Cotyledons
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Cotyledons
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to discuss cotyledons. Can anyone tell me what cotyledons are?

Are they the first leaves of the plant?

Good thought! Cotyledons are indeed the first leaves that emerge from a seed. They play a crucial role in the early stages of the plant's life. They store food for the developing embryo.

How many cotyledons does a monocot plant have?

Great question! Monocotyledons, like maize, have one cotyledon. This is different from dicotyledons such as beans, which have two.

What do the cotyledons do during germination?

During germination, cotyledons are crucial as they provide the initial nutrients needed for growth before the plant develops true leaves.

So, will they wither away as the plant grows?

Exactly! Cotyledons typically wither once the plant starts to grow its real leaves and can photosynthesize.

To summarize, cotyledons are essential for storing food and supporting the seed's growth into a mature plant.
Differences Between Monocots and Dicots
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s compare monocots and dicots with respect to their cotyledons. Who can remind me how many cotyledons each type has?

Monocots have one, and dicots have two!

Correct! Can anyone name an example of a monocot?

Maize!

Exactly! And what about a dicot?

Like beans or grams!

Perfect! Now, how do the functions of their cotyledons differ?

Monocots mainly utilize their cotyledon for storing nutrients, while dicots can also use their cotyledons to start the photosynthesis process.

Exactly right! Remember, this difference plays a significant role in their growth and development. Great work, everyone!
Importance of Cotyledons in Germination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive deeper into how cotyledons influence germination. What do you think happens to cotyledons during this process?

They help provide nutrients so the plant can start growing!

Exactly! They store food that the plant uses until it can perform photosynthesis. How do cotyledons differ in epigeal germination and hypogeal germination?

In epigeal germination, the cotyledons come above the soil!

Right! And in hypogeal germination, like in maize, the cotyledons stay below the surface. Good observation!

So, will the cotyledons in epigeal plants help with photosynthesis right after they emerge?

Yes, they can! This adaptation helps them get light sooner for growth. Remember, they're not just leaves; they're essential for the seed's success!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore the significance of cotyledons in seeds, differentiating between monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous seeds and their roles in nutrient storage and early development of plants.
Detailed
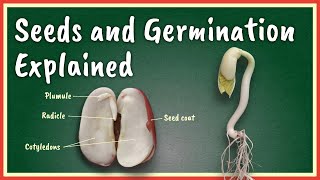
Cotyledons, often referred to as seed leaves, are vital components of seeds that serve critical functions in the early stages of plant growth. In monocotyledonous seeds, there is a single cotyledon, as seen in maize, while dicotyledonous seeds contain two cotyledons, characteristic of beans and grams. These structures are not only important for nutrient storage, ensuring the young plant receives the necessary elements for initial growth, but they also play a significant role in the germination process, where the cotyledons may eventually emerge above or below soil level depending on the germination type. Understanding cotyledons helps in comprehending the overall structure and functionalities associated with seed development, germination, and eventual plant maturation.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Cotyledons
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Cotyledons – Two fleshy structures that store food
Detailed Explanation
Cotyledons are an essential part of a dicot seed, which means they are present in seeds that have two cotyledons. These cotyledons are fleshy structures that have the primary function of storing food for the developing embryo. When the seed germinates, the energy stored in the cotyledons helps the young plant to grow, as it has not yet developed sufficient roots to absorb nutrients from the soil.
Examples & Analogies
Think of cotyledons like a packed lunch that a student takes to school. Just as the packed lunch provides nourishment to the student until they can buy food from the cafeteria, cotyledons provide the necessary food to the young plant until it can establish itself in the soil and begin photosynthesis.
Functionality in Seed Germination
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Cotyledons play a crucial role during the early stages of seed germination.
Detailed Explanation
When a seed begins to germinate, it relies heavily on the nutrients stored in its cotyledons. As water enters the seed and activates its metabolic processes, the embryo uses these stored nutrients to grow. The cotyledons will eventually emerge above the soil, and in some plants, they may photosynthesize and contribute to the plant's energy production after germination.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are starting a new business. In the beginning, you might rely on your savings (similar to cotyledons) to get started. As your business grows and begins to make profits, you can then reinvest that money. In the same way, a plant uses cotyledons to sustain itself while it’s establishing its roots and starting to grow leaves.
Difference Between Monocot and Dicot Cotyledons
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A distinction exists between monocots, which have one cotyledon, and dicots, which have two.
Detailed Explanation
Monocotyledonous plants have one cotyledon (like corn or rice), while dicotyledonous plants have two cotyledons (like beans and grams). This difference affects various aspects of the plants, including their growth patterns and the complexity of their structures. For example, the presence of two cotyledons in dicots allows them to store more food, which can be advantageous during the initial growth stages.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a one-layer cake versus a two-layer cake. A one-layer cake (monocot) might be simpler, but a two-layer cake (dicot) can have more filling and flavor. The two layers allow for greater richness, just like two cotyledons can provide more nutrients for a young plant than one.
Key Concepts
-
Cotyledons: First leaves that store nutrients and play an essential role in early plant development.
-
Monocots: Seeds with one cotyledon, e.g., maize, rice.
-
Dicots: Seeds with two cotyledons, e.g., beans, grams.
-
Germination: The process through which seeds grow into new plants.
-
Epigeal Germination: Type of germination where cotyledons emerge above the soil.
-
Hypogeal Germination: Type of germination where cotyledons remain below the soil.
Examples & Applications
Maize is a monocot that has one cotyledon, while beans are dicots with two cotyledons.
During epigeal germination, the cotyledons of a bean plant emerge above the soil, whereas in hypogeal germination, the cotyledons of maize remain underground.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Cotyledons, oh so round, store food from the ground, one in monocots, two for dicots found.
Stories
Once upon a time in a garden, two seeds lived together. One was a monocot and one a dicot. The monocot, named Maize, had just one leaf to rely on for food, while the dicot, named Bean, had two leaves that helped it grow taller and stronger under the sun!
Memory Tools
Remember: Mono has one cute cotyledon, while Di has two big, broad leaves!
Acronyms
MDC for remembering
for Monocot (one cotyledon)
for Dicot (two cotyledons)
for Cotyledons.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Cotyledon
The embryonic leaf in seed-bearing plants, crucial for nutrient storage in seedlings.
- Monocotyledon
A type of seed that has one cotyledon, such as maize or rice.
- Dicotyledon
A seed that has two cotyledons, such as beans or grams.
- Germination
The process by which a seed develops into a new plant.
- Epigeal Germination
A type of germination where cotyledons emerge above the soil.
- Hypogeal Germination
A type of germination where cotyledons remain below the soil.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
