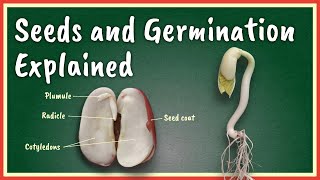
Radicle
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding the Radicle
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to learn about the radicle, which is the part of the seed that grows into the root. Can anyone tell me why roots are important for a plant?

Roots help plants absorb water and nutrients?

Exactly! Roots are essential for anchoring the plant and taking up nutrients. The radicle is the very first structure to emerge during germination. Let's summarize that roots support plant stability and nutrient absorption.

What happens if the radicle doesn't grow properly?

Great question, Student_2! If the radicle doesn't develop correctly, the plant may not be able to absorb the necessary water and nutrients, which could lead to its failure to grow.

How does the radicle grow out of the seed?

The radicle grows out by breaking through the seed coat. It relies on water uptake to swell and elongate, pushing through the outer layers. Remember, H2O is key for the radicle’s growth!

What’s the first thing the radicle does after it pops out?

The radicle anchors into the soil and begins to grow downward to establish a root system, while we can think of it as 'rooting to the ground.'

To conclude, the radicle is vital for root formation and overall plant health. Its role marks the beginning of the plant's lifecycle. Great job, everyone!
Functionality of the Radicle
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know what the radicle is, let’s discuss why it’s important for the plant's growth. What are some functions of roots?

Roots stabilize the plant.

They also transport nutrients and water.

Exactly! The radicle not only anchors the plant but also facilitates nutrient and water uptake, making it crucial for the seedling's survival. Can you think of any effects if the roots were damaged?

The plant might not get enough food or water and could die.

Precisely! Understanding the radicle's growth helps us appreciate how plants develop and why we need healthy root systems. Can anyone recall how the radicle differs in monocots and dicots?

Monocots have their radicle protected by coleorhiza, while dicots don’t!

Excellent recall! Remembering such differences enhances our understanding of plant biology. Let's wrap up by summarizing the significance of the radicle and its role in rooting and nutrient absorption.
Radicle and Plant Development
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we will evaluate how the radicle impacts plant health over time. How does a strong root system benefit a mature plant?

A strong root system can help the plant withstand storms!

Also, they access deeper water sources during droughts.

Exactly! The strength of a radicle sets the foundation for all that. Good root structure equals resilient plants. Can anyone think of agricultural practices that might promote strong roots?

Crop rotation; it helps keep the soil healthy!

Great idea! Healthy soil supports root growth, enabling strong radicle development. Never underestimate the importance of healthy foundations in agriculture too!

In summary, the radicle does not only launch the plant's journey; it ensures its long-term success, from stability to nutrient absorption. Wonderful engagement today!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The radicle is an essential structure within the seed's embryo, responsible for developing into the root of the new plant. Understanding its functions and significance is vital for grasping the overall process of seed germination and plant development.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
The radicle is a critical part of the seed embryo, which emerges during the germination process of seeds. It is responsible for forming the root system of the new plant. Upon germination, the radicle elongates and penetrates the soil, anchoring the plant securely while facilitating the uptake of water and essential nutrients for growth.
In dicot seeds such as beans, the radicle is joined by the cotyledons which initially support the early growth of the plant, while in monocot seeds like maize, the radicle is accompanied by structures such as the coleorhiza, which provides added protection. The successful emergence of the radicle is a vital first step in the growth process, marking the transition from a dormant seed to an active growing plant.
Overall, the radicle signifies the beginning of a plant's life cycle, establishing the foundation for further growth.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to the Radicle
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The radicle is part of the embryo that grows into the root of the plant.
Detailed Explanation
The radicle is the first part of the seedling that emerges when a seed germinates. It is crucial for the initial development of the plant because it forms the roots. Roots anchor the plant and also absorb water and nutrients from the soil, which are vital for the plant's growth.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the radicle as the foundation of a house. Just like a strong foundation keeps a house stable and secure, a well-developed radicle ensures that the plant stays anchored to the ground and can draw nourishment from it.
Function of the Radicle
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
It serves to anchor the plant in the soil and plays a key role in water and nutrient absorption.
Detailed Explanation
As the radicle develops into the root, it establishes a connection with the soil, enabling the plant to stabilize itself. Additionally, roots absorb essential minerals and moisture, which are crucial for the plant's growth and health. Without a functioning radicle, a plant would struggle to survive as it would lack the support and resources it needs.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to stand on a slippery surface without using your feet – you'd find it extremely hard to maintain balance. Similarly, a plant without a radicle would not be able to stand upright and gather the nutrients it needs from the soil.
Radicle in Germination
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
During the germination process, the radicle is the first part to breach the seed coat.
Detailed Explanation
Germination is the process where a seed begins to grow into a new plant. When the seed absorbs water, it swells and eventually breaks open. The radicle is the first structure to emerge from the seed, signaling the start of growth. Its early emergence is vital as it quickly establishes the root system.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a child learning to walk. The first steps are crucial for the development of their ability to stand and move. Similarly, the radicle’s emergence is crucial for the plant’s growth journey, laying the groundwork for the rest of the plant to flourish.
Key Concepts
-
Radicle: The part of a seed embryo that develops into the root.
-
Seed Germination: The process by which a seed sprouts into a new plant.
-
Roots: Essential for nutrient uptake and providing stability to the plant.
Examples & Applications
In dicot seeds like beans, the radicle emerges and forms the main root.
In monocot seeds like maize, the radicle is protected by a coleorhiza as it grows.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
The radicle goes down, roots so strong, helping plants thrive all day long.
Stories
Once upon a time, a little radicle dreamed of growing into a mighty tree; it pushed down into the soil, drinking water, anchoring itself, and eventually becoming strong and tall.
Memory Tools
R.A.D.I.C.L.E - Roots Anchoring, Drinking, Initiating, Creating Life Essentials.
Acronyms
R.O.O.T. - Responsible for Obtaining Our Toppings (nutrients).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Radicle
The part of a seed embryo that develops into the root of the plant.
- Cotyledons
The seed leaves that store food for the developing plant.
- Seed Germination
The process by which a seed develops into a new plant.
- Coleorhiza
The protective sheath covering the embryonic root in monocot plants.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
