sunlight and air to survive!

Exactly! The seed coat protects the embryo, but once it’s time, it must break for the young plant to access air and sunlight. Remember: 'Out with the coat, in with the light!' Let’s summarize today’s session.
Recap of Changes During Germination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Great job today, everyone! Can someone recap the main changes during germination?

First, the seed absorbs water, then enzymes convert food, and the radicle and plumule grow out before the seed coat breaks!

Perfect! You remembered everything! Now, always keep in mind that germination is an essential part of a plant’s lifecycle.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
During germination, seeds undergo significant changes, including the absorption of water through the micropyle, enzymatic conversion of stored food into usable forms, and the emergence of the radicle and plumule as the seedling grows. The seed coat breaks to allow the seedling to emerge.
Detailed
Changes During Germination
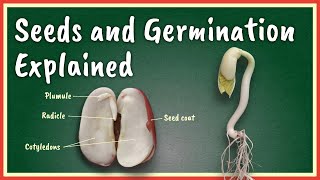
Germination is a pivotal process wherein a dormant seed undergoes a transformation to become a seedling. This section illustrates the significant changes that occur during this vital phase:
- Water Absorption: The process kicks off as the seed absorbs water through its micropyle, a small pore that plays a crucial role in hydration.
- Enzyme Activity: Once sufficiently hydrated, enzymes are activated to break down stored food materials in the seed into soluble forms, which are essential for nourishing the growing embryo.
- Embryo Development: As the embryo grows, the radicle (root) emerges first, establishing the foundation for the plant. Following this, the plumule (shoot) appears, which will eventually form the upper structure of the plant.
- Breaking of the Seed Coat: Finally, as the seedling expands, the seed coat breaks apart, allowing the young plant to grow free and initiate its life as an independent organism.
These changes are fundamental not only for the development of individual plants but also for agricultural practices and biodiversity.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Absorption of Water
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Seed absorbs water through micropyle
Detailed Explanation
The first step in germination is when the seed absorbs water through a small opening called the micropyle. This is essential as water activates enzymes and begins the germination process.
Examples & Analogies
Think of water as the fuel needed to start a car. Just like a car needs fuel to get going, seeds need water to activate their growth processes.
Conversion of Stored Food
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Enzymes convert stored food into soluble form
Detailed Explanation
Once water is absorbed, enzymes in the seed begin to break down stored food (like starch) into soluble forms. This transformation makes nutrients available to the growing embryo.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine preparing for a trip. You pack food that needs to be cooked. Just as you must cook the food to make it tasty and digestible, the seed must convert its stored food into usable forms for the embryo.
Embryo Growth
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Embryo grows:
○ Radicle emerges first → forms root
○ Plumule appears later → forms shoot
Detailed Explanation
As the seed continues to take in water and nutrients, the embryo starts to grow. The first part to emerge is the radicle, which will develop into the root of the plant. After the radicle, the plumule emerges, which will grow into the shoot.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a seed like a baby that first learns to crawl before it learns to walk. The radicle is like the baby's hands that help it move, while the plumule represents its legs, which will help it stand up tall.
Breaking of Seed Coat
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Seed coat breaks as the seedling emerges
Detailed Explanation
As the embryo continues to grow, the pressure from its development causes the seed coat to break open. This allows the seedling to emerge from the soil and start its life as a plant.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a chick breaking out of its eggshell. The chick pushes against the shell from inside until it finally breaks free. Similarly, the seedling pushes against the seed coat to begin its journey into the world.
Key Concepts
-
Water Absorption: Seeds absorb water through the micropyle to initiate germination.
-
Enzyme Activation: Enzymes convert stored nutrients into usable forms for the growing embryo.
-
Radicle Emergence: The radicle emerges first to develop the root of the plant.
-
Plumule Growth: The plumule appears after the radicle and develops into the shoot.
-
Breaking of Seed Coat: The seed coat breaks to allow the seedling to grow and thrive.
Examples & Applications
In bean seeds, the cotyledons rise above the soil during germination.
In maize seeds, the cotyledons remain below the soil as the radicle and plumule emerge.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Seeds need water, then enzymes start, radicle out first, then plumule takes part.
Stories
Once upon a time, a tiny seed was asleep underground. It dreamed of the sun and the sky. One day, it felt a warm splash of water through its micropyle, waking it up. It sent out its roots first to hold on tight, followed by a shoot that broke free into the sunlight.
Memory Tools
W.E.R.P - Water, Enzymes, Radicle, Plumule – the order of changes during germination.
Acronyms
G.E.R.M - Growth, Enzymes, Radicle, Micropyle – key aspects of germination.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Germination
The process by which a seed develops into a seedling.
- Radicle
The part of the embryo that will develop into the root.
- Plumule
The part of the embryo that will develop into the shoot.
- Micropyle
A small opening in the seed coat that allows water and air to enter.
- Enzymes
Proteins that facilitate biochemical reactions, such as breaking down stored food.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
