Introduction
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
What is a Seed?
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning, everyone! Today we will dive into the fascinating world of seeds. Can anyone tell me what a seed is?

Isn't a seed just what we plant to grow a new plant?

Exactly! A seed is the mature ovule that forms after fertilization. It contains the embryo that grows into a new plant. Think of it like the starter pack for new life. What do you think its role might be in nature?

It must help plants reproduce and spread out!

So, it’s like a way for plants to ensure more plants are grown?

Right! Seeds ensure the continuity of life by becoming new plants and play a vital role in the dispersal of plants.
Function of Seeds in the Ecosystem
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about why seeds are so important in ecosystems. Why do you think dispersal is essential?

Maybe it helps plants reach different environments to survive?

Yes! And it could help them avoid competing too much for resources like sunlight and water.

Exactly, that's spot on! Seeds help plants grow over a wide area, ensuring they can thrive in various conditions and maintain biodiversity.

So, seeds are crucial not only for individual species but for the entire ecosystem?

Absolutely! That’s why their study is vital in biology, as it connects to the survival and evolution of plant life.
Importance of Seeds
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s summarize the significance of seeds. Why are they critical for agriculture?

Seeds are how we grow our crops!

Exactly! Crops arise from seeds, which are fundamental for sustainable food production. Can anyone think of other ways seeds impact agriculture?

I think seeds can help in crop rotation and maintaining soil health!

And they’re vital for creating new varieties of plants!

Perfect! Seeds are intrinsically valuable, being crucial for food security and ecological balance. Without seeds, there would not be new plants, and that would disrupt entire ecosystems.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section introduces seeds as matured ovules formed after fertilization, highlighting their role in ensuring the continuity of life and the dispersal of plants. The biological significance of seeds as sources for new plants is emphasized.
Detailed
Introduction to Seeds
A seed constitutes the mature ovule formed post-fertilization, encapsulating the embryo that will develop into a new plant. The formation of seeds is critical not only for the continuation of life cycles in plant species but also plays a significant role in their dispersal across various environments. This capacity for dissemination ensures that plants can occupy new niches and adapt to changing conditions, thereby sustaining ecological balance and biodiversity.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of a Seed
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
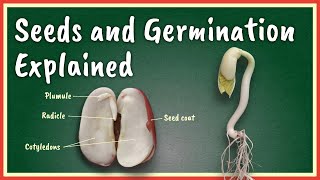
A seed is the mature ovule formed after fertilization. It contains the embryo which grows into a new plant.
Detailed Explanation
A seed is the result of the fertilization process, where the male gamete from pollen unites with the female gamete in the ovule. When this fertilization occurs, a mature ovule develops into a seed, which is a vital part of the plant's life cycle. Inside the seed, there is an embryo, which is an undeveloped plant that will grow into a new plant when conditions are favorable.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a seed as a baby in a womb; it has all the necessary information to grow into a fully developed person, just like a seed has what it needs to become a mature plant.
Role of Seeds in Plant Life
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Seed formation ensures continuity of life and helps in the dispersal of plants.
Detailed Explanation
Seeds play a crucial role in the life cycle of plants. They are the means by which plants reproduce and ensure that their species continues. When a seed is formed after fertilization, it can be spread to different locations. This dispersal helps plants colonize new areas, which is essential for their survival and adaptation to changing environments.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine planting flowers in a garden. When the flowers produce seeds, they will fall to the ground, and some might blow away by the wind or be carried by animals, just like how seeds spread to grow new plants in various places.
Key Concepts
-
Seed Formation: Refers to the process through which seeds are created following fertilization.
-
Embryo Development: The embryo within the seed grows to form a new plant, ensuring continuity of plant life.
-
Dispersal: The movement of seeds to new areas, crucial for the survival of plant species.
Examples & Applications
A seed from a bean plant can grow into a new bean plant after germination, illustrating the seed's role in plant reproduction.
The dispersal of dandelion seeds by the wind showcases how seeds can travel far and wide from their parent plant.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a seed, life begins, sprouting roots and green fins.
Stories
Once upon a time, a tiny seed dreamed of becoming a mighty tree. It traveled far and wide to find a perfect spot to grow, ensuring that its legacy continued.
Memory Tools
Remember 'S.E.E.D.' - Structure (parts), Embryo (new plant), Environment (dispersal importance), Development (from seed to plant).
Acronyms
S.E.E.D. - Seed, Embryo, Environment, Development
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Seed
The mature ovule of a plant that contains an embryo and develops into a new plant.
- Embryo
The developing stage of a plant contained within a seed, which grows into a new plant.
- Dispersal
The process by which seeds are spread to new locations to grow into new plants.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
