Endosperm
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Endosperm
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore the endosperm, found primarily in monocot seeds. Can anyone tell me what they think the role of the endosperm might be?

Is it like food for the plant?

Exactly! The endosperm acts as a food reserve, providing essential nutrients to the developing embryo until it can sustain itself.

So, is it only in monocots?

Great question! Yes, monocots have endospermic seeds, while dicots mainly store food in cotyledons.

What happens if the endosperm is not present?

Without the endosperm, the embryo may struggle to get the energy and nutrients it needs, leading to poor germination.

So, let's remember: 'Endosperm equals energy for embryo'—an easy acronym to recall!

In summary, the endosperm is crucial for nurturing the seedling until it can photosynthesize on its own.
Differences Between Monocots and Dicots
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's explore the different ways seeds store nutrients. Who can mention a type of seed that is monocotyledonous?

Maize!

That's correct! Maize stores its nutrients in the endosperm, making it nutritious for the developing plant.

What about beans? How do they store food?

Beans are dicots, and they rely on cotyledons for nutrient storage, instead of endosperm.

Why is that important?

It's crucial because it affects the germination process! Monocots often have energy readily available from the start.

Remember: 'Monocots need endosperm, dicots rely on cotyledons' to keep it straight!

Let's summarize: monocots have endosperm for quick energy while dicots depend on cotyledons.
Nutritional Composition of Endosperm
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll examine what the endosperm is made of. Can anyone tell me some nutrients found in the endosperm?

I think it's starch!

Correct! Starch is the primary component, along with proteins and some fats.

So, are all endosperms the same nutritionally?

Not at all! The nutritional contents can vary greatly among different plants.

Why is this variation significant?

Different species depend on their specific nutrient profiles to support their growth needs. It is essential for agriculture!

To remember this, think 'Starch, Protein, Fat - Endosperm's Nice Hat!'

In summary, endosperm consists of starch, proteins, and fats that vary between species, crucial for germination and establishment.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
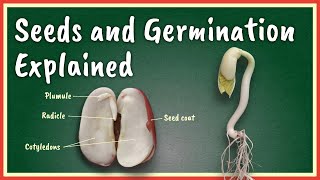
Endosperm is a tissue within seeds that supplies essential nutrients to the developing embryo during germination. It plays a vital role in seed development, and its presence varies among different types of seeds, particularly between monocots and dicots.
Detailed
Endosperm
The endosperm is a specialized tissue that forms within the seeds of flowering plants (angiosperms) after fertilization. It serves as a crucial food reserve for the developing embryo, supplying it with necessary nutrients during the early stages of germination. The endosperm is predominantly found in monocot seeds, such as maize and rice, which are classified as endospermic seeds. Contrastingly, dicot seeds, like beans and grams, store nutrients primarily in the cotyledons and are non-endospermic. The endosperm consists of various components including starch, proteins, and oils that provide energy and essential nourishment to the embryo until it can produce its own food through photosynthesis. Understanding the role of endosperm is significant in both plant biology and agriculture, as it directly impacts seed viability and plant growth.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Role of Endosperm in Seed Development
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Endosperm – Stores food for the embryo
Detailed Explanation
The endosperm is a crucial part of the seed structure. Its primary function is to store food, which will be used by the developing embryo as it grows into a new plant. This stored food is rich in nutrients necessary for the embryo's growth until it is able to perform photosynthesis on its own, usually after germination.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the endosperm like a lunchbox for the embryo. Just like a student needs their lunch to get through school until they can eat at home, the embryo uses the food stored in the endosperm until it can start making its own food through photosynthesis once it grows into a plant.
Types of Endosperm
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The endosperm can vary depending on the type of seed. In monocot seeds like maize, the endosperm is abundant and serves as the main source of nourishment for the embryo.
Detailed Explanation
In monocotyledonous seeds, such as maize, the endosperm is present in larger quantities compared to dicotyledonous seeds. This is because monocots rely heavily on the endosperm during the early stages of growth, while dicots usually have their cotyledons (the first leaves) that serve a similar purpose of storing food. The difference in endosperm development reflects the varied nutritional strategies of different plant types.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the endosperm like a supermarket versus a kitchen pantry. In monocots like maize, the endosperm acts as a full supermarket, providing a wide range of food during the early growth phase. In contrast, dicots may rely more on their 'pantries' (cotyledons), which may not be as stocked initially but can provide essential nutrients as needed.
Importance of Endosperm in Plant Growth
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The endosperm's storage function is vital to ensure that the embryo has enough energy to begin its development and establish itself as a new plant.
Detailed Explanation
The importance of the endosperm cannot be overstated. It provides the essential nutrients and energy that the embryo needs to sprout and grow. During germination, the embryo absorbs the nutrients from the endosperm, supporting its growth as it develops roots and shoots. Without the endosperm, the embryo would struggle to get the energy it needs to survive during its early stages.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to start a car without fuel. The endosperm acts as fuel for the young plant, providing it with the energy it needs to start its growth journey. Just as a car cannot run without gas, a seed cannot grow effectively without the nourishment supplied by the endosperm.
Key Concepts
-
Endosperm: A tissue that serves as a food reserve for the embryo during germination.
-
Monocots vs. Dicots: Monocots have endosperm; dicots store nutrients in cotyledons.
Examples & Applications
Maize (monocot) relies on endosperm for nourishment during germination.
Beans (dicot) depend on cotyledons for their nutrient source.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a seed, the endosperm, keeps the embryo firm, feeding it well, till it starts to swell.
Stories
Once upon a time, a little seed named Maize had a treasure chest called endosperm, filled with food to help it grow big and strong until it saw the sun.
Memory Tools
E for Endosperm, E for Energy! Remember that endosperm helps provide energy for the embryo.
Acronyms
N.E.E.D - Nourishment from Endosperm for Every Developing seed.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Endosperm
A tissue in seed that provides nourishment to the developing embryo.
- Monocot
Seeds that have one cotyledon, e.g., maize.
- Dicot
Seeds that have two cotyledons, e.g., beans.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
