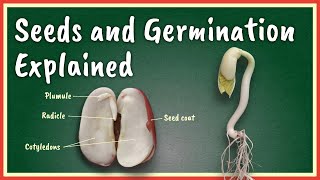
Coleoptile
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Coleoptile
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're going to learn about an essential part of monocot seeds known as the coleoptile. What do you think it might do?

Is it related to the growth of the plant?

Exactly! The coleoptile protects the young shoot, which is called the plumule, during germination.

How does it protect the plumule?

The coleoptile acts like a sheath. It covers the plumule as it pushes through the soil, preventing damage while ensuring it grows upwards!

So, it helps the plant reach sunlight?

Yes! Remember, we can think of the coleoptile as a 'guardian' for the young shoot. It helps keep the plant safe as it emerges.

That's cool! Is it only found in certain types of seeds?

Great question! The coleoptile is primarily found in monocot seeds, like maize and rice.

Now, let’s summarize what we learned: the coleoptile protects and directs the growth of the plumule in monocot seeds, ensuring successful germination.
The Role of Coleoptile in Germination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's expand on how the coleoptile helps during germination. Can anyone tell me what germination is?

It's when the seed starts to grow, right?

Correct! During germination, the coleoptile supports the plumule's emergence from the soil. Why is this important?

Because the plant needs to find sunlight!

That's right! The coleoptile ensures the plumule grows up towards the surface and sunlight without being harmed.

Can it also help with water intake?

While the coleoptile's main function is to support the plumule, the overall plant structure operates to absorb water effectively once it emerges.

So without it, the seed might have trouble growing?

Exactly! The coleoptile is crucial for ensuring a successful start for monocot plants. It’s like giving the plant a head start in life.

To summarize, the coleoptile plays a vital role by directing the plumule's growth during germination, ensuring it reaches for sunlight.
Comparing Coleoptile and Other Structures
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s compare the coleoptile to other structures found in seeds. What do you know about the radicle?

I think it grows into the root, right?

Very good! The radicle is indeed the part that develops into the root. How does that differ from the coleoptile?

The coleoptile protects the shoot, and the radicle protects the root?

Exactly! The coleoptile shields the plumule while the coleorhiza protects the radicle.

So, each part has a different role and protects different parts of the plant!

Yes! Understanding the functions of these seed structures highlights their collaborative efforts for successful plant development.

That makes sense! They work together like a team!

Precisely! To summarize: the coleoptile protects and directs growth of the shoot, while the radicle grows into the root, each playing critical roles in seed germination.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The coleoptile plays a crucial role in the germination of monocot seeds, such as maize. It safeguards the plumule as it breaks through the soil, facilitating the growth of the shoot upward while conducting important functions like directing growth and protecting the developing shoot.
Detailed
Coleoptile
The coleoptile is a vital structure in monocot seeds, specifically designed to protect the embryonic shoot (plumule) during the initial stages of germination. In seeds like maize, the coleoptile serves as a sheath that not only shields the plumule but also directs its growth upward as it emerges from the soil. Its unique design allows it to push through the soil more effectively, ensuring the young plant can access sunlight and begin photosynthesis. Additionally, this structure is important in regulating the growth direction, making it a crucial element for successful seedling establishment. Understanding the function of the coleoptile is essential as it highlights the complexities of plant development and the mechanisms plants use to adapt to their environments.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Coleoptile
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Coleoptile – Protective sheath for the plumule
Detailed Explanation
A coleoptile is a specialized structure found in monocot seeds, such as maize. It acts as a protective cover for the young shoot, known as the plumule, which will eventually grow into the stem and leaves of the plant. The coleoptile ensures that the delicate plumule is shielded as it pushes through the soil during germination, helping it to reach light effectively.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine wrapping a fragile plant shoot in a soft, protective sleeve as it breaks through the ground. Just like how this sleeve protects the plant from the harsh conditions in soil, such as other plant roots or rocks, the coleoptile safeguards the plumule until it can stand on its own.
Function of Coleoptile
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The coleoptile plays a crucial role in protecting the plumule as it emerges from the soil.
Detailed Explanation
The primary function of the coleoptile is to provide a safe passage for the plumule. This means that as the seed germinates and grows, the coleoptile pushes upward through the soil. It creates a narrow, streamlined path that minimizes resistance from the surrounding soil, allowing the plumule to rise freely and quickly touch the sunlight.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the coleoptile as a tunneling machine that helps a miner break through rock. Just as the tunneling machine protects the miner while creating a clear path to the surface, the coleoptile helps the young plant safely reach the light it needs to grow.
Importance for Germination
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Coleoptiles ensure successful emergence and growth of the shoot.
Detailed Explanation
In the process of germination, the coleoptile is vital for the success of the seedling's emergence. It prevents damage to the young plant as it grows out of the seed and into its environment. By securing the plumule and guiding it upwards, the coleoptile ultimately allows the plant to access sunlight and begin the process of photosynthesis, which is essential for its growth.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a construction elevator that transports workers safely to high floors of a building. Just as the elevator ensures the workers can access their workplace without any obstacles, the coleoptile ensures that the plumule can ascend successfully and start its journey toward growth and independence.
Key Concepts
-
Coleoptile: A protective sheath for the embryonic shoot (plumule) in monocot seeds.
-
Plumule: The part of the seed that develops into the main stem and leaves.
-
Monocot: A category of flowering plants that have one cotyledon.
Examples & Applications
The coleoptile in maize seeds protects the young shoot as it emerges through the soil.
The radicle grows downward into the soil while the coleoptile pushes upward towards sunlight.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Coleoptile is a protective style, helping the young shoot grow up the while.
Stories
Once upon a time in the soil, a little seed sprouted. The coleoptile, its knight in shining armor, protected the plumule as it pushed bravely through the soil to reach the sunlight.
Memory Tools
C.O.L.E. - Coleoptile Operates to Lift the Emergence of the shoot.
Acronyms
C.A.R.E. - Coleoptile Aids Root Emergence.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Coleoptile
A protective sheath that encases the plumule in monocot seeds, aiding its emergence during germination.
- Plumule
The embryonic shoot of a seed which develops into the stem and leaves of the plant.
- Radicle
The embryonic root of a seed that develops into the primary root.
- Monocot
A type of seed that has one cotyledon, such as maize and rice.
- Germination
The process through which a seed develops into a new plant under suitable conditions.
- Cotyledon
A significant part of the seed that typically provides nourishment to the developing plant.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
