Monocotyledonous (Monocot)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Structure of Monocot Seeds
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to learn about monocot seeds. Can anyone tell me what makes up a monocot seed?

I think it's just one part, like a single cotyledon.

Exactly! A monocot seed contains one cotyledon called the scutellum. Why do you think this can be beneficial?

It probably helps in storing food efficiently for the baby plant!

Great observation! The scutellum plays a role in nutrient storage. Another important part is the endosperm, which provides energy to the developing seedling. Remember, 'Scutellum stores, endosperm powers!'

What's the role of the embryo then?

The embryo consists of the radicle and plumule, where the radicle forms the roots, and the plumule forms the shoot. Together, they kickstart the plant’s growth!

That sounds important for the plant's development! Can you repeat those terms?

Of course! The key terms are: Scutellum, Endosperm, Radicle, Plumule. Make sure to visualize their roles in your mind!
Protection in Monocots
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's talk about how monocot seeds protect their embryos during germination. Can anyone name those protective structures?

Is it coleoptile and coleorhiza?

Yes! The coleoptile covers the plumule, and the coleorhiza shields the radicle. Think of them as the plant's 'armor'.

Why are they important?

They protect the developing shoots and roots as they push through the soil. Remember, 'Coleoptile for shoots, coleorhiza for roots'!

What happens if they get damaged?

Good question! Damage to these structures can hinder plant growth. If the shoot gets damaged, the plant may struggle to grow above the ground.

So keeping those safe is essential for healthy plants?

Absolutely! Protecting the embryo leads to a stronger, healthier plant. Now, let's summarize: Monocot seeds feature coleoptile and coleorhiza, providing armor during growth.
Examples of Monocots
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

I've covered a lot about monocot seeds. Can anyone name some examples?

Maize and rice are two examples!

Correct! Maize and rice are staple foods. Can you think of why it’s important to understand these plants?

Because they provide food for many people around the world?

Exactly! They're crucial for agriculture and food security. Now, can anyone list the features we discussed that contribute to their growth?

One cotyledon, endosperm for nutrients, and protective sheaths!

Right! Let's recap: Monocots like maize and rice have unique features that aid their growth and significance in agriculture.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section on monocotyledonous seeds delves into their structure, distinguishing features including the presence of a single cotyledon, endosperm, and unique protective sheaths for the embryo, with maize as a prime example. Understanding these characteristics is vital for recognizing how monocots differ from dicots and their role in plant reproduction and development.
Detailed
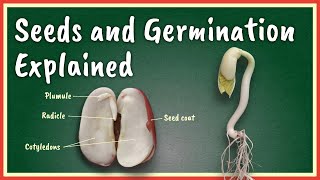
Monocotyledonous Seeds
Monocotyledonous seeds, commonly known as monocots, are seeds that possess only one cotyledon, a key differentiation from dicotyledonous seeds, which have two. The structure of a monocot seed is specialized for its role in plant growth and propagation, typically exemplified by crops such as maize (corn) and rice.
Key Features of Monocot Seeds:
- Single Cotyledon (Scutellum): This structure serves as the food storage organ, providing the necessary nutrients to the developing embryo before it can establish its own photosynthetic capabilities.
- Endosperm: In monocot seeds, the endosperm is a significant storage tissue that not only nourishes the embryo but also plays a crucial role in the germination process as it supplies energy until the seedling can photosynthesize.
- Embryonic Structures: The embryo consists of two main parts: the radicle and plumule. The radicle will develop into the root system of the plant, while the plumule develops into the shoot.
- Protective Structures: Monocots also feature specialized structures such as the coleoptile and coleorhiza, which protect the plumule and radicle, respectively, during germination and initial growth.
Significance:
Understanding the structure and function of monocot seeds is crucial not only in botany but also in agricultural practices, as many of the world’s staple crops belong to this category. Recognizing the morphological adaptations of monocots aids in better crop management and agricultural productivity.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Single Cotyledon
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Single cotyledon (Scutellum)
Detailed Explanation
In monocot seeds, there is only one cotyledon called the scutellum. The cotyledon serves as the first leaf or leaves of the plant that develop from the embryo. It plays a crucial role in storing nutrients that will be used during the initial stages of seed germination.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the cotyledon as a packed lunch for a student starting a new school. Just like that lunch provides the necessary nutrients until the student can access the cafeteria, the cotyledon nourishes the young plant until it can produce its own food through photosynthesis.
Endosperm
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Endosperm – Stores food for the embryo
Detailed Explanation
The endosperm is a tissue within the seed that serves as a food reserve for the developing embryo. When the seed germinates, the embryo utilizes the nutrients stored in the endosperm to fuel its initial growth until it can begin photosynthesis.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the endosperm like the pantry in a house. It stores all the food supplies needed until the family can establish itself in a new environment. Similarly, the endosperm provides the necessary energy and nutrients to the young plant until it can gather its food through leaves.
Embryo Development
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Embryo – With radicle and plumule
Detailed Explanation
The embryo of a monocot seed includes two main parts: the radicle and the plumule. The radicle will grow into the root, anchoring the plant and absorbing water and nutrients from the soil. The plumule will develop into the shoot, which will grow upwards towards sunlight.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the embryo as a tiny factory. The radicle is like a foundation that helps to secure the factory in place, while the plumule is the roof that shoots up toward the sun. Both parts work together to develop the plant into a mature organism.
Protective Sheaths
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Coleoptile – Protective sheath for the plumule
● Coleorhiza – Protective sheath for the radicle
Detailed Explanation
The coleoptile is a protective sheath that covers the plumule, shielding the young shoot as it emerges through the soil. The coleorhiza serves a similar purpose but protects the radicle as it grows downward. This protection is vital as the young plant encounters soil and other elements that could damage its delicate structures.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the coleoptile and coleorhiza as the protective packaging that surrounds a fragile gadget. Just as the packaging ensures that the gadget arrives intact to its destination, these sheaths safeguard the young plant parts during their critical first moments of growth.
Key Concepts
-
Single Cotyledon: Monocots have one cotyledon, crucial for initial plant growth.
-
Endosperm Function: Provides nutrition for the developing embryo in monocots.
-
Embryonic Structures: The radicle and plumule develop into essential parts of the plant.
-
Protective Sheaths: Coleoptile and coleorhiza protect the embryo during germination.
Examples & Applications
Maize (corn) and rice are common examples of monocot seeds.
Other examples include wheat and barley, which are staple crops worldwide.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
One cotyledon, scutellum's a winner, endosperm fuels, watch that plant get thinner.
Stories
In a small garden, there lived a seed named Maize. It had a single cotyledon and a cozy endosperm. With protective sheaths, it dreamed of seeing the sunlight while its radicle prepared for a deep root adventure.
Memory Tools
Remember: CECR - Cotyledon, Endosperm, Coleorhiza, Radicle. It helps recall the key components of a monocot seed!
Acronyms
For monocots, use the acronym 'CERC' - C for Cotyledon, E for Endosperm, R for Radicle, C for Coleoptile.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Monocotyledonous (Monocot)
A type of seed with a single cotyledon, characteristic of certain flowering plants.
- Cotyledon
The first leaf or leaves that develop from the embryo of a seed.
- Endosperm
A tissue produced inside the seeds of most flowering plants, surrounding the embryo and providing nutrition during germination.
- Radicle
The part of the embryo that develops into the root of a plant.
- Plumule
The part of the embryo that develops into the shoot of a plant.
- Coleoptile
A protective sheath covering the plumule in monocot seeds.
- Coleorhiza
A protective sheath covering the radicle in monocot seeds.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
