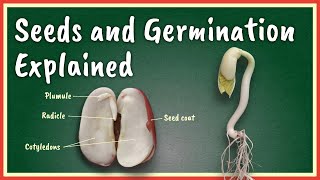
Micropyle
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Micropyle
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're learning about an essential part of the seed called the micropyle. It's a small opening located near the hilum. Can anyone tell me what the hilum is?

Isn't the hilum the scar that shows where the seed was attached to the fruit?

That's correct! Now, the micropyle is located next to the hilum. Its primary job is to allow water and oxygen to enter the seed. Why do you think water and oxygen are important for the seed?

Well, water is necessary for germination, and oxygen is needed for respiration!

Exactly! The micropyle plays an essential role in the life cycle of a seed. Remember, without it, the seed wouldn't be able to start growing.
Function of the Micropyle
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive deeper into how the micropyle works during germination. When a seed absorbs water through the micropyle, what happens next?

Doesn't it activate enzymes in the seed?

Correct! This activation leads to the conversion of stored food into a soluble form so the embryo can utilize it for growth. What part of the seed do you think emerges first during germination?

The radicle, which grows into the root!

Exactly! The radicle emerges first, followed by the plumule forming the shoot. The micropyle is the entry point for the water that kicks off this entire process.
Importance of the Micropyle in Seed Life Cycle
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's talk about why the micropyle is significant in the life cycle of a plant. Can someone summarize its importance?

It allows for the necessary resources like water and oxygen to enter the seed, which is crucial for germination.

That's a great summary! Without the micropyle, seeds would remain dormant and unable to grow into new plants. This is why understanding the micropyle is crucial for studying plant biology.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Located near the hilum of a seed, the micropyle serves as a crucial entry point for water and oxygen, aiding the germination process. Its function is essential for the successful growth of the embryo into a new plant.
Detailed
Micropyle
The micropyle is a vital part of the seed's structure, specifically located near the hilum, which marks the site of attachment to the fruit. This small pore enables the seed to absorb water and oxygen, essential elements required for germination. The entry of water through the micropyle softens the seed coat and activates enzymatic processes that promote growth. In understanding the germination of seeds, recognizing the role of the micropyle is critical, as it essentially triggers the transformation from a dormant seed to a growing embryo.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Micropyle
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Micropyle – Small pore near hilum; allows entry of water and oxygen
Detailed Explanation
The micropyle is a tiny opening found on the surface of a seed, specifically located near the hilum, which is the scar marking the point of attachment of the seed to the fruit. This small pore plays a crucial role in the seed's life as it facilitates the entry of vital elements like water and oxygen into the seed. Water is essential for the germination process, while oxygen is necessary for respiration, which is fundamental for the developing embryo.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a sealed bag of popcorn. For the popcorn to expand and pop, it needs some moisture inside the bag. The micropyle is like a small hole in that bag, allowing a bit of air and moisture to enter; this is what makes it possible for the popcorn to pop. Similarly, the micropyle lets water and oxygen inside the seed so it can grow.
Function of the Micropyle
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The micropyle allows essential substances to enter the seed during germination.
Detailed Explanation
During germination, the seed must absorb water to initiate the growth process. The micropyle acts as a pathway for water to enter the seed, as the seed coat is otherwise quite protective and impervious to water. Additionally, oxygen enters through this pore, enabling the embryo to perform respiration—a process critical for energy production during its development. Without the micropyle, the seed would struggle to begin its transformation into a seedling.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the micropyle as a keyhole on a door. Just like you need a key to unlock a door and enter a room, the seed needs the micropyle to receive the water and oxygen it needs to start growing inside its protective coat. It's a small opening, but it plays a significant role in allowing the new plant to access the resources it needs.
Key Concepts
-
Micropyle: A small opening that allows water and oxygen to enter the seed, crucial for germination.
-
Hilum: The scar that indicates where the seed was attached to the fruit.
Examples & Applications
In dicot seeds, such as beans, the micropyle allows water to enter, initiating growth.
In monocot seeds, like maize, the micropyle similarly facilitates hydration necessary for germination.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
The micropyle is small, but without its role at all, no growth shall be tall.
Stories
Imagine a tiny door on a seed, the micropyle, allowing water and air in as if it were a key to life's garden.
Memory Tools
Remember 'Mighty Water Oxygen (MWO)' - Micropyle lets in Mighty Water and Oxygen for growth!
Acronyms
MPO - Micropyle for Plant's Oxygen!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Micropyle
A small pore in the seed coat that allows water and oxygen to enter the seed during germination.
- Hilum
The scar on the seed coat marking the point of attachment to the fruit.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
