Hypogeal Germination
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Definition of Hypogeal Germination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into hypogeal germination! Can anyone tell me what they think it means?

Is it when the seed pushes its leaves above the soil?

Good guess, but that's actually the concept of epigeal germination. Hypogeal germination occurs when the cotyledons remain below the surface. For example, maize is a plant that uses this method. Can you remember the name of that plant?

It's maize!

Exactly! So during hypogeal germination, the shoot, or plumule, emerges while the cotyledons stay underground. This offers protection. Remember, 'below' starts with H for 'hypogeal'.
Key Features of Hypogeal Germination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's discuss some key features of hypogeal germination. Who can describe what happens to the cotyledons?

They stay underground, right?

Correct! They serve as a food source while remaining below the soil. Can someone explain why this is beneficial?

I think it protects them from the elements like sunlight or extreme weather.

Exactly! This is a survival adaptation. It allows the young plant to get established safely before facing the world.
Examples of Hypogeal Germination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's look at some practical examples of hypogeal germination. Who can name a plant that germinates this way?

Maize is one!

What about beans?

Great! But beans actually undergo epigeal germination, where the cotyledons rise above ground. Remember, 'hypo' keeps them 'hot' below the soil. Maize is our star here!

So does it mean not all seeds are the same in how they germinate?

Correct! Each type of germination has its advantages and adaptations to environments.
Comparison with Epigeal Germination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Who can summarize the difference between hypogeal and epigeal germination?

In epigeal, the cotyledons come above ground, while in hypogeal, they stay below.

Exactly! Hypogeal germination is beneficial because it allows plants like maize to conserve energy and grow sturdily. Can anyone think of a situation when this would be useful?

When there’s a lot of rain or harsh sun, right?

Yes! The seed can focus on developing strong roots and shoots without exposure to harsh conditions.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In hypogeal germination, during the germination of seeds like maize, the cotyledons stay buried in the soil while the epicotyl elongates and pushes the shoot above ground, allowing the plant to grow. This contrasts with epigeal germination where cotyledons emerge above the soil.
Detailed
Hypogeal Germination
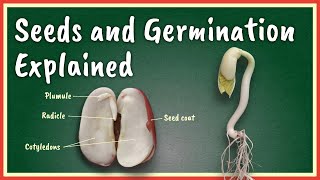
Hypogeal germination is a specific form of seed germination in which the cotyledons, or seed leaves, remain below the soil surface throughout the early stages of development. This contrasts sharply with epigeal germination, where the cotyledons emerge above the ground. Typical examples of plants that undergo hypogeal germination include maize (corn).
Key Points:
- Definition: Hypogeal germination involves the germination process where the cotyledons do not break the soil surface.
- Process: In this type of germination, the first visible growth is the shoot (plumule), which grows above the soil, while the cotyledons remain protected underground. The radiating growth from the radicle forms the root system.
- Examples: Maize is the most cited example of hypogeal germination, highlighting the practicality and distinctiveness of this evolutionary trait in certain plant species.
Importance:
Understanding hypogeal germination is crucial in agriculture and horticulture as it affects planting depth and seed placement to maximize growth potential, especially in crops like maize. Moreover, knowing this process helps in comprehending how different species adapt to their environments and optimize their chances for survival.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Hypogeal Germination
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Hypogeal Germination
- Cotyledons remain below the soil
- Example: Maize
Detailed Explanation
Hypogeal germination is a type of seed germination where the cotyledons, which are the first leaves that develop from a seed, stay below the surface of the soil. This is in contrast to epigeal germination, where the cotyledons emerge above the ground. In hypogeal germination, the primary focus is on the growth of the shoot, which pushes upward as the root goes downward.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a hypogeal germinating seed like a turtle hiding its head in a shell while it ventures forward. The seed’s 'head' (the shoot) is pushing out of the soil to look for sunlight and air, while the 'shell' (the cotyledons) remains safely underground.
Characteristics of Hypogeal Germination
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Cotyledons remain below the soil
- Example: Maize
Detailed Explanation
One key characteristic of hypogeal germination is that the seed's cotyledons remain buried in the soil while the stem and leaves grow upward. In plants like maize, this allows the plant to establish a strong root system before the leaves begin to develop. This type of germination is advantageous in certain environments where soil humidity can support seed growth while protecting the cotyledons from herbivores and environmental stress.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a soldier (the seed) digging into a trench (the soil) to remain hidden but sending up a lookout (the shoot) to watch for incoming danger. This way, the soldier can be safe underground while still scouting the area directly above.
Importance of Hypogeal Germination
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Example: Maize
Detailed Explanation
Hypogeal germination is particularly important for crops like maize because it enables the plant to take advantage of the nutrients and moisture in the soil while protecting the young leaves and cotyledons. The development of strong roots is crucial for stability and nutrient uptake, which leads to healthier plants and higher yields.
Examples & Analogies
Consider building a house. The foundation (hypogeal germination) must be strong and stable before you can put up the walls and roof (leaves and stem). If the foundation is solid, the house will stand strong against storms, just like a young maize plant with secure roots will thrive.
Key Concepts
-
Hypogeal Germination: The seed remains underground with cotyledons protecting growth.
-
Maize: A model example of a plant that exhibits hypogeal germination.
-
Cotyledons: Serve as the first leaves that aid in initial plant growth.
Examples & Applications
Maize is the classic example of hypogeal germination where the cotyledons are below soil during early growth.
In contrast, beans demonstrate epigeal germination with cotyledons emerging above the soil.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Hypogeal and maize are a pair, cotyledons below, safe from despair.
Stories
Once upon a time, in a garden, a maize seed stayed tucked in the soil while its shoot peeped above, safe from harsh winds and rain.
Memory Tools
Use 'H' in Hypogeal to remember 'Hidden' below ground.
Acronyms
Maize
for Maize
for Adaptation
for In soil
for Zapping up growth
for Energy conserved.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Hypogeal Germination
A type of seed germination where the cotyledons remain below the soil during early plant growth.
- Cotyledons
The first leaves that emerge from a germinating seed, which may store food for the developing plant.
- Plumule
The part of the embryo in a seed that develops into the shoot.
- Maize
A cereal plant that undergoes hypogeal germination and is a significant agricultural crop.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
