Seed Coat
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Seed Coat
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to dive into the seed coat, which is the outer protective covering of a seed. Can anyone tell me why they think the seed coat is important?

Is it to protect the seed from getting damaged?

Exactly! The seed coat acts like armor for the seed, protecting the embryo from harsh environmental conditions. It consists of two layers in dicots – the testa and the tegmen. Can anyone remember what these layers do?

The testa is the outer layer, right? And it’s tougher to protect the seed!

That's correct! The outer layer, or testa, is indeed more robust. The tegmen, on the other hand, is thinner and helps in moisture absorption. Remember this with the mnemonic 'Tough Testa' for the protective role.

How is this different for monocots?

Great question! Monocots have a single cotyledon and a simpler seed coat structure. We focus on the seed coat layering for dicots to understand its function better. Understanding this helps explain how seeds protect themselves.
Types of Seed Coats in Monocots and Dicots
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

We've discussed the layers of the dicot seed coat. Now, can anyone tell me which seeds are classified as monocots?

Would maize and rice be examples of monocots?

Correct! Monocots have one cotyledon and do not have the same layered structure as dicots. This means they operate slightly differently in terms of seed protection.

How does this affect germination?

Excellent point! The seed coat's structure affects how water enters the seed, which is critical during germination. The simpler structure in monocots may allow for quicker absorption.

So, the way seeds are structured can influence how they grow?

Absolutely! The efficiency of the seed coat can have significant implications for survival and growth. Keep asking these questions; they help deepen understanding!
Protective Functions of the Seed Coat
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's now look at the protective functions of the seed coat. Why might a seed need to protect its embryo?

To keep it safe from pests and diseases?

That's one of the key reasons! It also protects against physical damage and desiccation, aiding in survival until the right conditions for germination are met.

And how does it help in absorbing water?

Excellent inquiry! The seed coat, especially the tegmen, allows water to seep in when conditions are right. Remember, when you think of moisture, think of the term 'Hydration Helps Germination!'

That makes sense! So, the seed coat is not just about protection?

Correct again! It also plays a vital role in the seed's ability to germinate and sprout into a new plant. Wrapping these thoughts up will enhance your understanding of plant biology!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
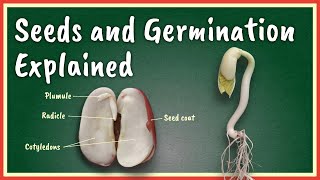
The seed coat serves as a protective covering for seeds, which can be classified into monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous types. In dicots, the seed coat consists of two layers, the testa and tegmen, while in monocots, it surrounds a single cotyledon. Understanding the structure of the seed coat is crucial for comprehending seed germination and plant growth.
Detailed
Seed Coat
The seed coat is the outer protective layer of a seed, crucial for safeguarding the embryo from environmental conditions and pathogens. When examining seeds, they generally fall into two categories based on cotyledon number: monocotyledonous (e.g., maize, wheat) and dicotyledonous (e.g., bean, gram).
Structure of the Seed Coat
In dicot seeds like the bean, the seed coat is divided into two distinct layers:
1. Testa: The outer layer, which provides robust protection.
2. Tegmen: The inner thin layer, which helps in regulating moisture absorption.
In monocot seeds, such as maize, the seed coat is less differentiated but still surrounds a single cotyledon (known as the scutellum) and protects the embryo within.
Understanding the structure and function of the seed coat is vital for studying seed germination processes, as it plays a direct role in water absorption and environmental resistance, thus affecting the plant's growth and establishment when it begins to germinate.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
What is the Seed Coat?
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The seed coat is the outer protective covering of a seed that consists of two layers:
- Testa – Outer layer
- Tegmen – Inner thin layer
Detailed Explanation
The seed coat serves as the first line of defense for the seed. It protects the delicate embryo and food reserves inside from physical damage, pathogens, and environmental factors. The two layers of the seed coat, the testa (outer layer) and tegmen (inner layer), work together to provide this protection.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the seed coat like the shell of a nut. Just as the hard shell protects the nut inside from moisture and pests, the seed coat safeguards the seed from the outside environment.
Layers of the Seed Coat
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Testa: This is the outer layer of the seed coat. It is thick and tough, providing strong protection against physical damage.
- Tegmen: This is the inner, thinner layer of the seed coat that closely surrounds the seed's embryo and food storage.
Detailed Explanation
The testa is often thicker and can have various textures that further help in protecting the seed, while the tegmen is more delicate. Together, they ensure that the seed can withstand harsh conditions until it is ready to germinate and grow into a new plant.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a packaged snack with two layers of wrapping. The thick outer layer protects the snack from being crushed, while the thinner inner layer keeps it fresh. Similarly, the seed coat layers work to safeguard the seed until it's time to grow.
Functions of the Seed Coat
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The seed coat has multiple important functions, including:
- Protecting the embryo from damage
- Preventing water loss
- Allowing for gas exchange through small apertures
Detailed Explanation
The seed coat not only protects but also helps in maintaining the appropriate conditions within the seed. It prevents the embryo from drying out and allows for gas exchange at the appropriate times during germination. This balance is crucial for the successful growth of the new plant.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the seed coat like a sealed plastic bag containing a sandwich. It keeps the sandwich fresh and intact while letting a bit of air in and out to prevent mold. Likewise, the seed coat helps keep the embryo healthy until conditions are right for it to sprout.
Key Concepts
-
Seed Coat: The outer protective covering of seeds that facilitates germination.
-
Testa and Tegmen: The two layers in the seed coat of dicots.
-
Differentiation: Monocots have a simpler seed structure compared to dicots.
Examples & Applications
A bean seed's coat has a hard outer layer, the testa, and a protective inner layer, the tegmen.
Corn (maize) seeds have a single cotyledon and simpler seed coats that allow them to germinate easily.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
The seed coat is tough and round, protecting the embryo underground.
Stories
Once upon a time, a brave little seed hid under a hard shell, waiting for rain's magic to help it swell. When the curtain of rain fell, it broke free from its protective shell, revealing the green plant inside.
Memory Tools
To remember the layers of dicots, think 'Tough Testa, Thin Tegmen'.
Acronyms
Remember 'T&T' for Testa and Tegmen.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Seed Coat
The outer protective layer of a seed that safeguards the embryo.
- Testa
The outer layer of the seed coat in dicotyledonous seeds.
- Tegmen
The inner thin layer of the seed coat in dicotyledonous seeds.
- Cotyledon
The first leaves that develop from the embryo of a seed, which store food.
- Monocot
A type of seed with one cotyledon, such as maize or rice.
- Dicot
A type of seed with two cotyledons, such as beans or peas.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
