Embryo - 6.2.2.5
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
The Structure of the Embryo
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll explore the embryo in seeds. The embryo is crucial for the development of the plant. What do you remember about its structure?

It has a radicle and a plumule, right?

Exactly! The radicle develops into the root, while the plumule forms the shoot. Can anyone tell me why this is important?

Because the roots need to absorb water and minerals, and the shoot supports leaves?

Right! Remember: 'Roots Run Radically, Shoots Shoot Skywards.' This rhyme can help you remember their functions!
Role of the Embryo in Germination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss the significance of the embryo during germination. Why is it considered essential?

Because it’s the part that starts to grow into a new plant?

Yes, good point! When conditions are favorable, the embryo initiates germination. What three conditions do seeds need to germinate?

Water, oxygen, and suitable temperature!

Correct! It's vital for the embryo to absorb water before it can begin to grow. Remember: 'Water Opens the Door to Growth.'
Differences Between Monocot and Dicot Embryos
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s differentiate between monocot and dicot embryos. What do we notice?

Monocots have one cotyledon, while dicots have two!

Exactly! Also, monocot embryos like maize have a structure called the scutellum. Can someone explain its function?

It stores food for the embryo during germination.

Right! Always remember: 'Mono One Scutellum; Dico Double Roots!' This will help you with their characteristics.
Factors Influencing Embryo Development
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

What factors do you think influence the growth of an embryo in a seed?

I think the quality of the seed and environmental conditions like soil and water.

Correct! The viability of the seed is paramount. Without the right conditions, even a healthy embryo can fail to develop. Remember: 'Healthy Seeds, Healthy Need!'
Significance of the Embryo in Plant Life Cycle
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's wrap up by discussing why the embryo is significant in the plant life cycle. Who can summarize that?

The embryo ensures the continuation of the plant species and contributes to crop production.

Exactly! The success of plants starts with the embryo. Always remember: 'Life Begins at the Embryo!'
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
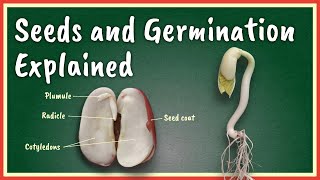
In seeds, the embryo consists of a radicle and a plumule, representing the future root and shoot of the plant respectively. Understanding the structure and function of the embryo is essential for comprehending the seed's role in plant reproduction and germination.
Detailed
In the seed's structure, the embryo plays a vital role as the future plant. It is formed through the fertilization of the ovule and consists of two main parts: the radicle and the plumule. The radicle will develop into the root system of the plant, anchoring it and extracting water and nutrients from the soil. Conversely, the plumule will grow into the shoot, carrying the leaves and flowers necessary for photosynthesis and reproduction. The health and viability of the embryo directly influence the success of seed germination, leading to the establishment of healthy plants.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of the Embryo
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The embryo develops into the new plant; consists of:
- Radicle – Grows into root
- Plumule – Grows into shoot
Detailed Explanation
The embryo is a critical part of the seed that will eventually grow into a new plant. It is made up of two main parts: the radicle and the plumule. The radicle is the part that will develop into the root, anchoring the plant into the soil, while the plumule will grow into the shoot, which will produce leaves and stems. Understanding the structure of the embryo is fundamental because it outlines how a seed will develop once it germinates.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the embryo like a blueprint for a house. Just as a blueprint provides the necessary instructions for constructing a building, the embryo contains all the genetic instructions and necessary structures like the radicle and plumule to create a new plant.
Role of the Radicle
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Radicle – Grows into root
Detailed Explanation
The radicle is the first part of the embryo to emerge during the germination process. Its primary role is to develop into the root system of the plant. The roots are vital for the plant as they absorb water and nutrients from the soil, providing the necessary support for the entire plant structure. The establishment of roots also helps anchor the plant in place, preventing it from being uprooted by wind or animals.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine when you build a tower; the base or foundation is essential to ensure that the tower does not fall over. In the same way, the radicle acts as the foundation for the plant by growing into the root, ensuring stability and access to food and water.
Role of the Plumule
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Plumule – Grows into shoot
Detailed Explanation
The plumule is another crucial part of the embryo, responsible for developing into the shoot of the plant. The shoot will eventually produce leaves, stems, and flowers, making it essential for photosynthesis and reproduction. This part of the embryo ensures that the plant can grow upwards towards sunlight, which is vital for its survival and growth.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how a student grows into an adult. Just as a student needs to learn and grow towards their goals, the plumule pushes upwards towards the light to gather sunlight necessary for the plant's energy through photosynthesis.
Key Concepts
-
Embryo: Contains the radicle (root) and plumule (shoot).
-
Importance of conditions for germination: Water, oxygen, temperature, and healthy seeds.
-
Differences in monocot and dicot embryos.
Examples & Applications
In beans (a dicot), the two cotyledons serve as food sources for the developing plant.
In maize (a monocot), the scutellum assists in nutrient uptake for the embryo.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Radicle down for roots to find, Plumule up, leaves intertwined!
Stories
Once upon a time, in a seed, a radicle and plumule lived together. The radicle dug deep into the earth, while the plumule reached for the sky, together nurturing life.
Memory Tools
R.P. - Remember: Radicle is for Roots, Plumule is for Plants!
Acronyms
REAP - Radicle, Embryo, Absorb, Plant.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Embryo
The developing part of a seed that forms the new plant.
- Radicle
The part of the embryo that develops into the root.
- Plumule
The part of the embryo that develops into the shoot.
- Cotyledon
The first leaves that appear from a germinating seed.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
