Epigeal Germination
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Epigeal Germination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will learn about epigeal germination. Can anyone tell me what the term 'epigeal' means?

Doesn't it refer to something that comes above the ground?

Exactly! In epigeal germination, the cotyledons rise above the soil. This is typical of many dicots, like beans. Why do you think this is important for the plant?

I think it's to absorb sunlight quickly.

Right. Absorbing sunlight allows the plant to start photosynthesis earlier. Remember, 'EPIGEAL' means 'above the earth'. Let’s move to specific examples!
Characteristics of Epigeal Germination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Epigeal germination also impacts how quickly a seedling establishes itself. Can someone give me an example of a plant that shows this type of germination?

Beans show epigeal germination!

Correct! In beans, the cotyledons emerge early and act like leaves initially. Why do you think this helps in terms of survival?

It helps the plant get a head start against competition for sunlight.

Excellent point! Being able to photosynthesize quickly increases their chances of survival. 'Emerge to thrive' can be a good mnemonic!
Comparison with Other Germination Types
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s compare epigeal germination with another type: hypogeal germination. Can anyone explain what hypogeal germination involves?

That's when the cotyledons stay below the ground, right?

Exactly! Maize is a prime example of hypogeal germination. What are some advantages of hypogeal germination?

Perhaps it protects the cotyledons from pests or harsh conditions since they're underground?

Great observation! Both types have unique advantages. A good way to remember is, 'EPIGEAL is above,' and 'HYPOGEAL is hidden!'
Conclusion and Summary
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To summarize, epigeal germination is when seedlings like beans grow cotyledons above ground for early photosynthesis. Why is this advantageous again?

It's better for getting sunlight which helps them grow faster!

Exactly! Remember, plants adapt their germination strategies to survive and thrive. Any final questions?

How do environmental factors affect this process?

Excellent question! Wetter soil and optimal temperature can enhance germination rates. Keep exploring how those factors affect all plants!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section primarily discusses epigeal germination, characterized by the cotyledons rising above the soil during the germination process. Examples like the bean plant highlight the significance of this type of germination in plant development.
Detailed
Epigeal Germination
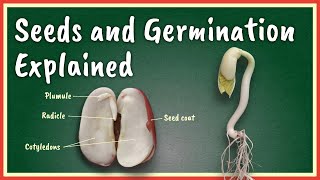
Epigeal germination refers to the growth process in which the cotyledons of a seed develop above the soil surface. This type of germination is commonly observed in certain dicotyledonous plants like beans. In contrast to hypogeal germination where the cotyledons remain underground, epigeal germination allows for the cotyledons to function in photosynthesis early in the seedling’s life. As a result, this nutrient-rich phase supports the young plant before it fully establishes its leaves. The importance of epigeal germination lies in its role in ensuring that the plant quickly adapts to its environment, achieves light absorption, and facilitates early growth. Thus, understanding this process is crucial for the study of plant biology.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Epigeal Germination
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Epigeal germination is when the cotyledons come above the soil.
Detailed Explanation
Epigeal germination refers to a specific type of seed germination where the cotyledons, which are the first leaves to appear, grow above the soil level. This process typically occurs when seeds absorb water and begin to sprout, causing the stem (hypocotyl) to elongate and lift the seed leaves out of the ground. In this way, the plant establishes early photosynthetic activity to support its growth.
Examples & Analogies
Think of epigeal germination like a new superhero emerging from the ground. Just as the superhero bursts forth to save the day, the young plant lifts its leaves above the soil to collect sunlight, which is critical for its survival and growth.
Examples of Epigeal Germination
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
An example of epigeal germination is the bean plant.
Detailed Explanation
The bean plant is a classic example of epigeal germination. When a bean seed is planted in the soil and conditions are right—meaning that it has enough water, oxygen, and warmth—it begins to germinate. The part of the seed that elongates is the hypocotyl, pushing the cotyledons above the soil surface. This allows the plant to start photosynthesizing sooner, which is crucial in its early life.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine planting a bean in a garden. As the bean starts to grow, you'll notice that the leaves poke out above the soil, ready to soak up sunlight. Just like a person stretching after getting out of bed in the morning, the bean strives to reach the sunlight and energize itself for the day ahead.
Key Concepts
-
Epigeal Germination: Germination type where cotyledons rise above ground.
-
Cotyledons: Seed leaves that store nutrients and may photosynthesize.
-
Importance of Early Photosynthesis: Rapid growth advantage during germination.
Examples & Applications
Beans exhibit epigeal germination, where cotyledons emerge above the soil.
Maize demonstrates hypogeal germination, keeping its cotyledons below ground.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In soil, the bean seed sprouts to see, E-pi-ge-al is the way to be!
Stories
A small bean seed dreamed of sunlight, so it pushed its cotyledons up through the soft, warm earth to greet the sun.
Memory Tools
To remember epigeal germination, think 'E for Exposed'.
Acronyms
EPIGEAL = Emerge Above Ground for Photosynthesis.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Epigeal Germination
A type of seed germination where cotyledons are pushed above the soil.
- Cotyledon
A seed leaf that grows from the embryo and can contain food for the plant.
- Photosynthesis
The process by which green plants use sunlight to synthesize foods from carbon dioxide and water.
- Hypogeal Germination
Type of germination where the cotyledons remain below the soil.
- Seedling
A young plant that develops from a seed.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
