Germination of Seeds
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Germination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore germination, which is the process where seeds grow into seedlings. Can anyone tell me what conditions might be necessary for this process?

I think water is important because seeds need it to grow.

Great point, Student_1! Water is essential to soften the seed coat and activate enzymes. What about other conditions?

Oxygen! Seeds need oxygen to breathe and carry out respiration.

Exactly, Student_2! Without oxygen, the seed cannot respire effectively. Let's remember 'WON' - Water, Oxygen, and Nutrients as key ingredients for germination. Can anyone name another condition?

The seed has to be viable, right?

Correct, Student_3! The seed must be alive and healthy. Now, who can explain the two types of germination?

There's epigeal and hypogeal. In epigeal, the cotyledons come above the soil like in beans.

Nice work! And hypogeal, like in maize, keeps the cotyledons below the soil, right?

Yes, that's correct!

Let's summarize today. Germination requires water, oxygen, temperature, and viability, and it occurs in two types: epigeal and hypogeal. Great interaction, everyone!
Conditions Necessary for Germination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's dive deeper into the conditions necessary for germination. How does water affect this process?

It helps activate enzymes, doesn't it?

Absolutely right! Water not only activates enzymes but also softens the seed coat, making it easier for the seedling to emerge. Can someone explain the role of temperature?

Temperature is important for enzymatic activity. It needs to be just right for the seed to germinate.

Excellent, Student_3! Too cold or too hot can hinder germination. Remember: **Think TAWN** - Temperature, Air, Water, Nutrients. Who can explain the importance of viable seeds?

If a seed isn't viable, it won't grow into a plant.

Precisely! Without a healthy seed, even perfect conditions won't lead to germination. To sum it up, we've discussed the critical factors: water, oxygen, temperature, and viability. Keep these in mind!
Changes During Germination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's talk about the changes that take place during germination. Who can describe what happens to a seed as it absorbs water?

I think it swells and the enzyme activity starts.

Exactly, Student_1! When the seed absorbs water, it swells, and that activates enzymes that help convert stored food into usable forms. What happens next?

The radicle comes out first to form the root, followed by the shoot.

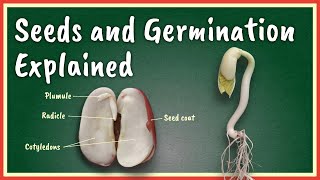
Well done, Student_2! The radicle does emerge first, establishing the root system. After that, the plumule forms the shoot. Can anyone tell me what happens to the seed coat as the plant emerges?

It breaks open, right?

Exactly! The seed coat breaks apart as the emerging seedling grows. So to summarize our session, we learned that water absorption, enzymatic activity, the emergence of the radicle and plumule, and the breaking of the seed coat are key changes during germination.
Significance of Germination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Germination is not just a scientific process but also hugely significant for plants and agriculture. Why do you think germination is vital for new plants?

It allows plants to grow and survive independently.

Correct! Germination leads to the establishment of new plants, which are essential for ecosystems. What else can germination impact?

It’s important for agriculture and crop production!

Absolutely! Successful germination can directly affect food supply and farming practices. Think about this: why is it important to study germination for agriculture?

If farmers know how to improve germination, they can grow more crops.

Exactly! Improved germination rates lead to better harvests. Let’s summarize: Germination is crucial for the life cycle of plants, ecosystem functioning, and agriculture. Great discussion, everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The germination of seeds represents a crucial stage in plant life cycles, requiring specific conditions such as water, oxygen, temperature, and viable seeds. It can occur through two types: epigeal, where cotyledons emerge above soil (e.g., beans), and hypogeal, where they remain below soil (e.g., maize).
Detailed
Germination of Seeds
Germination is the vital phase during which a seed develops into a seedling, ultimately growing into a new plant. This process is initiated under favorable environmental conditions. There are two primary types of germination: epigeal and hypogeal.
- Epigeal Germination: In this type, cotyledons rise above the soil. An example includes the bean seed.
- Hypogeal Germination: Here, cotyledons remain below the soil. An example of this is the maize seed.
Necessary Conditions for Germination
To successfully germinate, seeds require the following conditions:
- Water: Activates enzymes and softens the seed coat.
- Oxygen: Essential for the respiration process.
- Suitable Temperature: Needed for enzymatic activity.
- Viable Seed: The seed must be alive and healthy.
Changes During Germination
During the germination process, several changes occur:
- The seed absorbs water through the micropyle.
- Enzymes convert stored food within the seed into a soluble form.
- The embryo grows, starting with the radicle, which forms the root, followed by the plumule, which forms the shoot.
- Lastly, the seed coat separates as the seedling emerges.
Significance of Germination
Germination is essential for the growth and development of new plants, enabling them to become independent organisms and highlighting the importance of this phase in agriculture.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Germination
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Germination is the process by which the seed grows into a seedling (young plant) under suitable conditions.
Detailed Explanation
Germination refers to the transition of a seed from dormancy to growth, resulting in a seedling. This process begins when a seed absorbs water and swells, initiating biological activities that lead to the development of a young plant. It is crucial because it marks the beginning of a plant's life cycle.
Examples & Analogies
Think of germination like waking up in the morning. Just as you need a gentle nudge, like an alarm clock, to get out of bed and start your day, a seed needs the right conditions—like water, warmth, and oxygen—to 'wake up' and begin its journey to becoming a plant.
Types of Germination
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Types of Germination:
1. Epigeal Germination
- Cotyledons come above the soil
- Example: Bean
2. Hypogeal Germination
- Cotyledons remain below the soil
- Example: Maize
Detailed Explanation
There are two main types of germination observed in plants: epigeal and hypogeal. In epigeal germination, the cotyledons, which are seed leaves, emerge above the soil as seen in beans. This allows them to start photosynthesis and grow more rapidly. On the other hand, hypogeal germination, like that in maize, keeps the cotyledons below the soil, which protects them during the initial stages of growth while the plant extends its roots deeper into the ground.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a runner preparing for a race. In epigeal germination, the runner bursts out of the starting gate, just like the cotyledons that break through the soil, eager to reach the finish line. In hypogeal germination, the runner starts slowly, staying low and preparing for strength building while remaining in a protective position, mirroring how the cotyledons remain beneath the soil.
Key Concepts
-
Germination: The process by which seeds develop into seedlings.
-
Epigeal Germination: Cotyledons appear above the soil.
-
Hypogeal Germination: Cotyledons remain below the soil.
-
Necessary Conditions: Requirements for germination include water, oxygen, temperature, and seed viability.
-
Changes During Germination: Includes water absorption, enzyme activation, radicle, and plumule emergence.
Examples & Applications
A bean seed demonstrates epigeal germination as it pushes its cotyledons above soil.
Maize seed is an example of hypogeal germination, where cotyledons remain below the ground.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Seeds that germinate, oh what a sight, / With water and warmth, they take flight!
Stories
Once upon a time in a garden full of life, a tiny seed dreamed of becoming a big plant. It knew it needed the magic of water, the breath of air, and a cozy warm spot in the soil to wake up and grow.
Memory Tools
Remember to “W.O.W.” - Water, Oxygen, Warmth for germination.
Acronyms
To recall the need for germination, think 'WON' - Water, Oxygen, Nutrients.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Germination
Process by which a seed develops into a seedling under suitable conditions.
- Epigeal Germination
Type of germination where cotyledons come above the soil.
- Hypogeal Germination
Type of germination where cotyledons remain below the soil.
- Viable Seed
A seed that is alive and capable of germination.
- Radicle
The part of the embryo that develops into the root.
- Plumule
The part of the embryo that develops into the shoot.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
