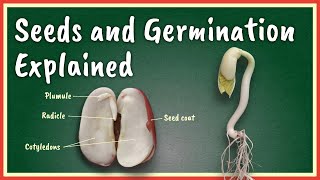
Significance of Germination
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Germination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss the significance of germination. Can anyone tell me what germination is?

Germination is when a seed starts to grow into a plant, right?

Exactly! Germination is crucial as it marks the beginning of a plant's life cycle. Why do you think it's important for plants to germinate?

I think it's important because without germination, there wouldn’t be any new plants.

Great point! This highlights the continuity of life in plants. Let's summarize: germination is essential for new plant growth and species continuation.
Independence of the Plant
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

After germination, what happens to the seed?

The seed grows into a seedling, and then it can live on its own.

Exactly! Once a seedling emerges, its true leaves appear, and it can perform photosynthesis. Why is this independence critical?

Because it can get food and water by itself.

Correct! Being able to photosynthesize means that plants can sustain themselves and contribute to the ecosystem. Let's summarize: the independence of the plant after germination allows it to thrive.
Agricultural Significance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss why germination is essential for agriculture.

Isn’t it important for growing crops?

Absolutely! Successful germination ensures healthy crops, which are crucial for food production and economy. Can you think of any crops that rely on proper germination?

Maize and beans need to germinate to grow, right? If they don’t, we won’t have food from them.

Correct! This illustrates how vital germination is for the economy linked to agriculture and food security. Let's recap: germination affects crop yields and overall agricultural success.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The germination process is essential for plant growth and development, enabling seeds to transform into new plants. This process is vital for agriculture and crop production, ensuring food supply and biodiversity.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of the Significance of Germination
Germination is the vital process where seeds grow into seedlings, marking the beginning of a plant's life cycle. This section emphasizes the significance of germination for several reasons:
- Growth and Development: Germination is the first step in a seed’s journey to becoming an independent organism. The transformation of a seed into a new plant is essential for sustaining plant life and ensuring the continuation of species.
- Independence of the Organism: Once a seed germinates, it begins to absorb water and nutrients from the soil, establishing itself as an independent organism capable of photosynthesis and growth.
- Agricultural Importance: Germination plays a critical role in crop production and agriculture. The timely and successful germination of seeds leads to healthy crops, which are crucial for food security and economic stability in agricultural societies.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Essential for Growth and Development
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Essential for growth and development of new plants
Detailed Explanation
Germination is crucial because it marks the start of a plant's life. When a seed germinates, it begins the process of growth. This involves the seed absorbing water and nutrients, which triggers the growth of the plant. Essentially, germination allows the genetic material in the seed to express itself, leading to the formation of roots, stems, and leaves, which are vital for the plant's development.
Examples & Analogies
Think of germination like starting a new project. Just as you need the right conditions and materials to create something new, a seed requires the right environment to grow into a plant. For example, when you plant a seed in the soil, just like beginning a new project, it starts to develop and eventually becomes a fully functioning plant.
Independence of the Organism
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Allows seed to grow into an independent organism
Detailed Explanation
Once a seed germinates and grows into a seedling, it becomes an independent organism that can photosynthesize, take up nutrients from the soil, and grow on its own. This transition from seed to seedling is vital, as it allows the plant to sustain itself and continue to grow without relying on the seed's stored nutrients. This independence is essential for the plant's survival in its environment.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine raising a child; initially, they rely on their parents for everything. However, as they grow and develop skills, they become more independent, able to take care of themselves. Similarly, once the seed germinates and starts to grow, it starts to function independently, just like a young adult forging their own path.
Importance for Crop Production
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Important for crop production and agriculture
Detailed Explanation
Germination is a critical step in agriculture because it directly affects crop production. Farmers depend on the successful germination of seeds to ensure healthy plants and good harvests. Without proper germination, the yield of crops can decline, impacting food supply and economy. Understanding the significance of germination helps farmers implement better cultivation practices to maximize production.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a gardener planting seeds for vegetables in their garden. If the seeds do not germinate due to poor conditions like insufficient water or incorrect temperature, the gardener will not have a bountiful harvest of vegetables. Just as a good foundation is vital for a stable building, successful germination is the foundation for successful agriculture.
Key Concepts
-
Germination: The process where seeds develop into seedlings.
-
Independent Organism: The seedling becomes capable of photosynthesis and growth, essential for its survival.
-
Agricultural Importance: Germination is crucial in producing healthy crops for food and economic stability.
Examples & Applications
The germination of a bean seed demonstrates epigeal germination as the cotyledons rise above the soil.
Maize seeds show hypogeal germination, where the cotyledons stay underground while the shoot emerges.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When seeds sprout in light or rain, new plants grow despite the strain.
Stories
Once, a tiny seed lay still in the soil, dreaming of sunshine. When it finally got water, it grew tall and proud, becoming a flower admired by all.
Memory Tools
Remember ‘GROW’: Germination Leads to Roots, then Onto Leaves!
Acronyms
GAS
Germination Activates Seedlings.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Germination
The process by which a seed develops into a new plant.
- Seedling
A young plant that develops after germination.
- Photosynthesis
The process by which green plants use sunlight to synthesize foods with the help of chlorophyll.
- Crop Production
The process of growing and harvesting crops for food, fiber, or other products.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
